Unveiling the Global Landscape of Nuclear Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nuclear Reactor Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Global Landscape of Nuclear Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nuclear Reactor Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Global Landscape of Nuclear Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nuclear Reactor Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Global Landscape of Nuclear Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nuclear Reactor Map
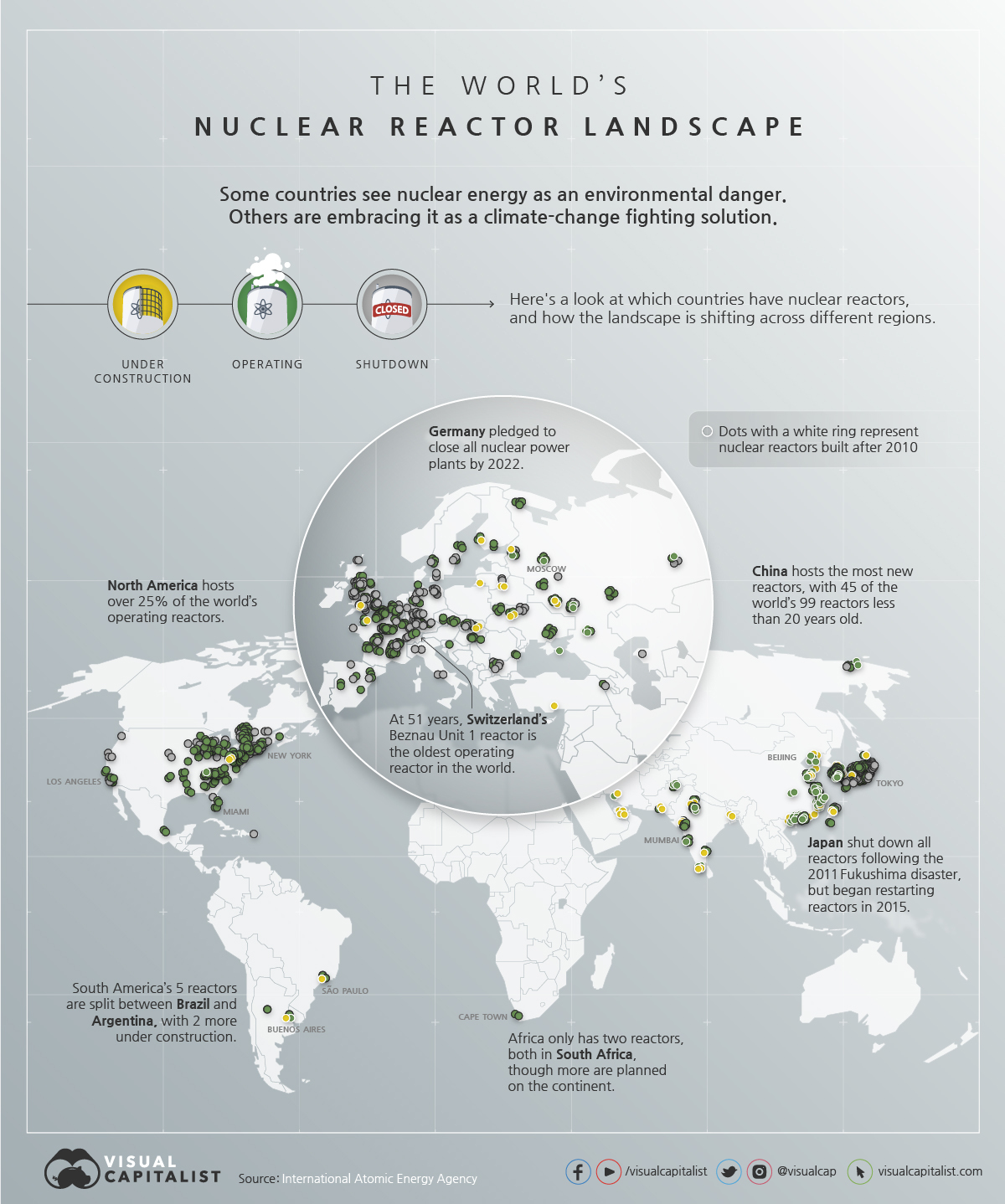
The world’s energy landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, with a growing emphasis on sustainable and reliable energy sources. Nuclear power, with its ability to generate vast amounts of electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, plays a crucial role in this transition. Understanding the global distribution of nuclear reactors is essential for comprehending the current state and future potential of this technology.
A Visual Representation of Nuclear Power:
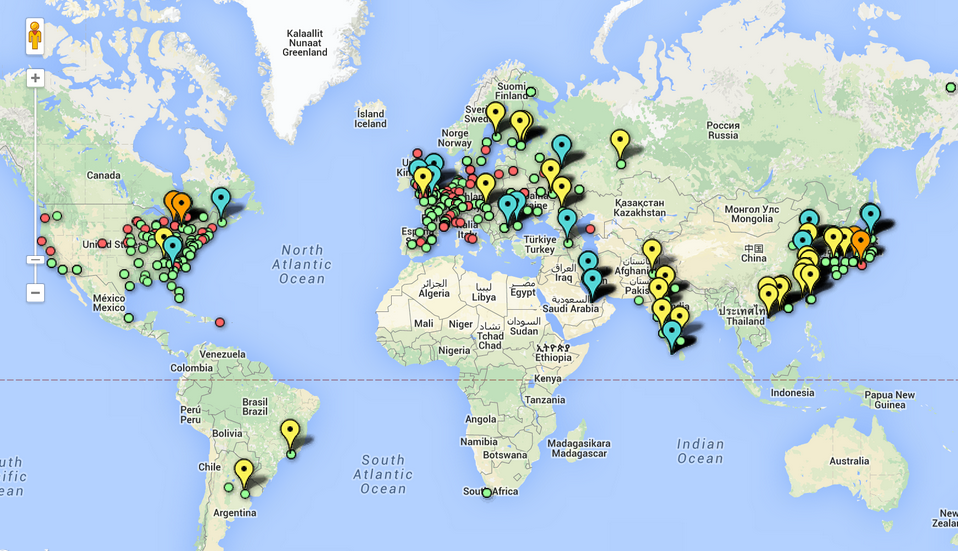
The nuclear reactor map is a powerful tool for visualizing the global landscape of nuclear power. It offers a snapshot of the countries currently utilizing this technology, the number of reactors in operation, and their geographical distribution. This map serves as a valuable resource for policymakers, researchers, and the general public interested in understanding the role of nuclear power in the global energy mix.
Navigating the Map: Key Insights and Interpretations:
The nuclear reactor map reveals several key insights about the global landscape of nuclear power:
- Global Distribution: The map highlights the geographical distribution of nuclear reactors, revealing that they are primarily concentrated in developed countries with established energy infrastructure. While some developing countries have embraced nuclear power, its adoption remains uneven across the globe.
- Regional Clusters: The map reveals clusters of nuclear reactors in specific regions, indicating a concentration of expertise and infrastructure in these areas. For instance, Europe and East Asia boast a significant number of nuclear power plants, reflecting their historical reliance on this technology.
- Reactor Types: The map can be further refined to include information about the types of reactors in operation. This allows for a more detailed understanding of the technological landscape, highlighting the prevalence of certain reactor designs and their associated advantages and drawbacks.
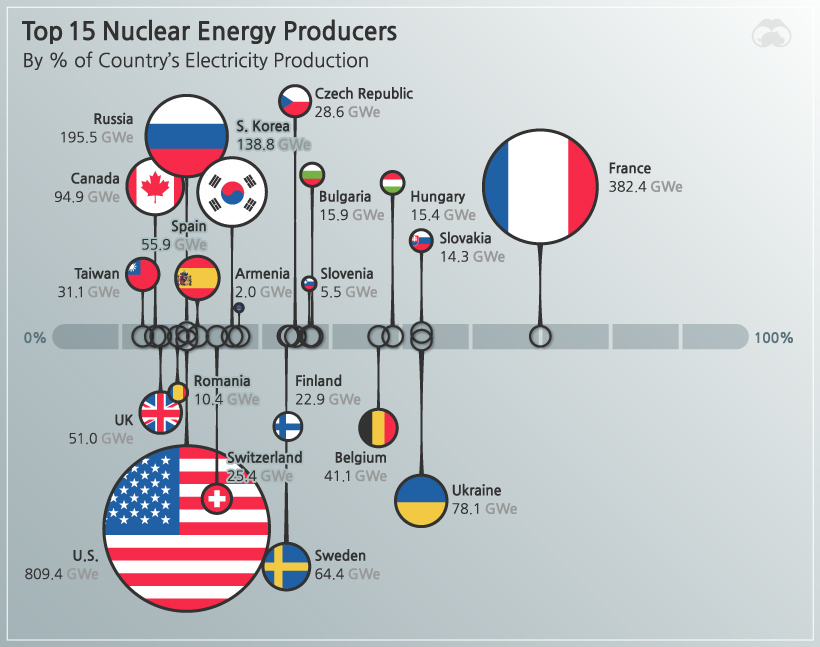
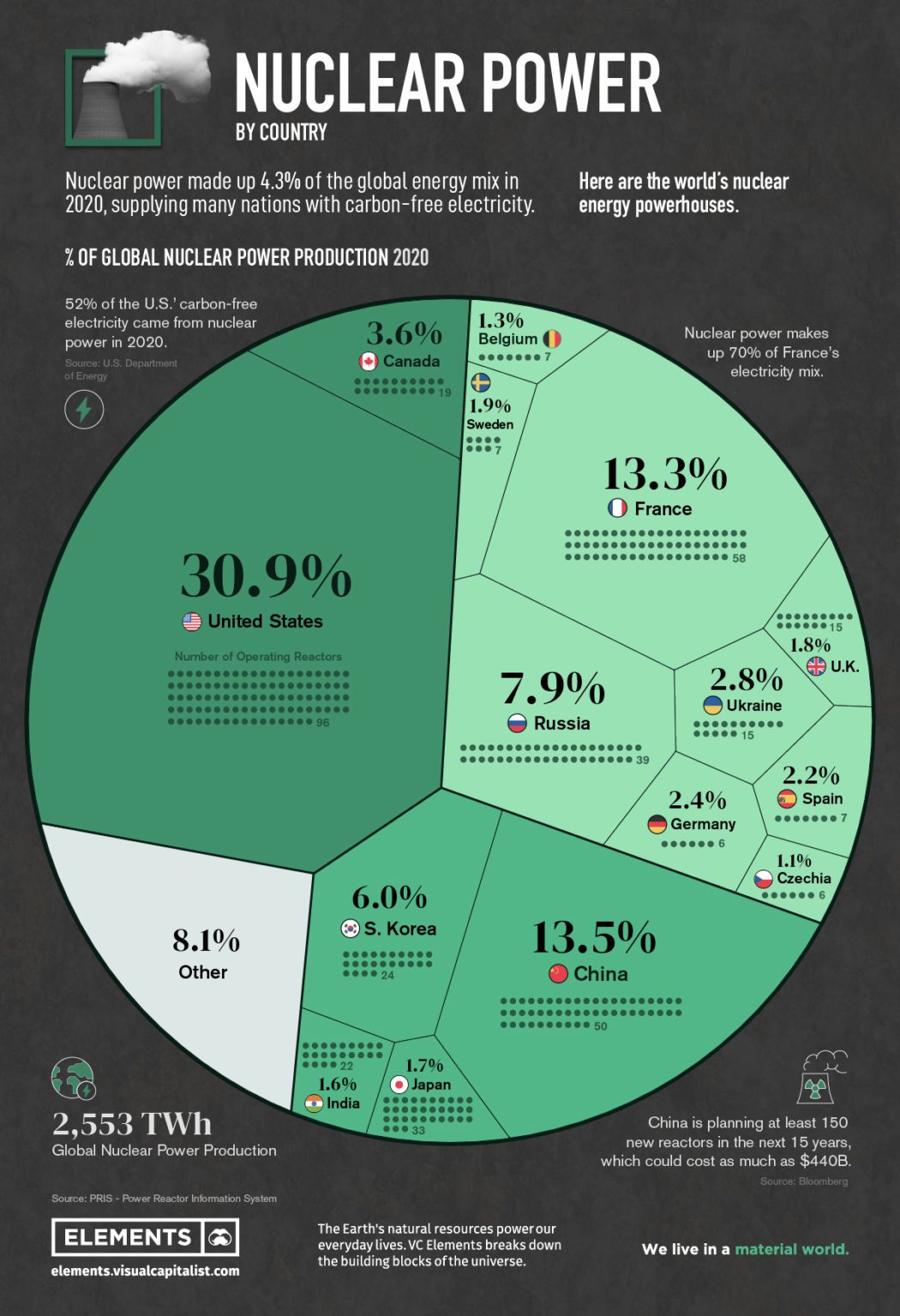
- Capacity and Output: The map can also display the capacity of each reactor, providing insights into the total energy output generated by nuclear power in different regions. This data is crucial for understanding the contribution of nuclear power to global energy production.
Beyond the Map: Exploring the Significance of Nuclear Power:
The nuclear reactor map is more than just a visual representation; it serves as a window into the broader significance of nuclear power:
- Reliable and Efficient Energy Source: Nuclear power plants provide a reliable and efficient source of electricity, operating continuously and independently of weather conditions. This makes them a valuable asset for ensuring energy security and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power generation emits negligible greenhouse gases, making it a key player in the fight against climate change. This is particularly important in countries with ambitious decarbonization targets.
- Economic Benefits: Nuclear power plants create jobs, stimulate local economies, and contribute to technological innovation. They also offer long-term economic stability by reducing reliance on volatile energy markets.
- Research and Development: The nuclear sector continues to innovate, developing advanced reactor designs with enhanced safety features and reduced waste generation. These advancements offer the potential for even greater benefits in the future.
Addressing Concerns and Challenges:
While nuclear power offers significant benefits, it is not without its challenges:
- Nuclear Waste Management: The safe and responsible management of nuclear waste remains a critical issue. While technologies for waste disposal are constantly evolving, public perception and concerns surrounding radioactive waste remain a significant obstacle.
- Nuclear Safety and Security: Ensuring the safety and security of nuclear power plants is paramount. Accidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima have highlighted the potential risks associated with this technology, emphasizing the need for robust safety regulations and security measures.
- Public Perception: Public perception of nuclear power is often influenced by historical accidents and concerns about safety and waste management. Bridging the gap between scientific understanding and public opinion is crucial for promoting the responsible use of nuclear power.
- Cost and Investment: The construction of nuclear power plants is a capital-intensive undertaking, requiring significant upfront investment. This can present a barrier to entry for some countries, particularly developing nations.
FAQs about the Nuclear Reactor Map:
1. What is the purpose of the nuclear reactor map?
The nuclear reactor map serves as a visual representation of the global landscape of nuclear power, providing information on the distribution, capacity, and types of reactors in operation. It is a valuable tool for understanding the current state and future potential of this technology.
2. How is the nuclear reactor map updated?
The nuclear reactor map is typically updated by organizations specializing in nuclear energy data, such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the World Nuclear Association, and national nuclear regulatory bodies. These organizations collect and analyze data on nuclear power plants, ensuring the map reflects the most current information.
3. What are the limitations of the nuclear reactor map?
The nuclear reactor map provides a snapshot of the global nuclear power landscape but does not capture all aspects of this complex technology. It does not necessarily reflect the full potential of nuclear power, including the development of advanced reactor designs and the ongoing research in this field.
4. How can I use the nuclear reactor map?
The nuclear reactor map can be used for various purposes, including:
- Understanding the global distribution of nuclear power: It provides a visual representation of the countries utilizing nuclear power and the geographical concentration of reactors.
- Assessing the role of nuclear power in different regions: It allows for comparisons of nuclear power capacity and output across various regions.
- Identifying trends in nuclear power development: It can be used to track changes in the number and type of reactors over time.
- Exploring the potential for nuclear power in the future: It provides a basis for understanding the potential for nuclear power to contribute to global energy security and climate change mitigation.
Tips for Using the Nuclear Reactor Map:
- Consider the map’s context: The nuclear reactor map is a valuable tool but should be used alongside other sources of information. It is important to consider the data sources, the map’s limitations, and the broader context of nuclear power.
- Focus on specific regions or countries: The map can be zoomed in to focus on specific regions or countries, providing a more detailed understanding of their nuclear power landscape.
- Explore the map’s features: Many nuclear reactor maps offer interactive features, allowing users to filter data, explore different reactor types, and access additional information.
- Consult other resources: The nuclear reactor map can be used in conjunction with other resources, such as reports, articles, and databases, to gain a comprehensive understanding of nuclear power.
Conclusion:
The nuclear reactor map offers a valuable visual representation of the global landscape of nuclear power. It provides insights into the geographical distribution, capacity, and types of reactors in operation, highlighting the role of this technology in the global energy mix. While nuclear power faces challenges, its potential for providing reliable, efficient, and low-carbon electricity remains significant. Understanding the nuclear reactor map is crucial for navigating the complex world of nuclear power and appreciating its role in shaping the future of energy.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Global Landscape of Nuclear Power: A Comprehensive Guide to the Nuclear Reactor Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!