Unveiling the Power of Chains Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Chains Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Chains Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Chains Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool

The realm of data analysis and visualization is constantly evolving, with new tools and techniques emerging to tackle complex challenges. Among these, chains maps stand out as a powerful and versatile visualization method, offering a unique perspective on data relationships and patterns. This comprehensive guide explores the concept of chains maps, delving into their functionalities, benefits, and applications across diverse fields.
Understanding the Essence of Chains Maps
Chains maps, also known as chain diagrams, are graphical representations of data that emphasize the sequential relationships between different elements. They are particularly effective in visualizing processes, workflows, and hierarchical structures, offering a clear and intuitive understanding of how individual components interact and contribute to the overall system.
Key Components of a Chains Map:
- Nodes: These represent individual elements within the data set, such as tasks, processes, or individuals.
- Links: These connect the nodes, indicating the relationships or dependencies between them. Links can be directed, showcasing the flow of information or processes, or undirected, highlighting connections without specifying direction.
- Labels: Labels are used to identify nodes and links, providing context and clarity to the visualization.
- Color and Shape: Different colors and shapes can be employed to visually differentiate nodes and links, enhancing the map’s readability and highlighting specific features.
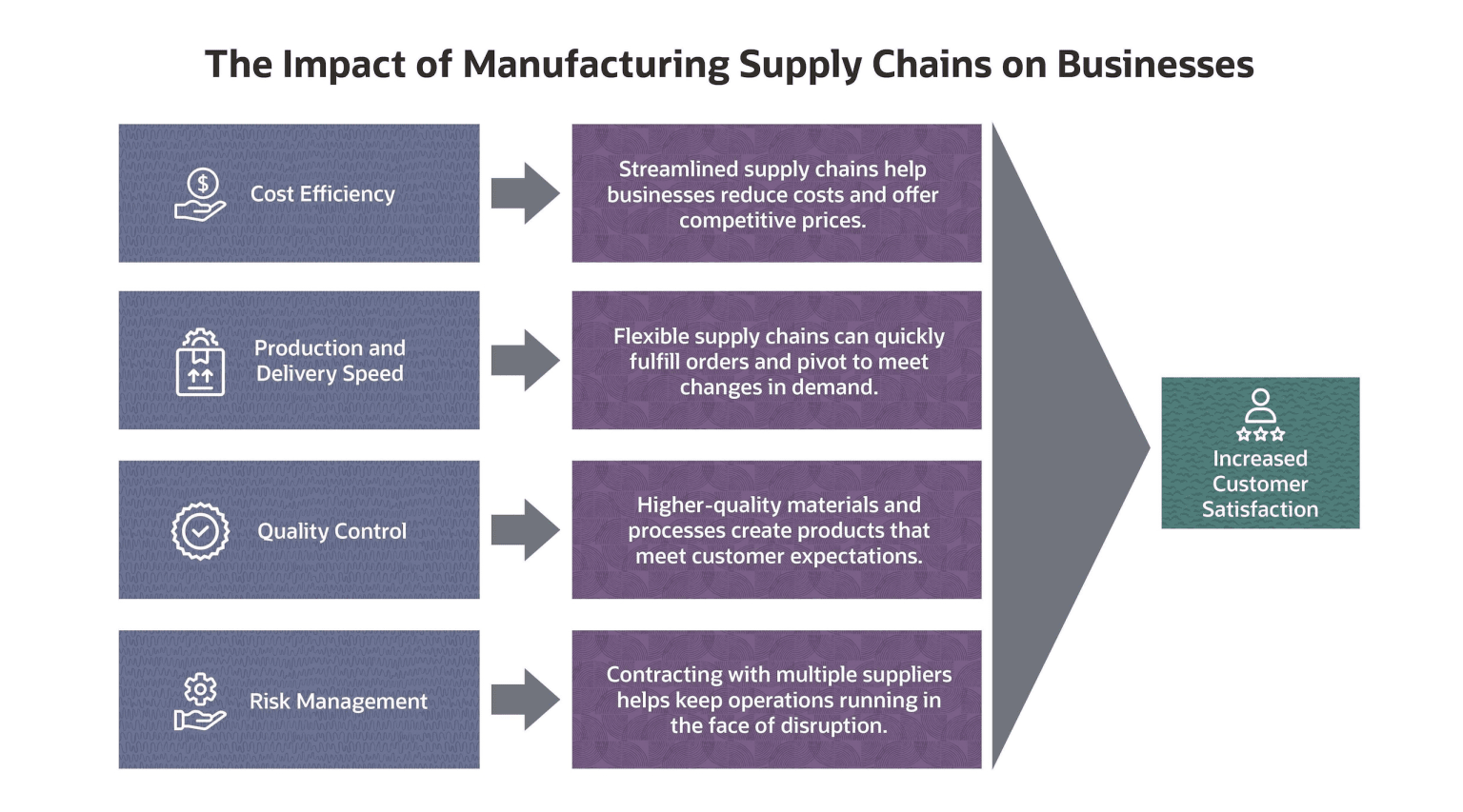
Benefits of Using Chains Maps:
- Enhanced Clarity: Chains maps provide a structured and visually appealing way to represent complex data, making it easier to understand and interpret.
- Process Visualization: They excel at depicting processes and workflows, revealing bottlenecks, redundancies, and opportunities for optimization.
- Hierarchical Representation: Chains maps effectively illustrate hierarchical structures, showing the relationships between different levels within an organization or system.
- Data Relationships: They highlight the connections and dependencies between data elements, fostering a deeper understanding of their interactions.
- Communication Tool: Chains maps serve as a powerful communication tool, enabling effective knowledge sharing and collaboration among stakeholders.
Applications of Chains Maps Across Diverse Fields:
Chains maps find widespread applications in various domains, including:
-
Business and Management:
- Process Mapping: Visualizing and analyzing business processes to identify areas for improvement and streamlining.
- Organizational Structure: Representing the hierarchical structure of an organization, highlighting reporting lines and team relationships.
- Project Management: Tracking project dependencies, identifying critical paths, and managing resource allocation.
-
Software Development:
- Software Architecture: Visualizing the relationships between different software components and modules.
- Workflow Analysis: Understanding the flow of data and processes within a software application.
-
Research and Education:
- Research Methodology: Illustrating the steps involved in a research project, from hypothesis formulation to data analysis.
- Educational Material: Presenting complex concepts in a clear and visually appealing manner.
-
Healthcare:
- Patient Flow: Visualizing the movement of patients through a healthcare system, identifying potential delays and bottlenecks.
- Treatment Pathways: Depicting the sequence of treatments and interventions for specific medical conditions.
-
Supply Chain Management:
- Supply Chain Network: Illustrating the flow of goods and materials throughout a supply chain.
- Logistics Planning: Optimizing transportation routes and inventory management.
Constructing a Chains Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a chains map involves a systematic approach to ensure clarity and effectiveness:
- Define the Scope: Clearly define the purpose of the chains map and the data to be represented.
- Identify Nodes and Links: Determine the key elements and their relationships within the data set.
- Choose a Layout: Select a layout that best suits the data and its relationships, such as linear, hierarchical, or radial.
- Assign Labels: Label nodes and links with clear and concise descriptions.
- Use Color and Shape: Employ different colors and shapes to enhance readability and highlight specific features.
- Iterate and Refine: Continuously refine the map based on feedback and insights gained during the process.
FAQs on Chains Maps:
Q: What are the limitations of chains maps?
A: While chains maps are powerful visualization tools, they have limitations. They may become complex and difficult to interpret when dealing with a large number of nodes and links. Additionally, they may not be suitable for representing all types of data, particularly those with non-linear relationships.
Q: What are some alternative visualization methods?
A: Other visualization methods, such as network graphs, treemaps, and flowcharts, can provide complementary perspectives on data relationships.
Q: How can I create chains maps using software tools?
A: Several software tools, such as Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and Draw.io, offer features for creating chains maps and other diagrams.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective chains maps?
A:
- Keep it simple and focused: Avoid overloading the map with unnecessary details.
- Use clear and concise labels: Ensure that labels are easily understandable and relevant.
- Employ color and shape effectively: Use color and shape to differentiate nodes and links, but avoid excessive use that could be distracting.
- Test the map with stakeholders: Seek feedback from relevant individuals to ensure the map effectively conveys its intended message.
Conclusion:
Chains maps provide a valuable tool for visualizing and understanding complex data, offering a unique perspective on relationships and patterns. Their ability to depict processes, hierarchies, and dependencies makes them essential for various fields, from business and management to research and healthcare. By effectively utilizing chains maps, individuals and organizations can gain deeper insights into their data, facilitate communication, and drive informed decision-making. As data visualization continues to evolve, chains maps will remain a powerful and indispensable tool in the quest for clarity and understanding.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Chains Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Essential Tool. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!