Understanding the Complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian Landscape: A 2021 Perspective
Related Articles: Understanding the Complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian Landscape: A 2021 Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian Landscape: A 2021 Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian Landscape: A 2021 Perspective

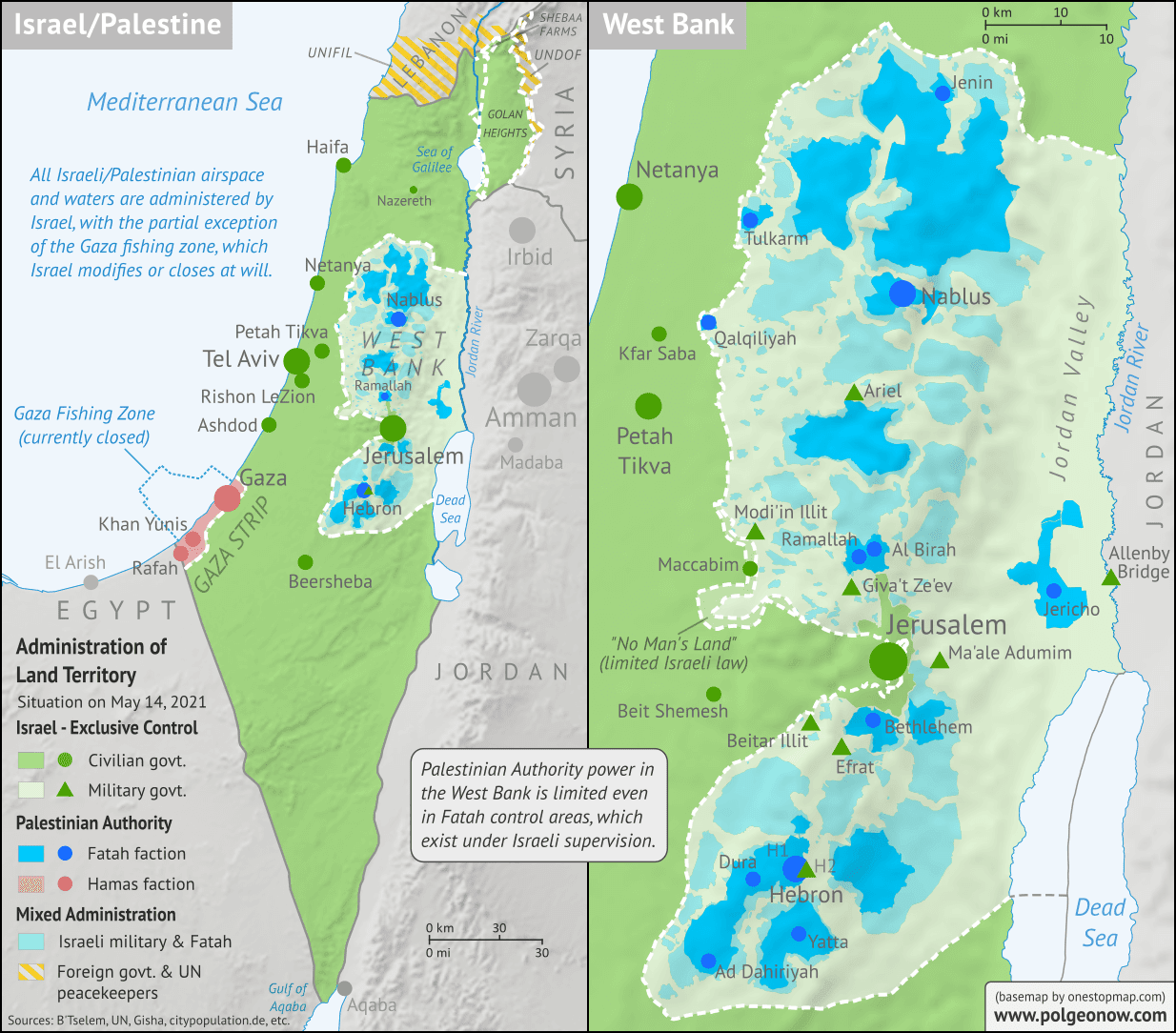
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a deeply rooted and multifaceted issue with a long and complex history. Understanding this conflict requires a comprehensive understanding of the geographical, political, and social factors at play. One crucial element in comprehending this intricate situation is the Israeli-Palestinian map.
This article delves into the significance of the Israeli-Palestinian map in 2021, providing a clear and informative analysis of its current state and the various perspectives it represents.
The Evolving Landscape: A Historical Context
The Israeli-Palestinian map is not static; it has undergone significant transformations throughout history, reflecting the evolving dynamics of the conflict.
- Pre-1948: Prior to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948, the region was known as Palestine, under British Mandate rule. This period witnessed the emergence of Zionist aspirations for a Jewish state alongside the growing Palestinian Arab national movement.
- 1948-1967: The 1948 Arab-Israeli War led to the creation of Israel and the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, an event known as the Nakba. The resulting map saw Israel controlling a larger territory than originally intended under the UN Partition Plan.
- 1967-Present: The 1967 Six-Day War saw Israel capture the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip from Jordan and Egypt. This expansion significantly altered the map, leading to the ongoing Israeli occupation of these territories.
The Current Landscape: A Divided Territory
The Israeli-Palestinian map in 2021 reflects the current reality of a divided territory with distinct political and social realities.
- Israel: Occupies the largest portion of land, encompassing areas within the pre-1967 borders and territories captured in the 1967 war. Israel has annexed East Jerusalem and maintains significant control over the West Bank.
- West Bank: A Palestinian territory under Israeli occupation. The Palestinian Authority administers parts of the West Bank, but Israeli settlements and military control remain pervasive.
- Gaza Strip: A Palestinian territory under Hamas control, which has been under an Israeli blockade since 2007. The territory faces significant humanitarian challenges and is subject to frequent Israeli military operations.
- East Jerusalem: A contested territory claimed by both Israelis and Palestinians. Israel annexed East Jerusalem in 1967, but Palestinians consider it the capital of their future state.
The Importance of the Map: A Window into the Conflict
The Israeli-Palestinian map serves as a crucial tool for understanding the complexities of the conflict:
- Visual Representation: It provides a tangible representation of the territorial divisions and contested spaces that lie at the heart of the conflict.
- Historical Context: It illustrates the historical evolution of the conflict, highlighting the impact of key events and the changing geopolitical landscape.
- Political and Social Dynamics: It reflects the power dynamics between Israel and the Palestinians, showcasing the impact of occupation, settlements, and the ongoing struggle for self-determination.
- International Perspective: It provides a framework for understanding the international community’s involvement and the various positions taken on the conflict.
- Peace Negotiations: The map serves as a reference point for peace negotiations, highlighting the core issues of land, borders, and Jerusalem.
The Challenges of the Map: A Complex Reality
Despite its importance, the Israeli-Palestinian map also presents significant challenges:
- Contested Boundaries: The boundaries between Israel and the Palestinian territories are hotly contested, with different interpretations and claims.
- Settlements: The presence of Israeli settlements in the West Bank, considered illegal under international law, further complicates the territorial picture.
- Jerusalem: The status of Jerusalem, claimed as a capital by both Israelis and Palestinians, remains a major obstacle to peace.
- Security Concerns: The ongoing conflict and the presence of security barriers and checkpoints create a complex and volatile environment.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the Map
1. What are the key differences between the 1967 and pre-1967 borders?
The 1967 borders refer to the territories captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, including the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip. The pre-1967 borders refer to the territory of Israel before the 1967 war. The difference lies in the extent of Israeli control and the inclusion of these territories in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
2. What is the significance of the Green Line?
The Green Line represents the 1949 armistice line between Israel and its neighbors, marking the boundary between Israel and the West Bank and Gaza Strip. It is often considered a potential basis for future borders in a peace agreement.
3. What is the status of Israeli settlements in the West Bank?
Israeli settlements in the West Bank are considered illegal under international law, as they are built on occupied Palestinian territory. They are a major source of tension and controversy, hindering peace negotiations and contributing to the ongoing conflict.
4. What is the role of the Palestinian Authority?
The Palestinian Authority is a self-governing body that administers parts of the West Bank. It is responsible for providing basic services and promoting Palestinian self-determination. However, its authority is limited by Israeli control over security and other aspects of governance.
5. What are the main obstacles to peace in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict?
The main obstacles to peace include the issue of land, borders, and settlements, the status of Jerusalem, the Palestinian refugee issue, and the lack of trust between the parties.
Tips for Navigating the Complexities
- Contextualize the Map: Remember that the map is a dynamic representation of a complex and evolving situation.
- Consider Multiple Perspectives: Recognize the diverse perspectives and narratives surrounding the map, including those of Israelis, Palestinians, and the international community.
- Engage with Primary Sources: Access reliable information from official sources, academic institutions, and reputable news organizations.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of current events and developments in the region to understand the evolving dynamics.
Conclusion: Towards a Future of Peace and Coexistence
The Israeli-Palestinian map is a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of the conflict and its historical trajectory. It highlights the challenges and opportunities for achieving a just and lasting peace. While the path towards peace remains arduous, the map serves as a reminder of the shared land and the potential for a future of coexistence and mutual respect.
It is crucial to approach the map with a critical and informed lens, recognizing the diverse perspectives and the complexities of the issues involved. By engaging with the map and its historical context, we can contribute to a deeper understanding of this enduring conflict and foster a more informed and nuanced dialogue towards a peaceful resolution.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian Landscape: A 2021 Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!