Understanding the Female Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Guide to Lymph Nodes
Related Articles: Understanding the Female Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Guide to Lymph Nodes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Female Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Guide to Lymph Nodes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Female Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Guide to Lymph Nodes

The lymphatic system is a vital component of the human body’s defense mechanism, playing a crucial role in immunity, fluid balance, and waste removal. Within this complex network, lymph nodes serve as critical checkpoints, filtering lymph fluid and housing immune cells that combat infections and diseases. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate anatomy and function of lymph nodes in females, emphasizing their significance in maintaining overall health.
Lymph Nodes: The Body’s Immune Sentinels
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped organs distributed throughout the body, connected by a network of lymphatic vessels. These vessels transport lymph fluid, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the body. As lymph fluid passes through the lymph nodes, it is filtered by immune cells, primarily lymphocytes, which identify and destroy foreign invaders like bacteria, viruses, and cancerous cells.
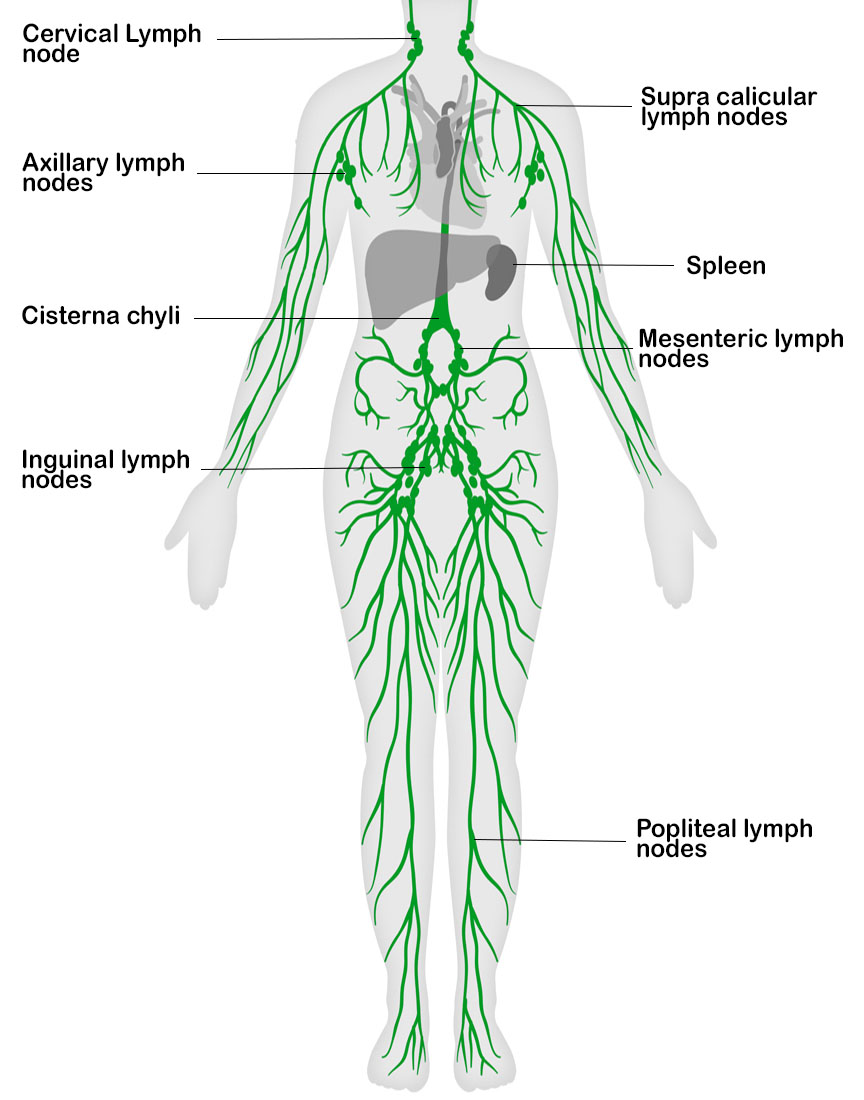
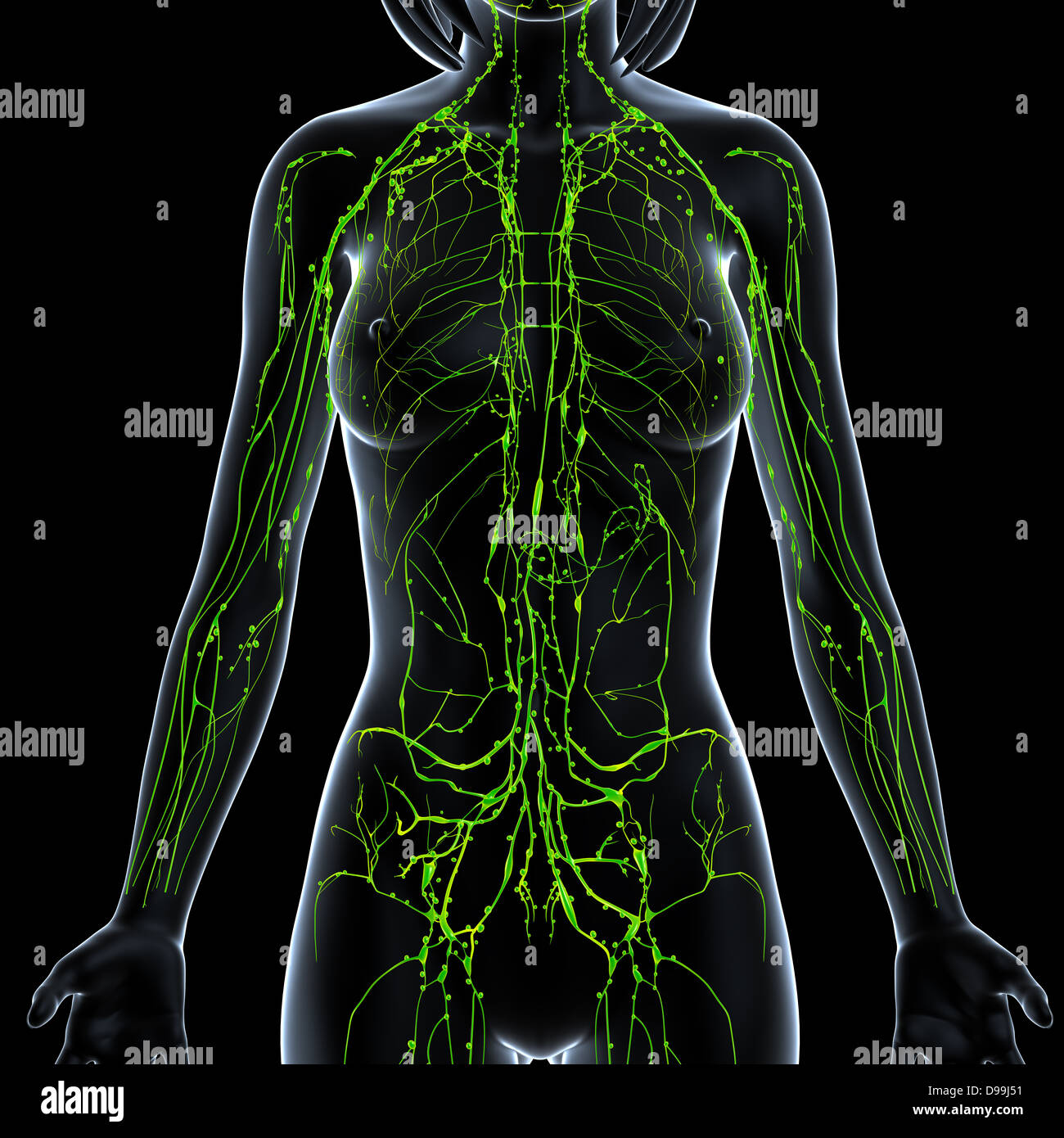
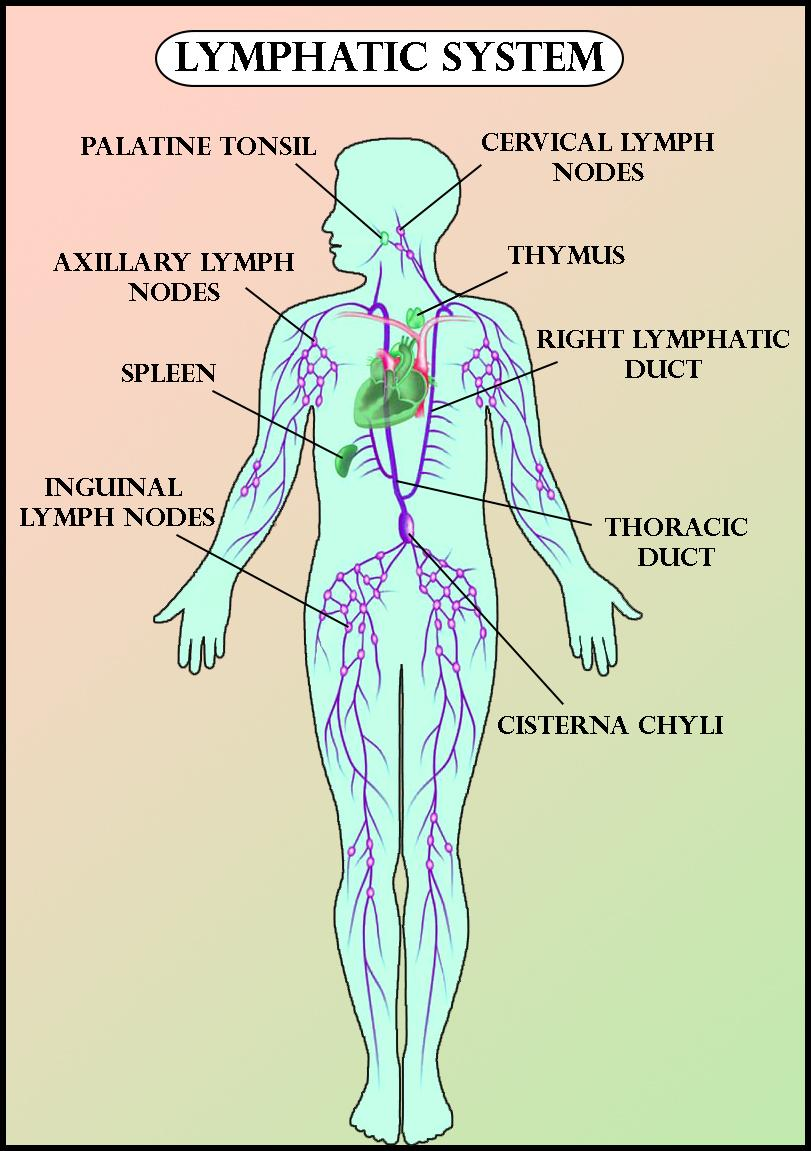
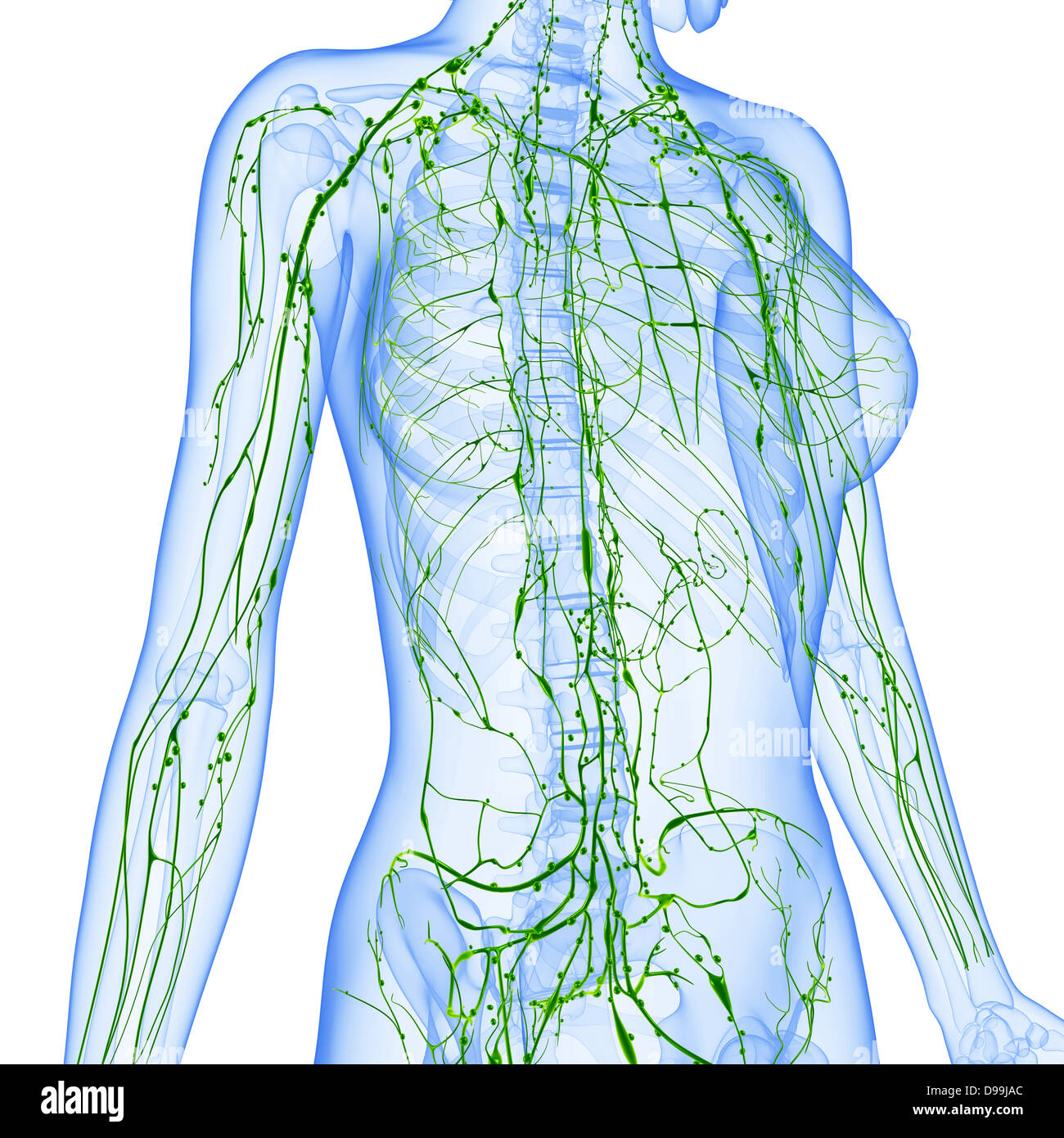
Mapping the Female Lymphatic System
The female lymphatic system mirrors the male system, with a few notable differences related to reproductive organs. The lymph nodes are strategically located in various regions of the body, with specific clusters associated with particular organs and systems. A detailed map of female lymph nodes can be divided into several key areas:
1. Head and Neck:
- Cervical Lymph Nodes: Located in the neck region, these nodes drain lymph from the head, neck, and upper chest. They are further subdivided into superficial and deep cervical nodes.
- Submandibular Lymph Nodes: Situated under the jawbone, these nodes drain lymph from the mouth, tongue, and lower face.
- Submental Lymph Nodes: Located under the chin, these nodes drain lymph from the lower lip, chin, and anterior part of the tongue.
- Preauricular Lymph Nodes: Found in front of the ears, these nodes drain lymph from the scalp, face, and external ear.
- Postauricular Lymph Nodes: Located behind the ears, these nodes drain lymph from the scalp and posterior ear.
- Occipital Lymph Nodes: Situated at the back of the head, these nodes drain lymph from the scalp and posterior neck.
2. Upper Limbs:
- Axillary Lymph Nodes: Found in the armpit, these nodes drain lymph from the upper limbs, chest wall, and breast.
- Epitrochlear Lymph Nodes: Located above the inner elbow, these nodes drain lymph from the forearm and hand.
3. Thorax:
- Mediastinal Lymph Nodes: Located in the chest cavity, these nodes drain lymph from the lungs, heart, and esophagus.
- Parasternal Lymph Nodes: Situated along the sternum (breastbone), these nodes drain lymph from the anterior chest wall.
- Intercostal Lymph Nodes: Found between the ribs, these nodes drain lymph from the chest wall and intercostal muscles.
4. Abdomen:
- Para-aortic Lymph Nodes: Located along the aorta, the main artery in the abdomen, these nodes drain lymph from the abdominal organs, including the kidneys, pancreas, and intestines.
- Iliac Lymph Nodes: Found in the pelvic region, these nodes drain lymph from the lower limbs, pelvic organs, and abdominal organs.
- Inguinal Lymph Nodes: Located in the groin, these nodes drain lymph from the lower limbs, external genitalia, and lower abdomen.
5. Lower Limbs:
- Popliteal Lymph Nodes: Located behind the knee, these nodes drain lymph from the lower leg and foot.
- Superficial Inguinal Lymph Nodes: Found in the groin, these nodes drain lymph from the lower limbs, external genitalia, and lower abdomen.
- Deep Inguinal Lymph Nodes: Located deeper in the groin, these nodes drain lymph from the lower limbs, pelvic organs, and lower abdomen.
6. Pelvis:
- Pelvic Lymph Nodes: Located within the pelvic cavity, these nodes drain lymph from the reproductive organs, bladder, and rectum.
The Importance of the Female Lymphatic System
The female lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, particularly in relation to reproductive health, immune function, and disease prevention. Some key functions include:
- Immune Defense: Lymph nodes house immune cells that filter lymph fluid and identify and destroy foreign invaders, preventing infections and diseases.
- Fluid Balance: The lymphatic system collects excess fluid from tissues and returns it to the bloodstream, maintaining proper fluid balance and preventing swelling (edema).
- Waste Removal: The lymphatic system removes waste products from tissues, including cellular debris and toxins, contributing to overall tissue health.
- Reproductive Health: The lymphatic system plays a vital role in draining lymph from the reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. This drainage helps to prevent infections and maintain proper function of these organs.
Swollen Lymph Nodes: A Sign of Infection or Disease
Swollen lymph nodes, also known as lymphadenopathy, can be a sign of infection, inflammation, or even cancer. While swollen lymph nodes are often a symptom of a minor infection, they can also indicate more serious conditions. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent or unusual swelling of lymph nodes.
Factors Affecting Lymph Node Health
Several factors can affect the health and function of lymph nodes, including:
- Infections: Infections, such as bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, can cause inflammation and swelling of lymph nodes.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can affect the lymphatic system, leading to inflammation and swelling of lymph nodes.
- Cancer: Cancerous cells can spread to lymph nodes, causing them to enlarge.
- Medications: Some medications can cause side effects that affect the lymphatic system, leading to swollen lymph nodes.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, and smoking can negatively impact the lymphatic system’s function.
Tips for Maintaining Lymphatic Health
Maintaining a healthy lymphatic system is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some tips to support lymphatic health:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps to thin lymph fluid, facilitating its flow through the lymphatic system.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity stimulates lymphatic circulation, promoting drainage and waste removal.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: Consuming fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides the nutrients necessary for a healthy lymphatic system.
- Get Enough Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for immune function, which is closely linked to lymphatic health.
- Manage Stress: Stress can suppress the immune system, potentially affecting lymphatic function.
- Consider Lymphatic Drainage Massage: This specialized massage technique can help to stimulate lymphatic circulation and promote drainage.
FAQs about the Female Lymphatic System
1. What are the common causes of swollen lymph nodes in females?
Common causes of swollen lymph nodes in females include infections, such as colds, flu, or ear infections, as well as autoimmune diseases, allergies, and certain medications.
2. When should I be concerned about swollen lymph nodes?
If swollen lymph nodes persist for more than two weeks, are accompanied by fever, chills, or unexplained weight loss, or feel hard or rubbery, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
3. What are the potential risks of a compromised lymphatic system?
A compromised lymphatic system can increase the risk of infections, impair immune function, and contribute to chronic inflammation and disease.
4. Can I improve my lymphatic system health through lifestyle changes?
Yes, lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and getting enough sleep, can significantly improve lymphatic system health.
5. How is the lymphatic system affected during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, the lymphatic system undergoes significant changes to support the growing fetus and accommodate hormonal fluctuations. This can lead to increased fluid retention and swelling in the legs and ankles.
Conclusion
The female lymphatic system is a complex and vital network that plays a crucial role in immunity, fluid balance, and waste removal. Understanding the anatomy and function of lymph nodes is essential for maintaining overall health and recognizing potential issues. By adopting healthy habits and seeking medical attention when necessary, women can support the health of their lymphatic system and contribute to their overall well-being.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Female Lymphatic System: A Comprehensive Guide to Lymph Nodes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!