Understanding the Complexities of Drought: Decoding the NOAA Drought Monitor
Related Articles: Understanding the Complexities of Drought: Decoding the NOAA Drought Monitor
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Complexities of Drought: Decoding the NOAA Drought Monitor. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Complexities of Drought: Decoding the NOAA Drought Monitor

Drought, a pervasive and often devastating natural phenomenon, poses significant challenges to ecosystems, agriculture, and human populations worldwide. Recognizing the critical need for a comprehensive and standardized approach to drought monitoring, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) established the U.S. Drought Monitor (USDM), a vital tool for understanding and responding to drought conditions.
This article delves into the intricacies of the NOAA Drought Monitor, exploring its methodology, data sources, interpretation, and implications. We will examine how this invaluable resource aids in understanding drought severity, forecasting future trends, and informing crucial decision-making for water resource management, agricultural planning, and disaster preparedness.
The Foundation of the Drought Monitor: A Multifaceted Approach
The NOAA Drought Monitor is not merely a static map depicting drought conditions. It is a dynamic and collaborative effort involving a diverse team of experts, including:
- Climatologists: Analyzing long-term weather patterns and climate variability to identify drought triggers and trends.
- Hydrologists: Assessing water availability in rivers, lakes, and groundwater systems, providing crucial insights into water resource depletion.
- Agricultural specialists: Evaluating the impact of drought on crops, livestock, and agricultural productivity.
- State climatologists: Providing localized expertise and data from individual states, ensuring regional nuances are incorporated.
These experts work together to synthesize data from various sources, including:
- Meteorological data: Precipitation, temperature, humidity, wind speed, and other atmospheric variables collected from weather stations, satellites, and radar systems.
- Hydrological data: Streamflow, groundwater levels, reservoir storage, and soil moisture measurements.
- Agricultural data: Crop yields, livestock conditions, and agricultural water usage statistics.
- Satellite imagery: Remote sensing data providing insights into vegetation health, soil moisture, and snow cover.
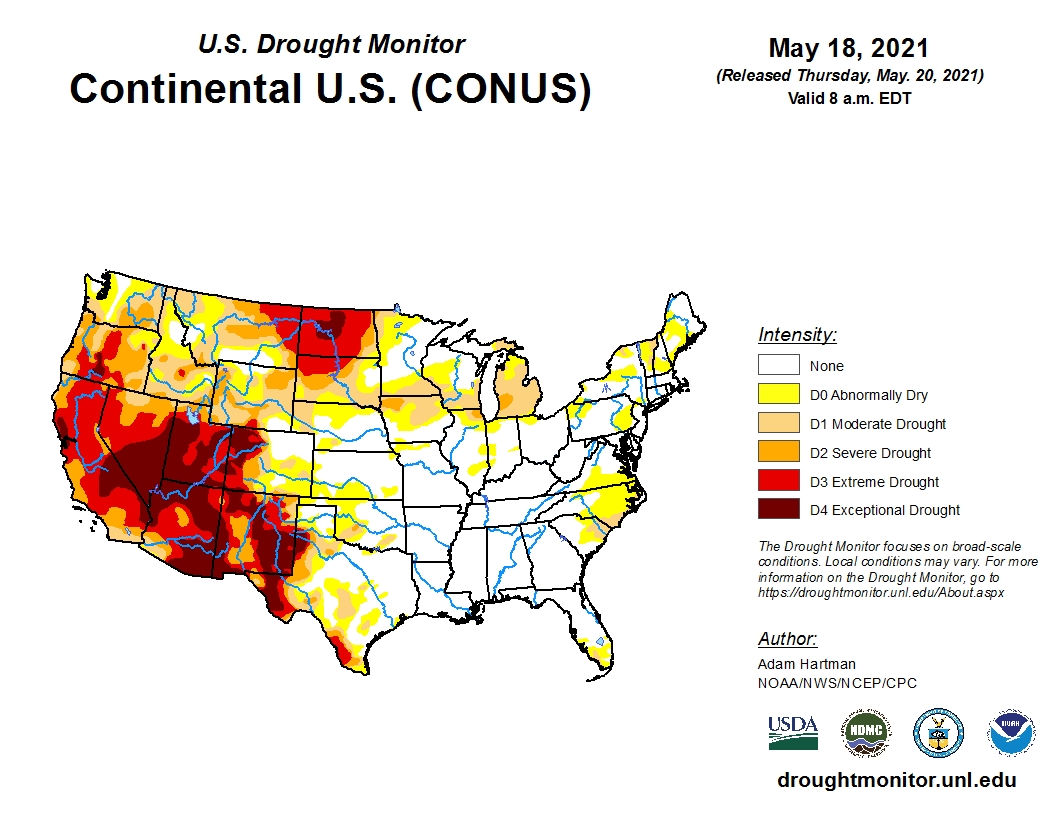
Interpreting the Drought Monitor: A Spectrum of Severity
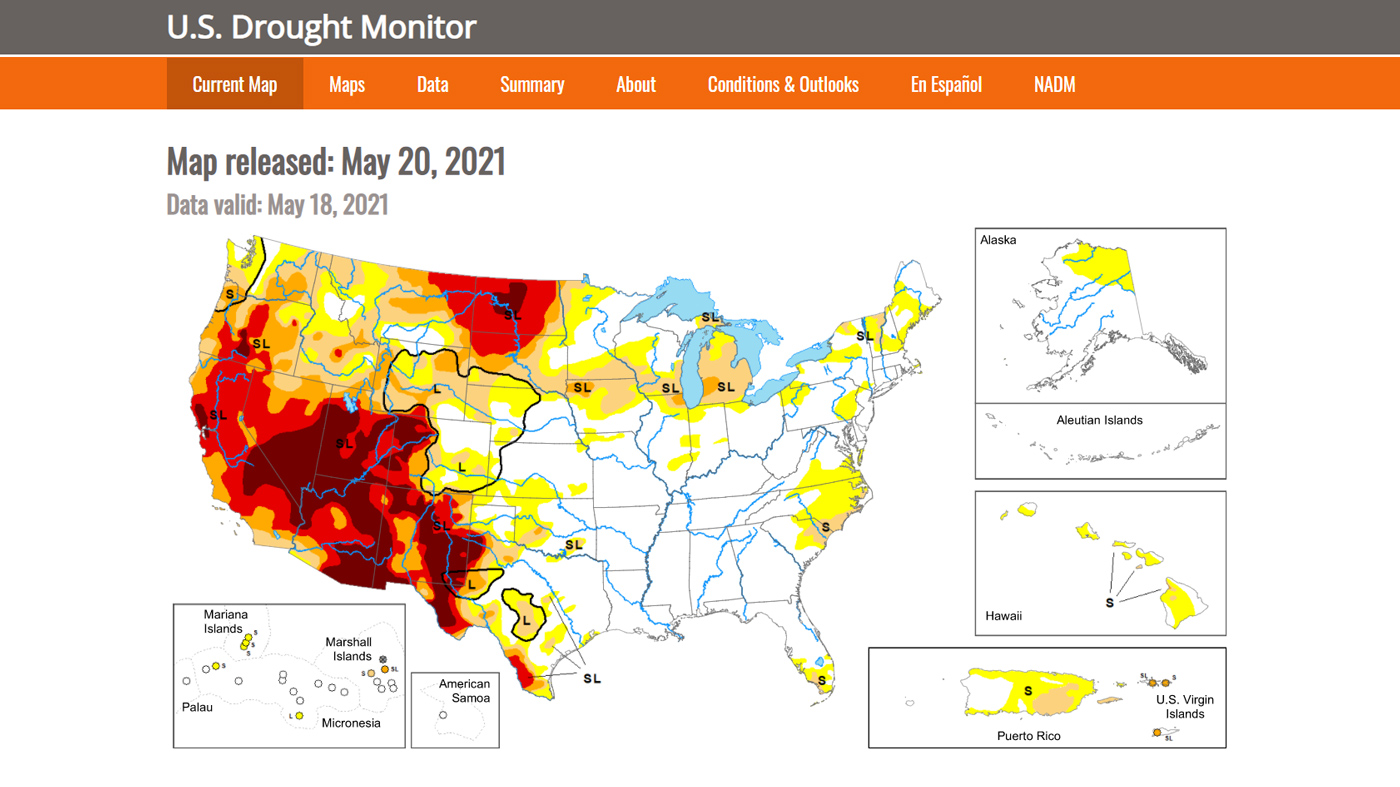
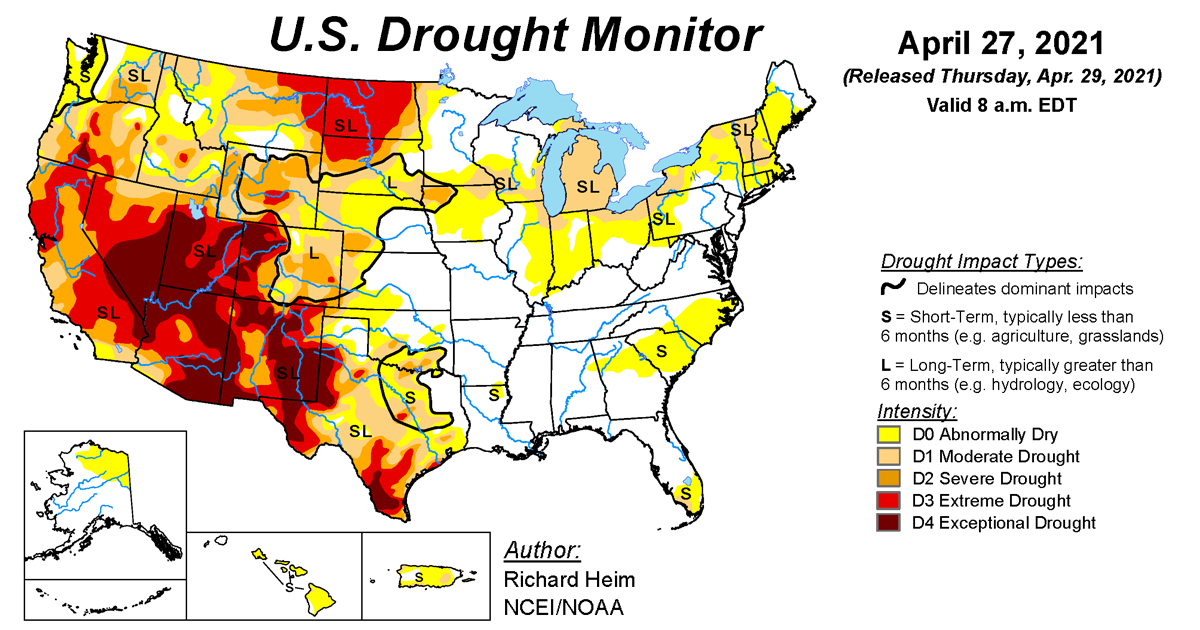
The NOAA Drought Monitor classifies drought conditions using a standardized color-coded scale, ranging from "None" to "Exceptional Drought." Each category represents a different level of drought severity, with corresponding impacts on water availability, agriculture, and ecosystems:
- D0 – Abnormally Dry: Precursor to drought, characterized by below-average precipitation and potential for water stress in sensitive areas.
- D1 – Moderate Drought: Mild drought conditions, with noticeable impacts on vegetation, water resources, and agricultural production.
- D2 – Severe Drought: Significant water shortages, impacting agricultural yields, water supply, and ecosystem health.
- D3 – Extreme Drought: Severe water shortages, leading to widespread crop failures, livestock losses, and potential for wildfires.
- D4 – Exceptional Drought: Exceptional and unprecedented drought conditions, with devastating impacts on water resources, agriculture, and human populations.
Benefits of the Drought Monitor: A Powerful Tool for Mitigation
The NOAA Drought Monitor plays a pivotal role in drought mitigation, providing numerous benefits for various stakeholders:
- Early Warning System: The Drought Monitor serves as an early warning system, alerting communities to potential drought conditions and enabling proactive measures to mitigate potential impacts.
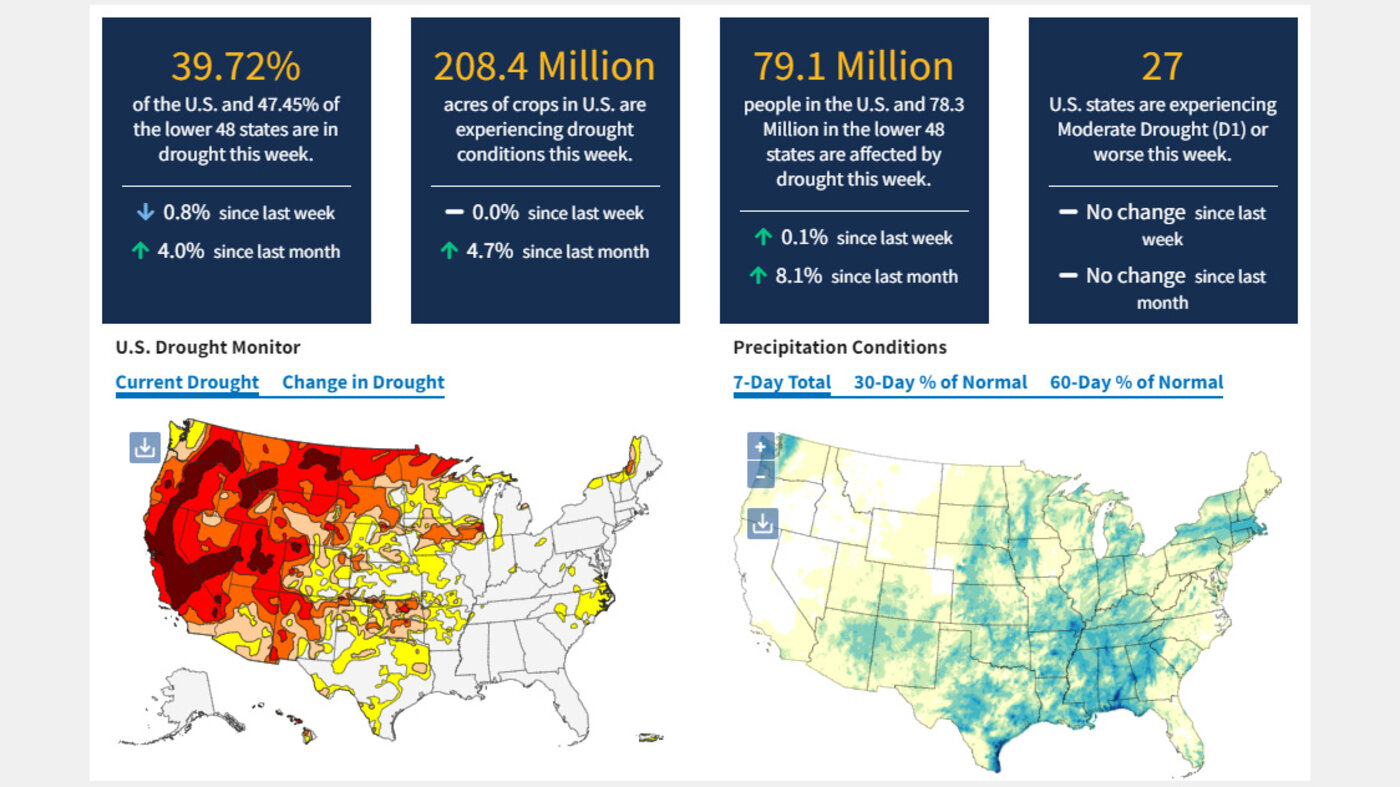
- Resource Management: By providing a comprehensive assessment of drought severity, the Drought Monitor informs water resource management decisions, ensuring sustainable water use and allocation.
- Agricultural Planning: Farmers and ranchers can use the Drought Monitor to assess drought risks, adjust planting schedules, and implement drought-resistant farming practices.
- Disaster Preparedness: The Drought Monitor helps communities prepare for potential drought-related disasters, such as wildfires, water shortages, and agricultural losses.
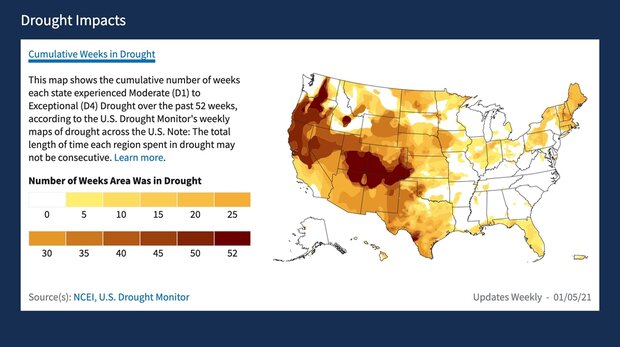
- Research and Monitoring: The Drought Monitor provides a valuable dataset for researchers and scientists studying drought dynamics, climate change impacts, and drought mitigation strategies.
FAQs about the NOAA Drought Monitor
1. How frequently is the Drought Monitor updated?
The NOAA Drought Monitor is updated every Thursday, reflecting the most current drought conditions across the United States.
2. What are the limitations of the Drought Monitor?
The Drought Monitor relies on data from various sources, and its accuracy can be affected by data availability, spatial resolution, and potential reporting biases.
3. How can I access the Drought Monitor data?
The Drought Monitor data is freely available on the NOAA website, including interactive maps, data tables, and detailed reports.
4. How does the Drought Monitor contribute to climate change adaptation?
The Drought Monitor provides valuable information about drought trends and impacts, enabling communities to adapt to a changing climate and mitigate the effects of drought.
5. How can I get involved in the Drought Monitor?
You can contribute to the Drought Monitor by reporting local drought conditions, participating in drought monitoring programs, and engaging in drought awareness initiatives.
Tips for Utilizing the Drought Monitor
- Regularly monitor drought conditions: Stay informed about drought trends and potential impacts by regularly checking the Drought Monitor.
- Understand the color-coded scale: Familiarize yourself with the drought severity categories and their corresponding impacts.
- Utilize the data for decision-making: Integrate the Drought Monitor data into your water resource management, agricultural planning, and disaster preparedness strategies.
- Share the information: Spread awareness about drought conditions and the importance of drought mitigation by sharing the Drought Monitor information with your community.
Conclusion: A Vital Resource for a Changing World
The NOAA Drought Monitor stands as a vital resource for understanding and responding to drought conditions, a critical component of a changing world facing increasing climate variability and extreme weather events. By providing a comprehensive and standardized assessment of drought severity, the Drought Monitor empowers communities, businesses, and governments to make informed decisions, mitigate drought impacts, and build resilience in the face of this growing challenge.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Complexities of Drought: Decoding the NOAA Drought Monitor. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!