Understanding the Geographic Landscape of Islam: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Islamic Countries
Related Articles: Understanding the Geographic Landscape of Islam: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Islamic Countries
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Geographic Landscape of Islam: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Islamic Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Geographic Landscape of Islam: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Islamic Countries
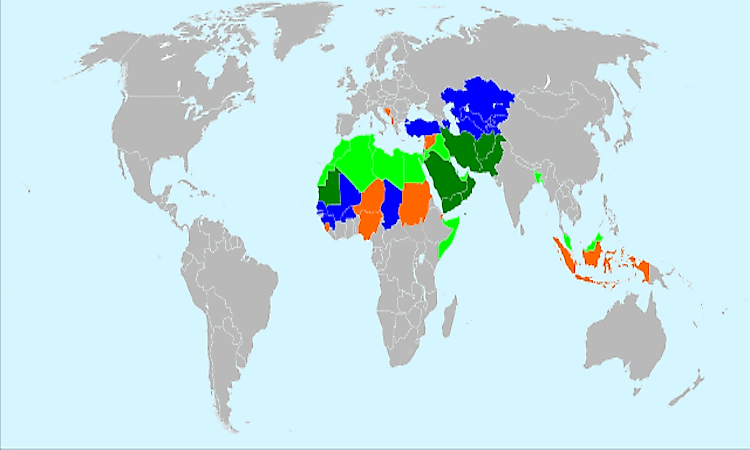
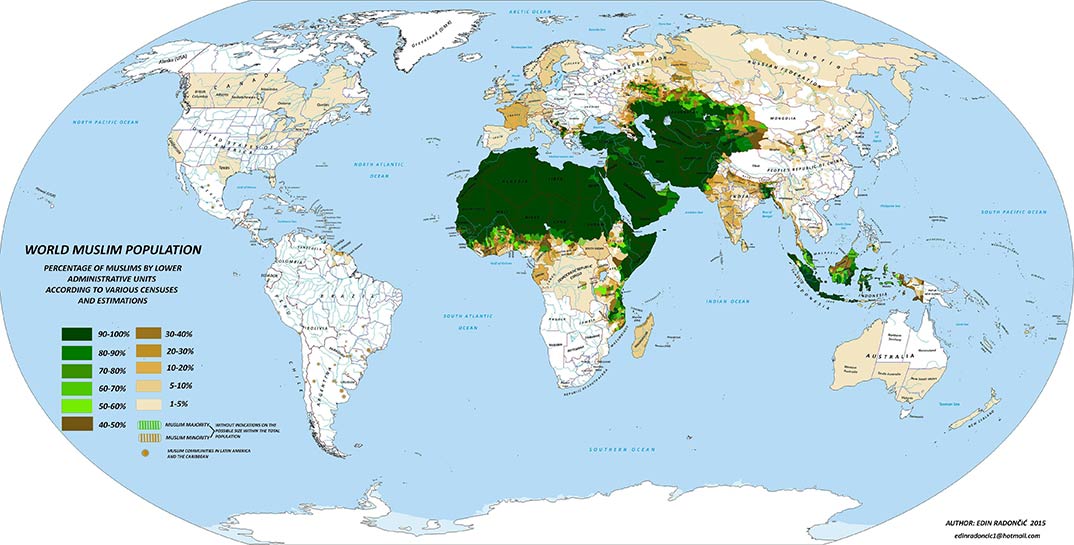
The geographic distribution of Islam is a complex and dynamic phenomenon, shaped by historical, cultural, and political factors. A map of Islamic countries provides a visual representation of this vast and diverse community, highlighting its presence across continents and its influence on global affairs.
Defining "Islamic Country": A Matter of Perspective
Before delving into the map, it’s crucial to understand the nuances of defining an "Islamic country." While the term commonly refers to nations with a Muslim majority population, the reality is more nuanced.
- Majority Muslim Population: Many countries, such as Indonesia, Pakistan, and Egypt, are considered Islamic due to their majority Muslim populations. This signifies a significant cultural and religious influence on society.
- State Religion: Some countries, like Saudi Arabia and Iran, have Islam as their official state religion, reflecting its central role in governance and law.
- Historical and Cultural Significance: Even in countries with a smaller Muslim population, Islam may hold historical and cultural significance, shaping the nation’s heritage and identity.
A Global Mosaic: Mapping the Spread of Islam
The map of Islamic countries reveals a sprawling mosaic across the globe, encompassing vast regions and diverse cultures.
- The Middle East and North Africa: This region, often referred to as the "Arab world," forms the heartland of Islam, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Morocco holding a prominent position in the Islamic world.
- Southeast Asia: Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei are home to significant Muslim populations, reflecting the historical spread of Islam through trade routes.
- South Asia: Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India have large Muslim communities, influenced by centuries of cultural and religious interaction.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: Countries like Nigeria, Senegal, and Somalia demonstrate the presence of Islam in this region, often intertwined with local traditions and beliefs.
- Central Asia: Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan have strong historical ties to Islam, evident in their cultural heritage and architectural marvels.
Beyond Borders: The Global Reach of Islam
The map highlights the global reach of Islam, extending beyond national boundaries.
- Diaspora Communities: Muslim communities exist in virtually every corner of the world, forming vibrant diasporas in Europe, North America, and other regions.
- Cultural Exchange: Islam’s presence fosters cultural exchange and understanding, enriching societies with diverse perspectives and traditions.
- International Cooperation: The map underscores the importance of international cooperation and dialogue among Islamic nations, fostering peace and understanding.
Navigating the Map: Understanding the Dynamics
The map of Islamic countries is not static; it reflects the dynamic nature of the Islamic world.
- Political Shifts: Political changes, including independence movements, revolutions, and border adjustments, can impact the map’s configuration.
- Demographic Trends: Population growth, migration patterns, and religious conversions contribute to shifts in the distribution of Muslims worldwide.
- Religious Diversity: It’s important to acknowledge the internal diversity within Islam, encompassing various schools of thought, interpretations, and practices.
The Importance of Understanding the Map
Understanding the map of Islamic countries is crucial for several reasons:
- Global Perspective: It provides a global perspective on the presence and influence of Islam in the world.
- Cultural Awareness: It fosters cultural awareness and appreciation for the diverse communities and traditions within the Islamic world.
- International Relations: It contributes to better understanding and cooperation among nations, fostering peace and dialogue.
- Historical Context: It provides context for understanding historical events and cultural exchanges that have shaped the Islamic world.
FAQs about the Map of Islamic Countries
1. What is the largest Islamic country by population?
Indonesia is the largest Islamic country by population, with over 230 million Muslims.
2. What is the oldest Islamic country?
Yemen is often considered the oldest Islamic country, with Islam being introduced in the 7th century CE.
3. Are there any countries with no Muslims?
While a vast majority of countries have Muslim populations, some countries, such as Iceland, Andorra, and Nauru, have very small or negligible Muslim populations.
4. What is the difference between a "Muslim country" and an "Islamic country"?
While often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference. A "Muslim country" refers to a nation with a majority Muslim population, while an "Islamic country" typically implies that Islam is the official state religion or has a significant influence on the legal and social system.
5. How does the map of Islamic countries change over time?
The map of Islamic countries is constantly evolving due to political shifts, demographic trends, and religious conversions. For example, the breakup of the Soviet Union led to the emergence of new independent nations with significant Muslim populations.
Tips for Using the Map of Islamic Countries
- Explore Beyond the Map: Go beyond the map to learn about the history, culture, and traditions of individual Islamic countries.
- Engage in Dialogue: Seek out opportunities to engage in dialogue with people from different cultural and religious backgrounds, fostering understanding and respect.
- Embrace Diversity: Recognize the internal diversity within the Islamic world, appreciating the various schools of thought, interpretations, and practices.
- Challenge Stereotypes: Be critical of stereotypes and generalizations about Islam and Muslim communities, seeking accurate and nuanced information.
Conclusion
The map of Islamic countries serves as a powerful visual representation of the global presence and influence of Islam. It underscores the diversity, complexity, and dynamism of the Islamic world, emphasizing the importance of understanding and appreciating its rich cultural heritage and contributions to global society. By engaging with the map and its associated information, we can foster a deeper understanding of the Islamic world, promoting dialogue, cooperation, and mutual respect among diverse communities.
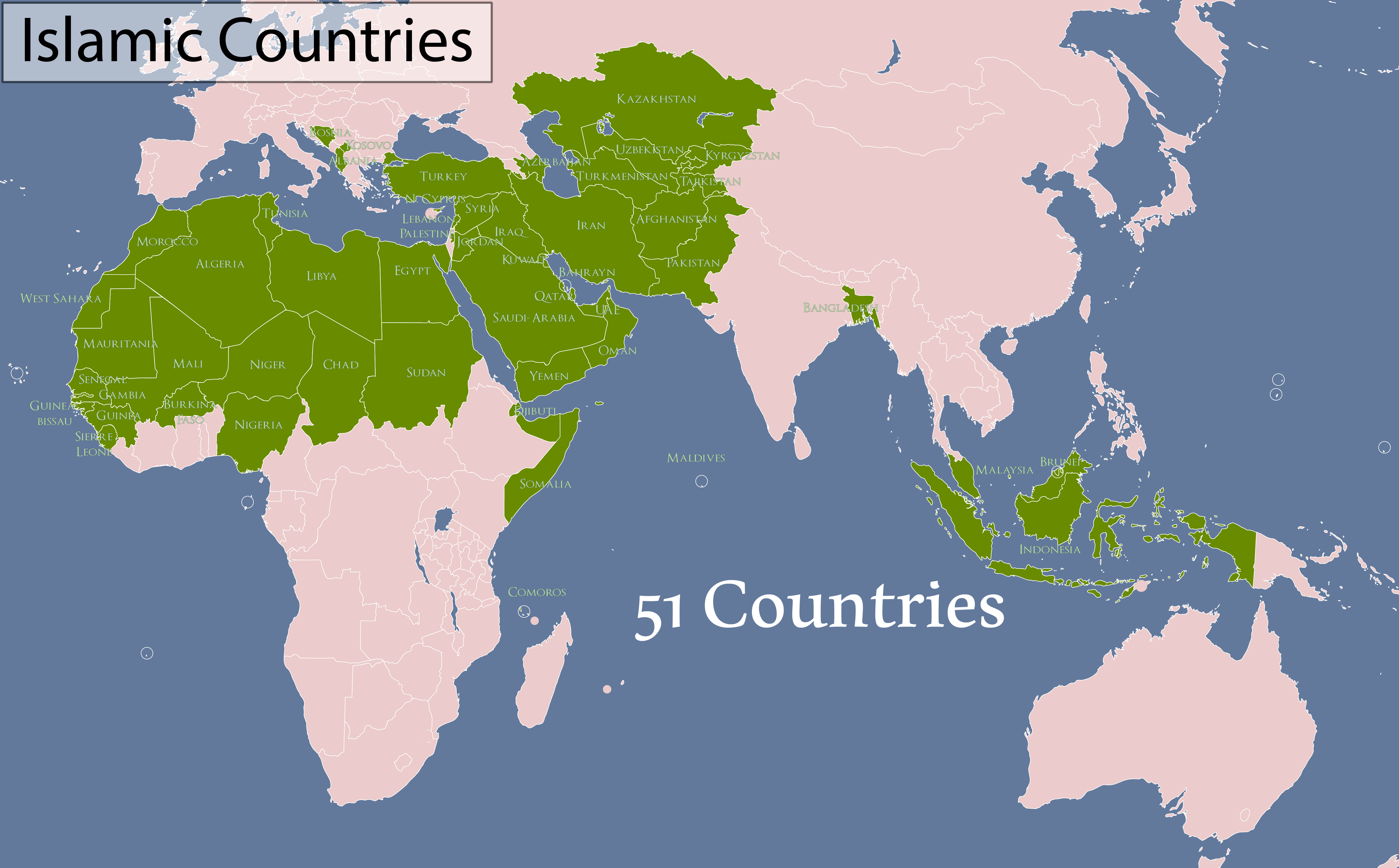
![Islam - Human Geography! :]](https://whatisthislife.weebly.com/uploads/1/6/4/3/16433764/753919813_orig.jpg)

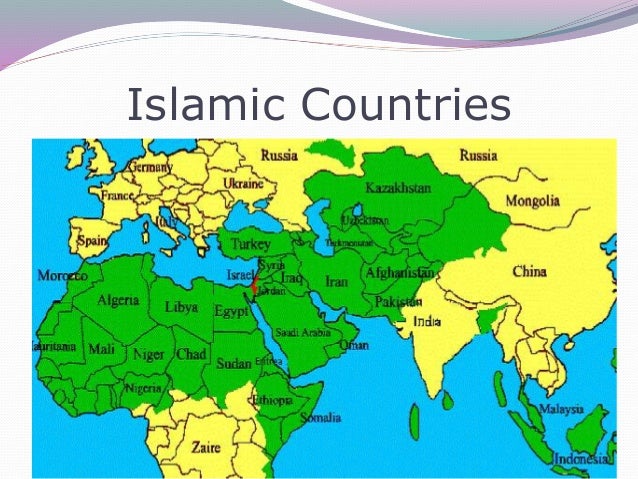
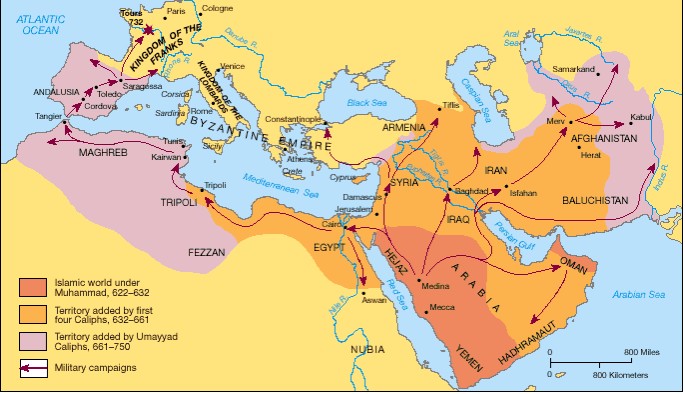


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Geographic Landscape of Islam: A Comprehensive Look at the Map of Islamic Countries. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!