Unveiling the Secrets of Winter: Understanding NOAA’s Snow Cover Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Winter: Understanding NOAA’s Snow Cover Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Winter: Understanding NOAA’s Snow Cover Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Winter: Understanding NOAA’s Snow Cover Maps
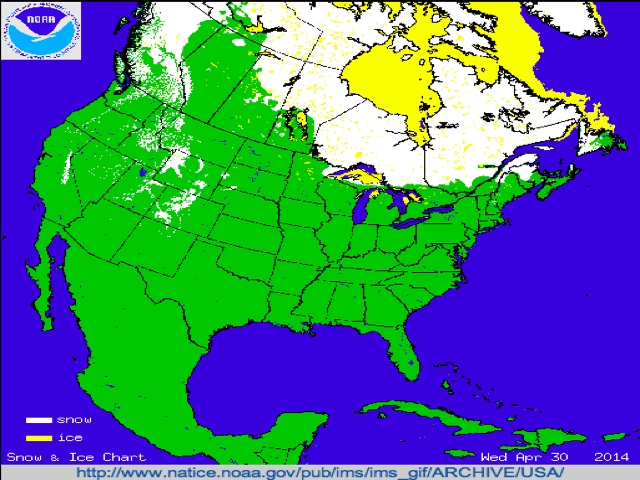
The winter landscape, blanketed in white, holds a captivating beauty. Yet, beneath the surface of this serene scene lies a complex interplay of weather patterns, hydrological processes, and ecological impacts. Understanding this dynamic environment is crucial for a wide range of applications, from predicting natural disasters to managing water resources. This is where the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) steps in, providing invaluable insights through its comprehensive snow cover maps.
A Window into the Winter World:
NOAA’s snow cover maps, accessible through the agency’s website and various platforms, offer a visual representation of snow distribution across the globe. These maps are not static snapshots; they are constantly updated, reflecting the ever-changing nature of snow cover. This dynamic data is derived from a combination of satellite imagery, ground-based observations, and advanced algorithms.
Beyond the Visual:
While the maps provide a clear picture of snow cover extent, their significance lies in the wealth of information they encapsulate. Each pixel on the map, representing a specific location, carries a wealth of data, including:
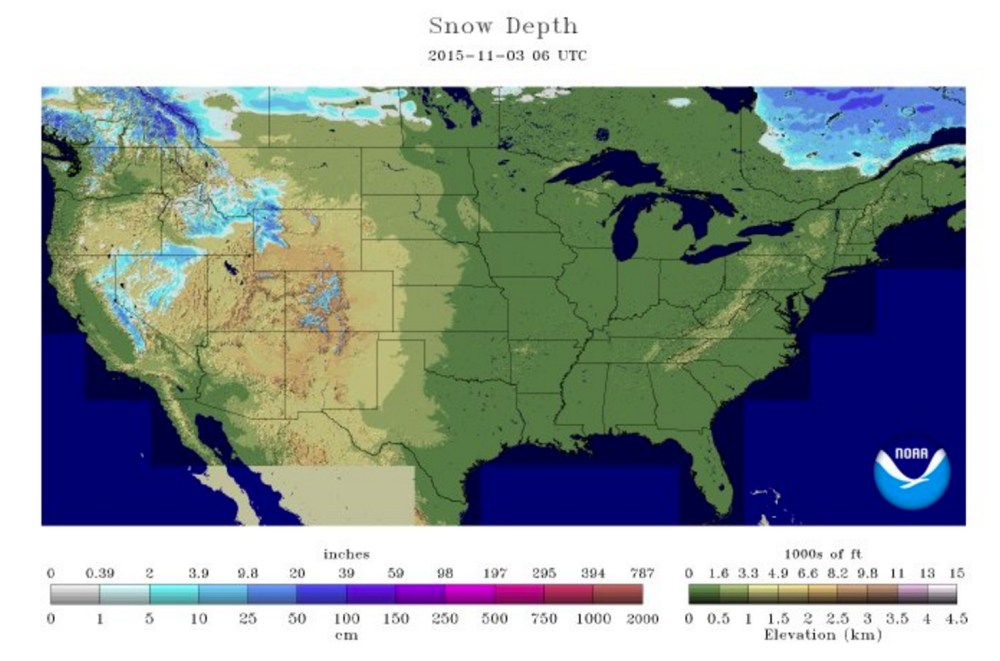
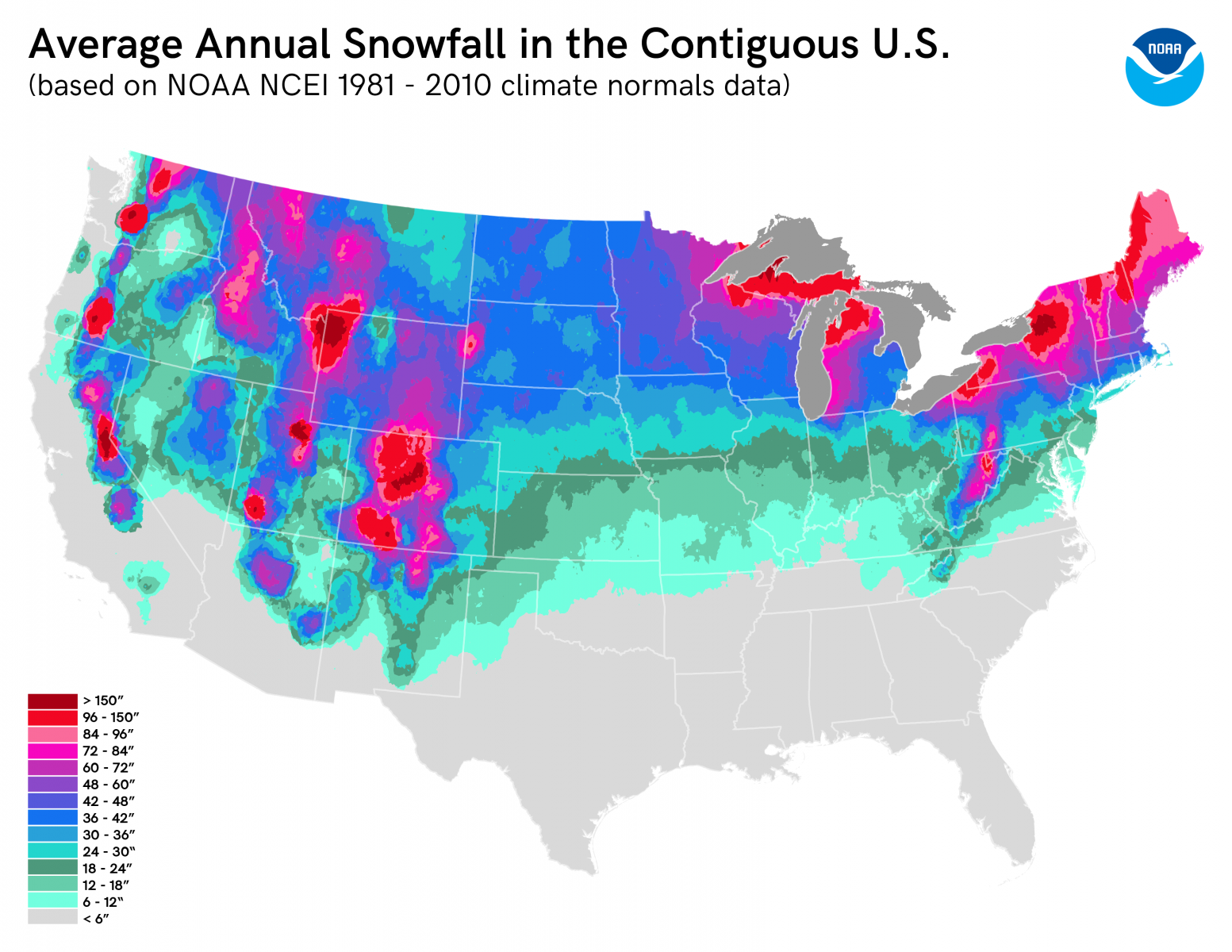
- Snow Depth: This metric indicates the depth of snow accumulation at a given location, providing crucial information for hydrological modeling and avalanche risk assessment.
- Snow Water Equivalent (SWE): This metric quantifies the amount of water contained within the snowpack. SWE is a critical parameter for managing water resources, particularly in regions reliant on snowmelt for water supply.
- Snow Age: This metric indicates the duration of snow cover at a location, offering insights into the snowpack’s stability and potential for meltwater runoff.
Navigating the Benefits:
The data derived from NOAA’s snow cover maps serves a wide range of purposes, impacting various sectors and benefiting countless individuals:
- Hydrological Modeling: Accurate snow cover data is essential for hydrological models, enabling scientists to predict water flow, manage reservoir levels, and anticipate potential flooding events.
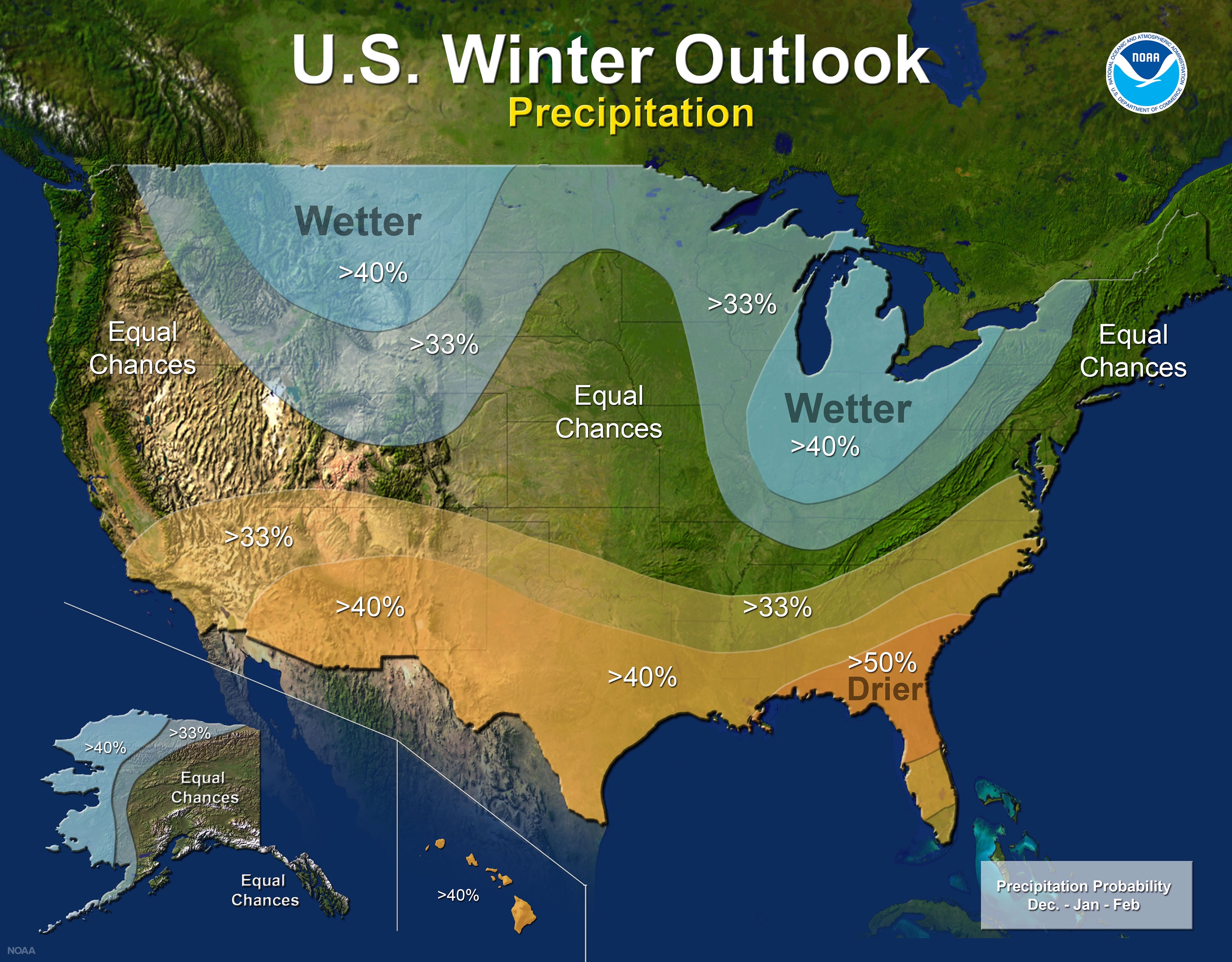
- Water Resource Management: Snowmelt is a vital source of water for many communities, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. NOAA’s maps provide critical information for managing water resources, ensuring sustainable water availability.
- Agriculture: Snow cover plays a significant role in soil moisture and agricultural productivity. Farmers rely on snow cover data for planning crop rotations, irrigation strategies, and livestock management.
- Disaster Preparedness: Snow cover can contribute to avalanche risk and influence the severity of winter storms. NOAA’s maps provide valuable data for disaster preparedness efforts, enabling communities to mitigate potential risks and respond effectively to emergencies.
- Climate Change Research: Studying snow cover trends over time provides crucial insights into climate change impacts. NOAA’s data supports research efforts, helping scientists understand the effects of climate change on snowpack dynamics and hydrological cycles.
FAQs: Demystifying the Data
Q: How are NOAA’s snow cover maps created?
A: NOAA’s snow cover maps are generated through a complex process involving:
- Satellite Imagery: Sensors aboard satellites capture images of the Earth’s surface, detecting the presence of snow and ice.
- Ground-Based Observations: Snow depth and SWE measurements are collected from ground stations, providing validation for satellite data.
- Algorithms: Advanced algorithms process the satellite and ground-based data, generating maps that represent snow cover extent, depth, and SWE.
Q: How frequently are the maps updated?
A: NOAA’s snow cover maps are updated daily, reflecting the dynamic nature of snow cover. This frequent updating ensures that the data is as accurate and current as possible.
Q: What are the limitations of NOAA’s snow cover maps?
A: While NOAA’s snow cover maps provide valuable information, it’s essential to recognize their limitations:
- Spatial Resolution: The resolution of satellite imagery can influence the accuracy of snow cover mapping, particularly in complex terrain.
- Cloud Cover: Cloud cover can obscure the Earth’s surface, limiting the effectiveness of satellite-based snow cover observations.
- Data Gaps: In remote areas with limited ground-based observations, data accuracy may be compromised.
Q: What are some tips for interpreting NOAA’s snow cover maps?
A: To effectively interpret NOAA’s snow cover maps, consider the following tips:
- Map Legend: Pay close attention to the map legend, understanding the color scales and symbols used to represent snow cover extent, depth, and SWE.
- Spatial Context: Consider the geographic location of the map and its surrounding terrain, as these factors can influence snow cover patterns.
- Temporal Context: Recognize the date and time of the map, understanding that snow cover can change rapidly due to weather events.
Conclusion:
NOAA’s snow cover maps provide a vital tool for understanding the dynamics of the winter landscape. By leveraging satellite imagery, ground-based observations, and advanced algorithms, these maps offer a wealth of information that benefits a wide range of applications. From managing water resources to predicting natural disasters, NOAA’s snow cover maps play a crucial role in supporting informed decision-making and fostering a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of our planet.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Winter: Understanding NOAA’s Snow Cover Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!