Unveiling the Power of Bivariate Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Powerful Tool
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Bivariate Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Powerful Tool
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Bivariate Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Powerful Tool. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Bivariate Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Powerful Tool
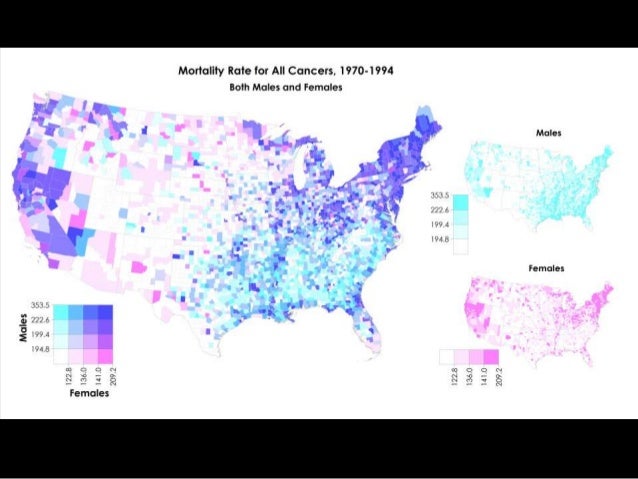
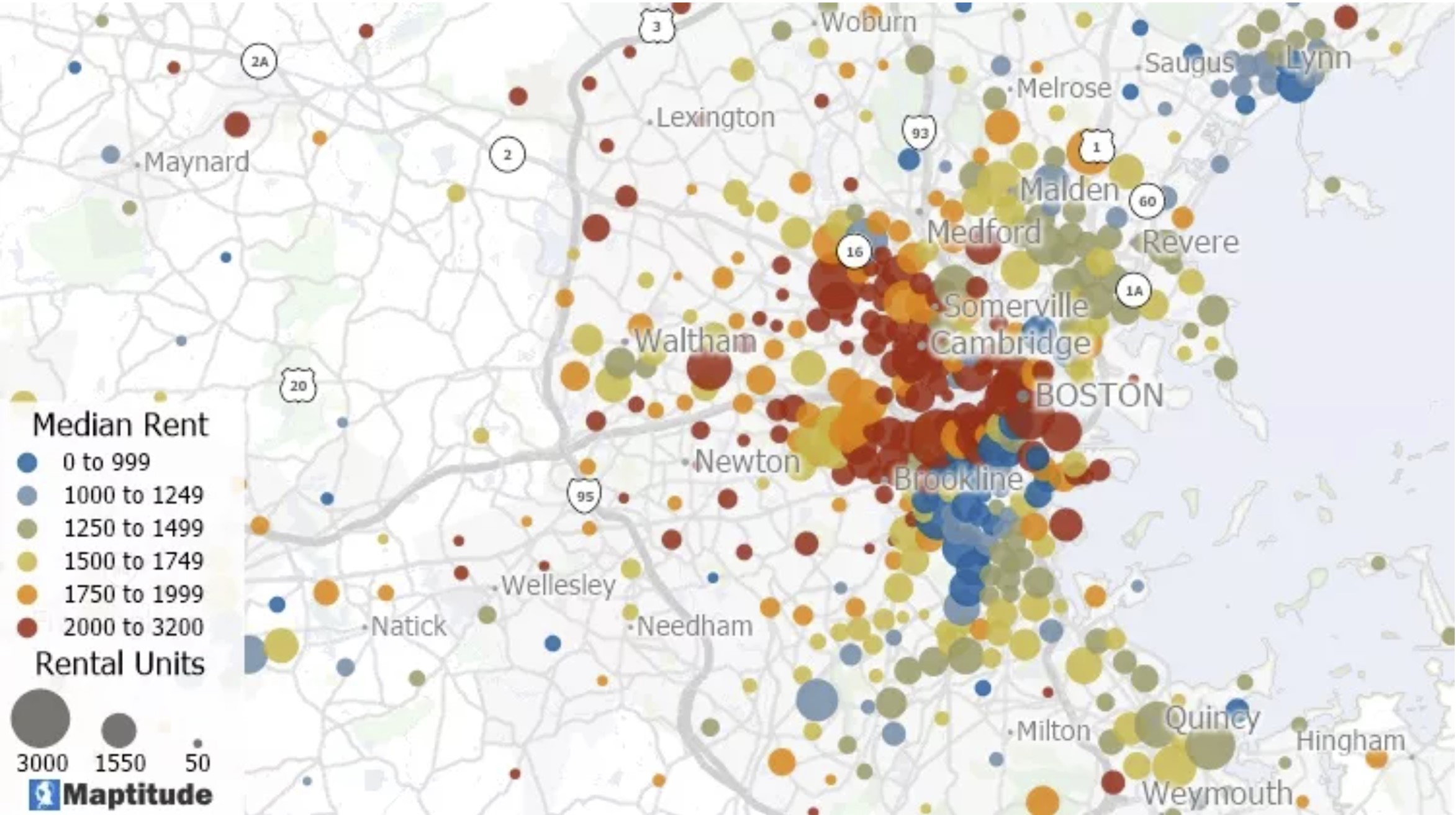
In the realm of data visualization, the ability to effectively convey complex relationships between two variables is paramount. While traditional maps excel at showcasing spatial distributions, they often fall short when it comes to illustrating the interplay between different data sets. This is where bivariate maps emerge as a powerful and versatile tool, offering a unique perspective on the intricate connections within geographic data.
Understanding the Essence of Bivariate Maps
A bivariate map, as the name suggests, simultaneously represents two variables on a single map. Unlike conventional maps that use a single color or symbol to depict a single data attribute, bivariate maps utilize a combination of colors, patterns, or symbols to communicate the relationship between two distinct variables. This dual representation allows for a deeper understanding of spatial patterns, revealing insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
The Building Blocks of Bivariate Maps
The construction of a bivariate map relies on the careful selection and combination of two data sets. The variables chosen should have a clear and meaningful relationship, allowing for a compelling narrative to emerge from their spatial interaction. The visual representation of these variables is equally critical. Common techniques include:
- Color Combinations: This approach utilizes a color scheme where each color represents a specific range of values for one variable, while the hue or saturation of the color reflects the corresponding value of the second variable.
- Symbol Combinations: Different shapes or sizes of symbols can be used to represent different values of one variable, while the color of the symbol represents the corresponding value of the other variable.
- Pattern Combinations: Different patterns, such as stripes or dots, can be used to represent different values of one variable, while the color of the pattern represents the corresponding value of the other variable.
The Significance of Bivariate Maps: Unveiling Hidden Connections
Bivariate maps provide a unique lens through which to analyze geographic data, revealing hidden connections and insights that might remain obscured when examining data in isolation. Their significance lies in their ability to:
- Identify Spatially-Driven Relationships: By visualizing the simultaneous distribution of two variables, bivariate maps can uncover patterns and trends that might not be apparent when examining each variable individually.
- Enhance Data Interpretation: The visual representation of two variables on a single map facilitates a more comprehensive understanding of the relationships between them, leading to more informed interpretations and conclusions.
- Uncover Spatial Correlation: Bivariate maps can effectively demonstrate the degree to which two variables are spatially correlated, revealing whether they tend to co-occur in specific areas or exhibit opposing spatial patterns.
- Support Decision-Making: By providing a clear and concise visual representation of complex data relationships, bivariate maps can aid in decision-making processes, particularly in fields such as urban planning, environmental management, and public health.
Applications of Bivariate Maps: Across Diverse Disciplines
The versatility of bivariate maps extends across various disciplines, making them valuable tools for a wide range of applications. Some notable examples include:
- Environmental Science: Bivariate maps can illustrate the spatial distribution of pollution levels alongside demographic data, revealing potential environmental justice issues and informing pollution control strategies.
- Urban Planning: By visualizing population density alongside access to public transportation, bivariate maps can highlight areas with potential for urban renewal or areas requiring improved infrastructure.
- Public Health: Bivariate maps can be used to map the distribution of disease incidence alongside socioeconomic factors, providing insights into health disparities and informing public health interventions.
- Economics: Bivariate maps can illustrate the relationship between economic indicators, such as income levels and employment rates, across different regions, providing insights into regional economic disparities.
- Social Sciences: Bivariate maps can be used to analyze the spatial distribution of social phenomena, such as crime rates or voting patterns, alongside factors such as socioeconomic status or ethnicity, shedding light on potential social inequalities.
Exploring the Benefits of Bivariate Maps: A Powerful Tool for Data Visualization
The advantages of utilizing bivariate maps extend beyond their ability to reveal hidden connections. They offer a range of benefits that make them an indispensable tool for data visualization and analysis:
- Enhanced Clarity and Comprehension: By visually representing two variables on a single map, bivariate maps provide a clear and concise representation of complex data relationships, facilitating a deeper understanding of the data.
- Improved Communication: Bivariate maps offer an effective means of communicating complex data relationships to a wider audience, including those without specialized technical knowledge.
- Increased Efficiency: By integrating two variables on a single map, bivariate maps streamline the analysis process, reducing the need for multiple maps and facilitating a more efficient understanding of the data.
- Data Exploration and Discovery: Bivariate maps can be used to explore the relationships between different variables, leading to the discovery of previously unknown patterns and trends.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: By providing a comprehensive visual representation of complex data relationships, bivariate maps can support informed decision-making in a variety of fields.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bivariate Maps
Q: What are the key considerations when choosing variables for a bivariate map?
A: When choosing variables for a bivariate map, it is essential to select variables that have a clear and meaningful relationship. The variables should be relevant to the research question or objective, and they should be measured in comparable units or scales. The relationship between the variables should also be statistically significant, indicating a real connection rather than a random association.
Q: How can I effectively choose a color scheme for a bivariate map?
A: The choice of color scheme for a bivariate map is crucial for ensuring clear and accurate communication of the data. It is recommended to use a color scheme that is both visually appealing and easily interpretable. The color scheme should be consistent with the chosen variables, using colors that are associated with the respective values or ranges of values. It is also important to consider the potential for colorblindness, choosing colors that are easily distinguishable for individuals with color vision deficiencies.
Q: What are some common software tools for creating bivariate maps?
A: A variety of software tools can be used to create bivariate maps. Some popular options include:
- ArcGIS: A widely used geographic information system (GIS) software that offers powerful capabilities for creating and analyzing bivariate maps.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software that provides similar functionality to ArcGIS, making it a cost-effective option for creating bivariate maps.
- R: A statistical programming language that offers a wide range of packages for data visualization, including packages specifically designed for creating bivariate maps.
- Tableau: A data visualization software that provides a user-friendly interface for creating interactive bivariate maps.
Tips for Creating Effective Bivariate Maps
- Choose appropriate variables: Select variables that are relevant to the research question and have a clear and meaningful relationship.
- Use a clear and concise color scheme: Opt for a color scheme that is both visually appealing and easily interpretable, taking into account potential colorblindness.
- Maintain consistency: Ensure that the color scheme, symbols, or patterns used to represent the variables are consistent throughout the map.
- Provide clear labels and legends: Include clear labels and legends to explain the meaning of the colors, symbols, or patterns used on the map.
- Consider the map’s audience: Tailor the map’s design and complexity to the intended audience, ensuring that the information is presented in a way that is accessible and understandable.
Conclusion: The Power of Bivariate Maps in Uncovering Hidden Connections
Bivariate maps offer a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing geographic data, revealing hidden connections and insights that might otherwise remain obscured. By integrating two variables on a single map, bivariate maps provide a more comprehensive understanding of spatial patterns, enhancing data interpretation and supporting informed decision-making. Their versatility extends across diverse disciplines, making them valuable tools for a wide range of applications, from environmental science to urban planning and public health. As we continue to navigate a world increasingly reliant on data, the ability to effectively visualize and interpret complex relationships will be crucial for making informed decisions and solving critical challenges. Bivariate maps provide a powerful framework for achieving this goal, offering a unique lens through which to explore the intricate connections within geographic data.
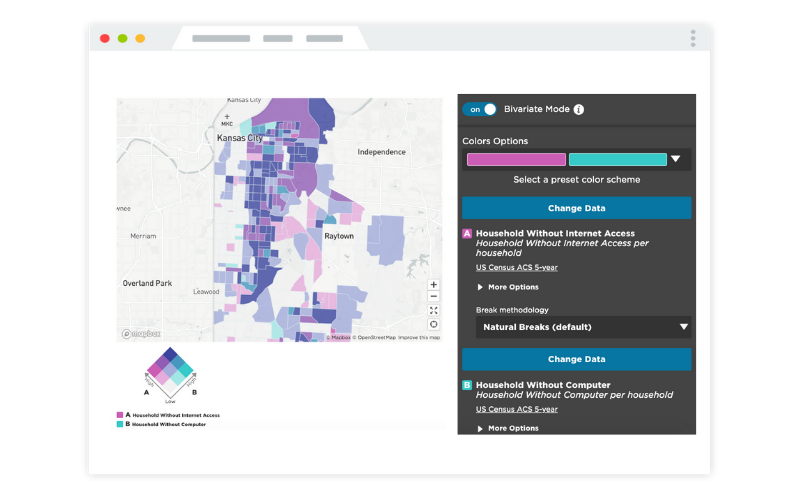
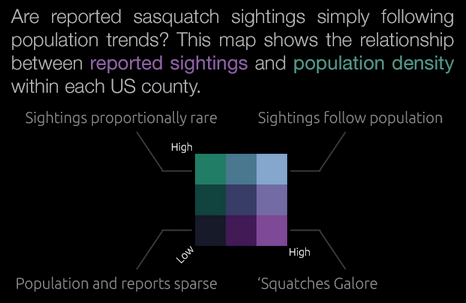

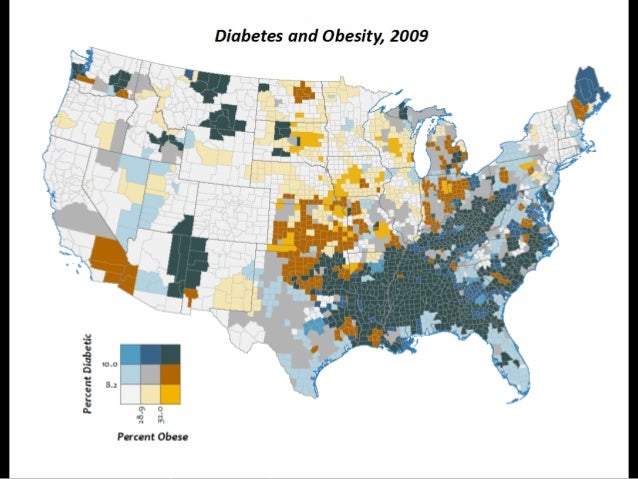



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Bivariate Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Utilizing This Powerful Tool. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!