Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps
- 3.1 Defining the Datum: A Framework for Geographic Accuracy
- 3.2 Understanding the Importance of Datum Maps
- 3.3 Different Types of Datum Maps: A Global Perspective
- 3.4 The Impact of Datum Mismatches: A Potential Source of Error
- 3.5 Datum Transformation: Bridging the Gap Between Different Datums
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Datum Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Working with Datum Maps
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Importance of Datum Maps in Geographic Data
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps
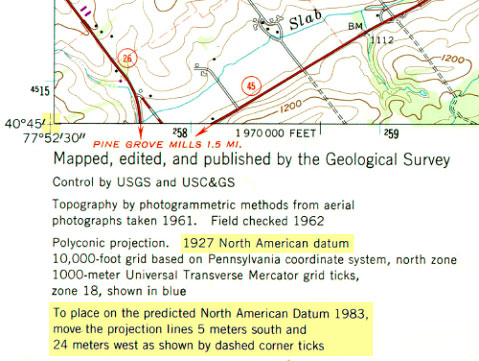
In the realm of geographic information systems (GIS) and mapping, accuracy and consistency are paramount. To ensure these qualities, a fundamental concept known as the datum plays a crucial role. A datum serves as a reference framework, defining the shape and size of the Earth, along with the origin and orientation of coordinates. It essentially provides a common language for describing locations on the planet, enabling the seamless integration of data from diverse sources. This article delves into the intricacies of datum maps, exploring their significance and providing a detailed understanding of their applications.
Defining the Datum: A Framework for Geographic Accuracy
Imagine trying to pinpoint a location on a map without a clear reference point. This is precisely the challenge that arises without a datum. A datum provides a foundational framework, a set of mathematical parameters that define the Earth’s shape and size, along with the origin and orientation of the coordinate system. These parameters serve as a common language for representing geographic data, ensuring that different maps and datasets can be accurately combined and analyzed.
Key Components of a Datum:
- Ellipsoid: A mathematical model that approximates the Earth’s shape, typically an oblate spheroid (slightly flattened at the poles and bulging at the equator).
- Geodetic Reference Point: A specific location on the Earth’s surface used as a reference point for the datum.
- Orientation: The relationship between the ellipsoid and the Earth’s surface, defining the direction of the coordinate axes.
Understanding the Importance of Datum Maps
The significance of datum maps lies in their ability to ensure consistency and accuracy in geographic data. When different maps and datasets are based on the same datum, they can be seamlessly integrated, providing a unified view of the geographical landscape. This is essential for various applications, including:
- Navigation: GPS systems rely on accurate datum information to provide precise location coordinates.
- Mapping and Surveying: Datum maps are fundamental for creating accurate maps, surveying land, and measuring distances.
- Environmental Monitoring: Accurate geographic data is crucial for monitoring environmental changes, natural disasters, and resource management.
- Infrastructure Planning: Datum maps are essential for planning and managing infrastructure projects, ensuring that roads, bridges, and other structures are built in the correct locations.
- Spatial Analysis: Datum maps enable the analysis of spatial relationships between different geographic features, providing insights into population distribution, land use patterns, and environmental trends.
Different Types of Datum Maps: A Global Perspective
The Earth’s shape is complex, and different datums have been developed to best represent various regions. Here are some of the most commonly used datums:
- WGS 84 (World Geodetic System 1984): This is the most widely used datum globally, adopted by the United States Department of Defense. It is used by GPS systems and numerous mapping applications.
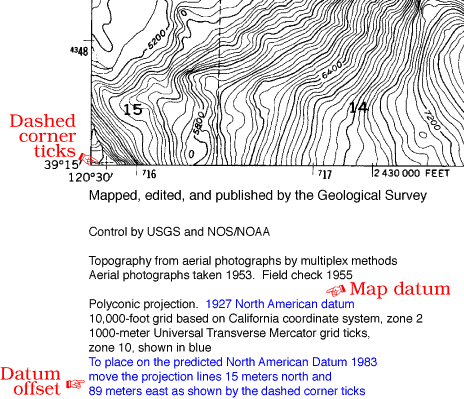
- NAD 83 (North American Datum 1983): Primarily used in North America, NAD 83 is a geocentric datum that aligns with WGS 84.
- NAD 27 (North American Datum 1927): This is an older datum, primarily used in the United States. It is a local datum, meaning it is based on a specific region of the Earth.
- European Datum 1950 (ED50): Commonly used in Europe, ED50 is a local datum based on the reference ellipsoid of Hayford.
- Tokyo Datum: This datum is used in Japan and is based on the Bessel ellipsoid.
The Impact of Datum Mismatches: A Potential Source of Error
Using different datums for various datasets can lead to discrepancies in geographic data, resulting in inaccuracies and inconsistencies. For instance, if a map based on NAD 83 is overlaid with data from a map using NAD 27, the features might appear misaligned, leading to incorrect spatial analysis and decision-making.
Consequences of Datum Mismatches:
- Inaccurate measurements: Distances, areas, and coordinates may be incorrect when using data from different datums.
- Misaligned features: Geographic features may appear shifted or distorted when datasets from different datums are combined.
- Incorrect spatial analysis: Mismatches in datum can lead to flawed results in spatial analysis applications.
Datum Transformation: Bridging the Gap Between Different Datums
To overcome the challenges posed by datum mismatches, datum transformation techniques are employed. These techniques involve mathematical calculations to convert coordinates from one datum to another, ensuring that data from different sources can be seamlessly integrated.
Common Datum Transformation Methods:
- Helmert Transformation: A rigid transformation that involves translation, rotation, and scaling.
- Molodensky Transformation: A three-parameter transformation that accounts for differences in the ellipsoid and origin.
- Grid Transformation: A method that uses grids to define the relationship between two datums.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Datum Maps
1. What is the difference between a datum and a coordinate system?
A datum defines the shape and size of the Earth, while a coordinate system provides a framework for representing locations on the Earth’s surface using latitude and longitude. A datum provides the foundation for the coordinate system.
2. Why are there different datums?
Different datums are developed to best represent specific regions of the Earth, taking into account the varying shapes and sizes of the geoid (the actual shape of the Earth’s surface) in different locations.
3. How can I determine the datum of a map or dataset?
The datum information is typically included in the metadata of the map or dataset. You can also consult the source of the data or refer to documentation for specific mapping software.
4. What are the implications of using the wrong datum?
Using the wrong datum can lead to inaccurate measurements, misaligned features, and incorrect spatial analysis. It is crucial to ensure that all data used in a project is based on the same datum.
5. How can I transform data from one datum to another?
Datum transformation tools are available in GIS software and online services. These tools employ mathematical calculations to convert coordinates from one datum to another.
Tips for Working with Datum Maps
- Understand the datum used for your data: Always ensure that you are aware of the datum used for your maps and datasets.
- Use the same datum for all data: When combining data from different sources, ensure that all data is based on the same datum.
- Transform data to a common datum: If you need to combine data from different datums, use datum transformation techniques to convert the data to a common reference frame.
- Consult documentation: Refer to documentation for your mapping software or data sources to understand the datums used and how to perform datum transformations.
Conclusion: The Importance of Datum Maps in Geographic Data
Datum maps are an essential component of geographic information systems, providing a foundational framework for representing and analyzing spatial data. Their ability to ensure accuracy, consistency, and seamless integration of data from diverse sources makes them crucial for various applications, including navigation, mapping, environmental monitoring, infrastructure planning, and spatial analysis. Understanding the concepts of datums, datum transformations, and the potential consequences of datum mismatches is essential for anyone working with geographic data. By adhering to best practices and utilizing the appropriate tools, professionals can leverage the power of datum maps to unlock valuable insights from spatial information and make informed decisions based on accurate geographic data.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Foundation of Geographic Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Datum Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!