Unveiling the Network’s Backbone: A Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Optic Cable Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Network’s Backbone: A Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Optic Cable Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Network’s Backbone: A Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Optic Cable Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Network’s Backbone: A Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Optic Cable Maps

The digital world we inhabit is intricately woven together by an invisible network of cables, carrying the vast flow of information that powers our lives. At the heart of this network lies the fiber optic cable, a marvel of modern technology that transmits data at lightning speeds. Understanding the intricate layout of these cables, visualized through fiber optic cable maps, is crucial for navigating the complexities of the digital landscape.
What is a Fiber Optic Cable Map?
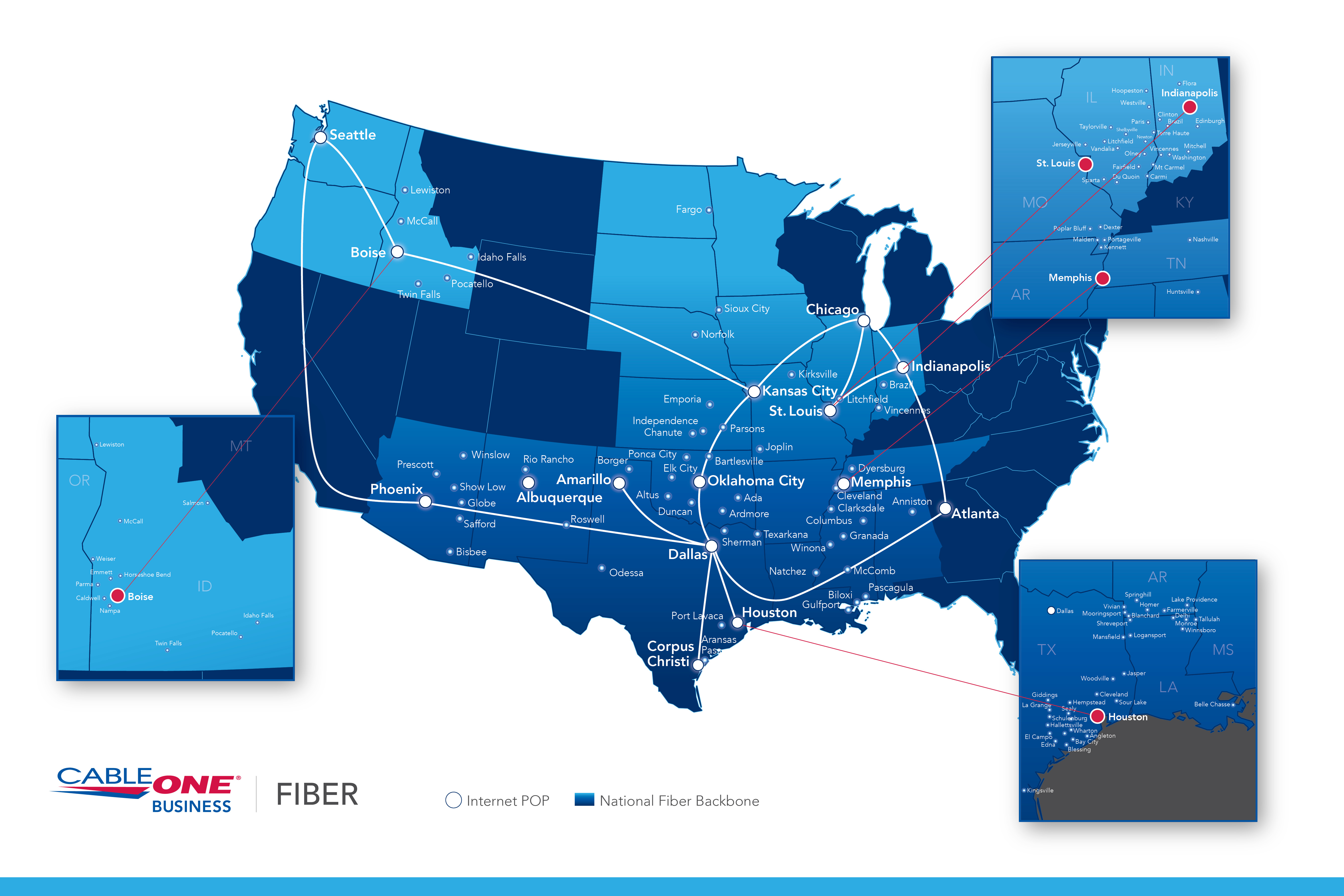
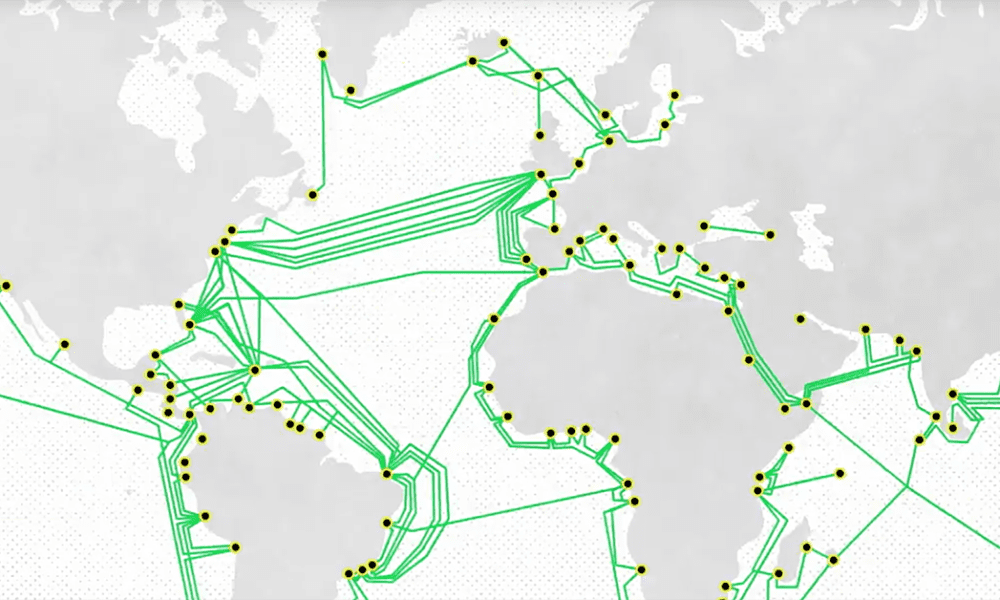
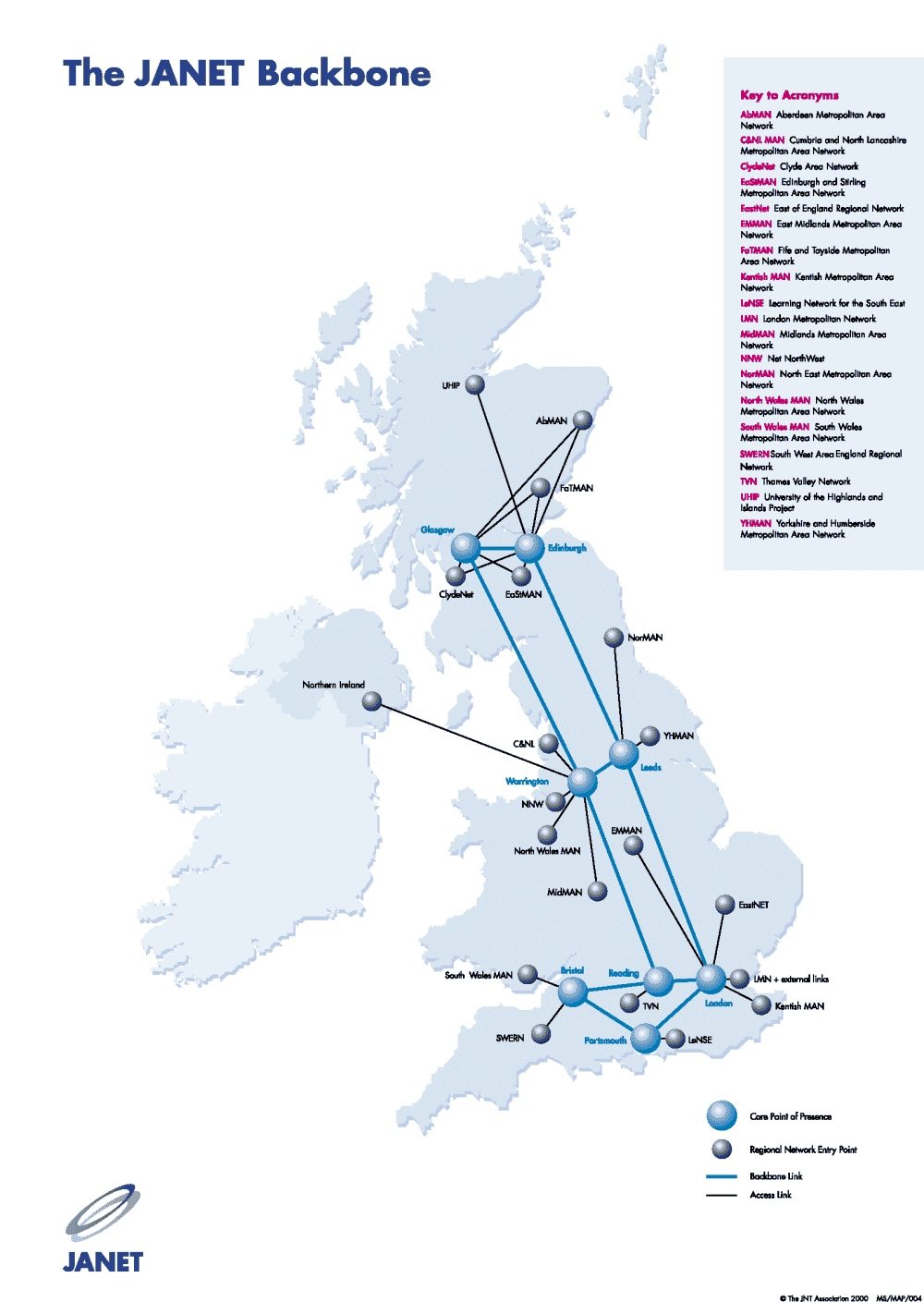
A fiber optic cable map is a visual representation of the intricate network of fiber optic cables that connect various locations. It serves as a blueprint, outlining the physical infrastructure that underpins modern communication and data transfer. These maps are essential for a multitude of stakeholders, from network operators and telecommunications companies to government agencies and businesses.
The Importance of Fiber Optic Cable Maps
The significance of fiber optic cable maps extends beyond mere visualization. These maps are instrumental in:
- Network Planning and Design: They provide a comprehensive understanding of existing infrastructure, allowing for efficient planning and design of new networks or expansions.
- Troubleshooting and Maintenance: When network outages occur, fiber optic cable maps facilitate rapid identification of the affected cable segment, enabling swift troubleshooting and repairs.
- Capacity Management: By visualizing the network’s capacity, these maps help optimize resource allocation and ensure seamless data flow, even during peak demand periods.
- Security and Resilience: Fiber optic cable maps play a crucial role in enhancing network security by identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate safeguards. They also aid in ensuring network resilience by mapping out alternate routes for data transmission in case of disruptions.
- Regulatory Compliance: In many jurisdictions, network operators are required to maintain accurate fiber optic cable maps for regulatory compliance purposes. These maps are essential for demonstrating network coverage and ensuring adherence to safety standards.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Fiber optic cable maps provide valuable insights into network connectivity and infrastructure, enabling informed strategic decisions regarding network investments, expansion, and service offerings.
Types of Fiber Optic Cable Maps
Fiber optic cable maps come in various forms, tailored to specific needs and applications:
- Physical Maps: These maps depict the actual physical location of fiber optic cables, often overlaid on geographic maps or aerial imagery. They provide detailed information on cable routes, termination points, and associated infrastructure.
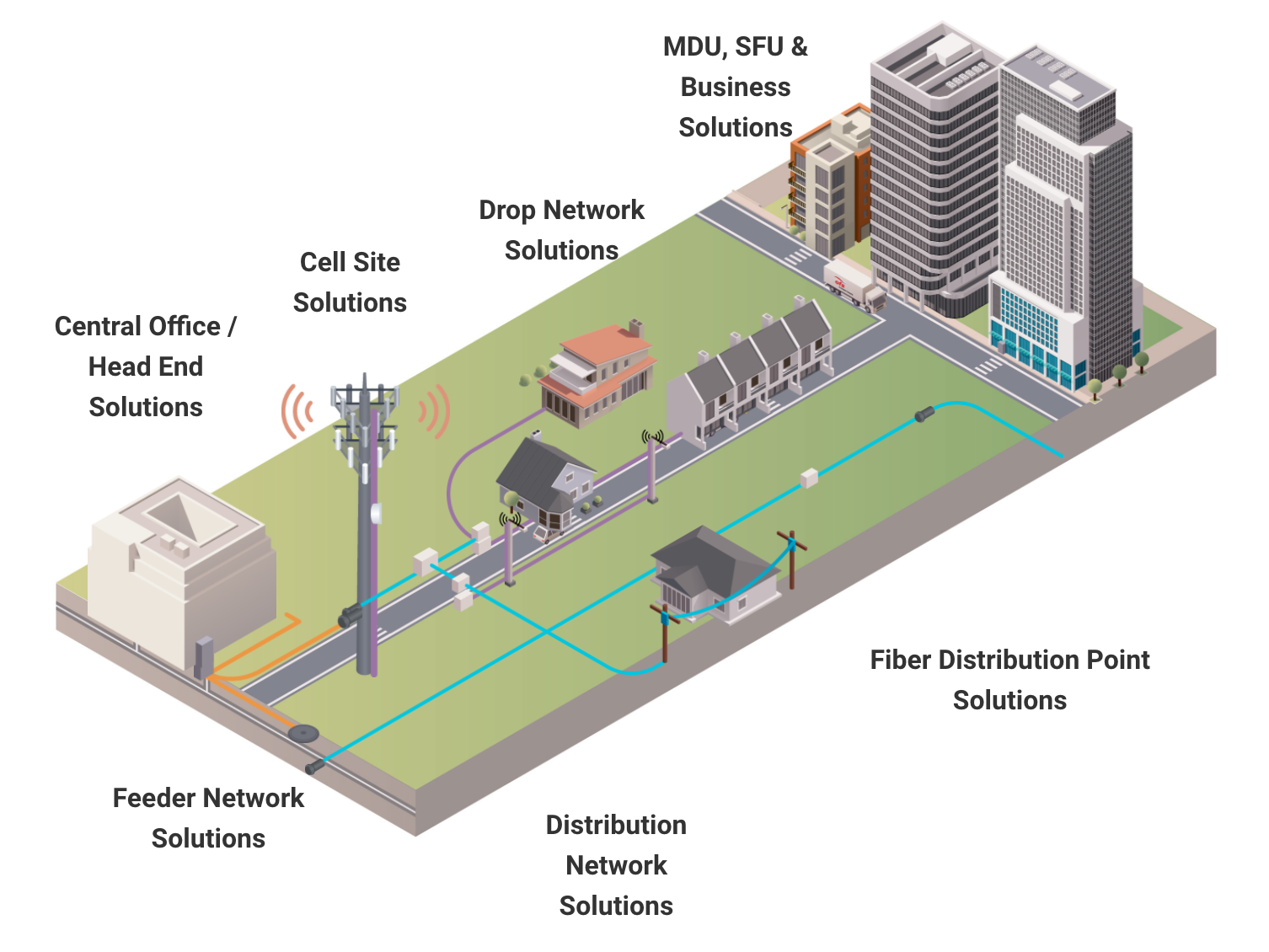
- Logical Maps: These maps focus on the logical connections between network devices, highlighting the flow of data through the network. They are particularly useful for network administrators and engineers.
- Network Topology Maps: These maps illustrate the overall structure and layout of the network, including the various nodes, links, and devices. They provide a high-level overview of the network’s architecture.
- Service Maps: These maps focus on the specific services provided over the fiber optic network, such as internet access, telephony, and video streaming. They are valuable for understanding service coverage and availability.
Data Sources for Fiber Optic Cable Maps
Creating accurate and up-to-date fiber optic cable maps requires access to reliable data sources. These sources include:
- Network Operator Records: Network operators maintain extensive databases containing detailed information about their fiber optic cable infrastructure, including cable routes, specifications, and maintenance records.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS platforms provide geospatial data, including aerial imagery, topographic maps, and property boundaries, which can be integrated with fiber optic cable data to create accurate physical maps.
- Third-Party Data Providers: Specialized data providers offer pre-compiled fiber optic cable maps and related information, often aggregated from various sources.
- Field Surveys: Conducting field surveys to verify existing data and identify new cable installations is essential for ensuring map accuracy.
Creating Fiber Optic Cable Maps
The process of creating fiber optic cable maps involves several steps:
- Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from various sources, including network operator records, GIS platforms, and field surveys.
- Data Cleaning and Validation: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency by removing duplicates, correcting errors, and verifying information against existing records.
- Data Visualization: Selecting appropriate mapping software and tools to visually represent the data in a clear and informative manner.
- Map Development: Designing the map layout, selecting appropriate symbols and colors, and adding labels and annotations to enhance readability and understanding.
- Map Maintenance: Regularly updating the maps with new data and changes to the network infrastructure to ensure ongoing accuracy and relevance.
Benefits of Using Fiber Optic Cable Maps
The use of fiber optic cable maps offers a multitude of benefits:
- Improved Network Visibility: Providing a clear and comprehensive understanding of the network infrastructure, facilitating proactive planning and management.
- Enhanced Network Performance: Optimizing network capacity, reducing latency, and ensuring reliable data transmission.
- Faster Troubleshooting and Repairs: Quickly identifying the root cause of network issues, enabling swift resolution and minimizing downtime.
- Increased Network Security: Identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate safeguards to protect sensitive data.
- Cost Savings: Optimizing resource allocation, reducing unnecessary infrastructure investments, and minimizing maintenance costs.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring reliable and high-quality services, enhancing customer experience and satisfaction.
FAQs about Fiber Optic Cable Maps
Q: Are fiber optic cable maps publicly available?
A: The availability of fiber optic cable maps varies depending on the region and the specific network operator. Some operators may publicly share limited information about their network infrastructure, while others may keep their maps confidential due to security and competitive reasons.
Q: How often should fiber optic cable maps be updated?
A: The frequency of map updates depends on the rate of change in the network infrastructure. For rapidly evolving networks, regular updates, even on a monthly or quarterly basis, may be necessary. For more stable networks, annual updates may suffice.
Q: What software is used to create fiber optic cable maps?
A: Various software tools are available for creating fiber optic cable maps, including Geographic Information Systems (GIS) platforms, network management software, and specialized mapping applications. The choice of software depends on the specific requirements and the desired level of detail.
Q: What are the challenges associated with creating and maintaining fiber optic cable maps?
A: Creating and maintaining accurate fiber optic cable maps can be challenging due to factors such as:
- Data availability: Accessing comprehensive and reliable data about the network infrastructure can be challenging, especially for large and complex networks.
- Data accuracy: Ensuring data accuracy and consistency requires rigorous validation and verification processes.
- Dynamic network changes: Network infrastructure is constantly evolving, requiring frequent updates to the maps to reflect these changes.
- Cost and resources: Creating and maintaining fiber optic cable maps can be resource-intensive, requiring specialized software, skilled personnel, and ongoing maintenance efforts.
Tips for Effective Use of Fiber Optic Cable Maps
- Collaborate with stakeholders: Engage with network operators, telecommunications companies, and other relevant stakeholders to gather accurate data and ensure map consistency.
- Use standardized data formats: Employ standardized data formats and conventions to ensure data interoperability and facilitate map integration with other systems.
- Regularly review and update maps: Conduct periodic reviews and updates to ensure map accuracy and relevance, reflecting changes in the network infrastructure.
- Implement a map management system: Establish a systematic approach for managing fiber optic cable maps, including data storage, version control, and access permissions.
- Train personnel on map use: Provide training to relevant personnel on the interpretation and use of fiber optic cable maps, empowering them to leverage the information effectively.
Conclusion
Fiber optic cable maps are indispensable tools for navigating the complexities of the digital world. They provide a visual representation of the network’s infrastructure, enabling efficient planning, troubleshooting, and management. By leveraging the power of these maps, stakeholders can enhance network performance, optimize resource allocation, and ensure the seamless flow of data that fuels our digital lives. As technology continues to evolve and the demand for high-speed connectivity grows, the importance of fiber optic cable maps will only continue to increase.

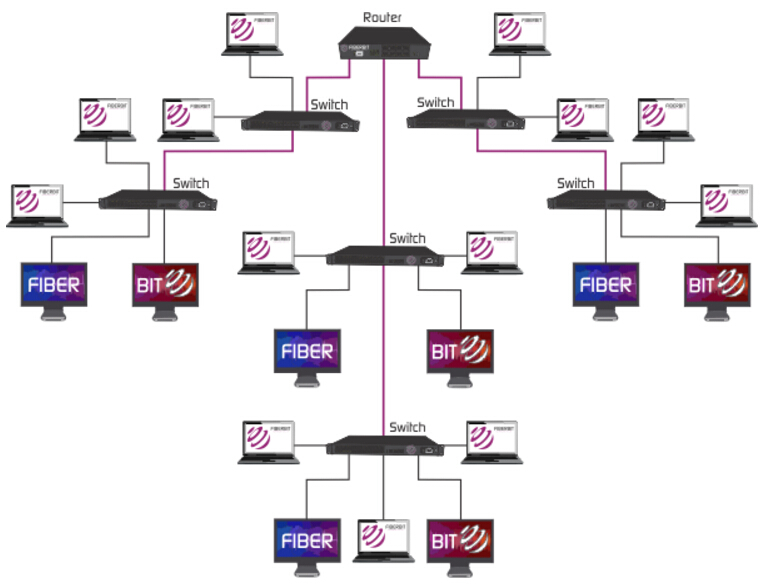
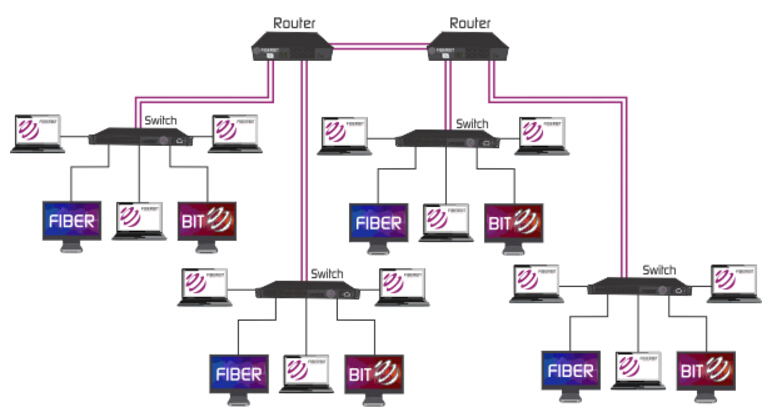
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Network’s Backbone: A Comprehensive Guide to Fiber Optic Cable Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!