Tokyo Bay: A Gateway to a Thriving Metropolis
Related Articles: Tokyo Bay: A Gateway to a Thriving Metropolis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Tokyo Bay: A Gateway to a Thriving Metropolis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tokyo Bay: A Gateway to a Thriving Metropolis

Tokyo Bay, a vast expanse of water nestled along the eastern coast of Japan, serves as a vital artery for the bustling metropolis of Tokyo. Its strategic location, encompassing a diverse array of natural and man-made features, has profoundly shaped the city’s history, economy, and cultural landscape. This article delves into the intricate details of Tokyo Bay, exploring its geographic features, historical significance, economic importance, and environmental challenges.
The Geographic Canvas of Tokyo Bay
Tokyo Bay’s geographical characteristics are as diverse as its role in the city’s life. It stretches approximately 90 kilometers from east to west and 30 kilometers from north to south, encompassing a surface area of around 1,320 square kilometers. The bay’s shoreline is a complex tapestry of natural inlets, reclaimed land, and artificial islands, each contributing to its unique character.
A Symphony of Islands and Inlets:
Tokyo Bay is punctuated by several islands, each with its own distinct history and purpose. The most prominent among them are:
- Izu Islands: A volcanic archipelago lying south of Tokyo Bay, these islands offer breathtaking natural beauty and are popular tourist destinations.
- Miyakejima: Known for its volcanic activity and hot springs, this island is a testament to the dynamic geological forces shaping the region.
- Ogasawara Islands: A remote chain of islands located further south, these islands are renowned for their unique flora and fauna, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The bay’s shoreline is also marked by several inlets, each playing a crucial role in the region’s development. These inlets, such as Tokyo Bay itself, Sagami Bay, and the inlets surrounding the Izu and Ogasawara Islands, offer sheltered harbors for navigation and fishing.
The Legacy of Reclamation:
Throughout history, Tokyo Bay has been the subject of extensive land reclamation projects. The city’s relentless expansion, fueled by population growth and economic development, has led to the creation of artificial islands and the extension of the shoreline. This transformation has significantly altered the bay’s geography, creating new land for urban development, industrial zones, and transportation infrastructure.
The Importance of the Mouth of the Bay:
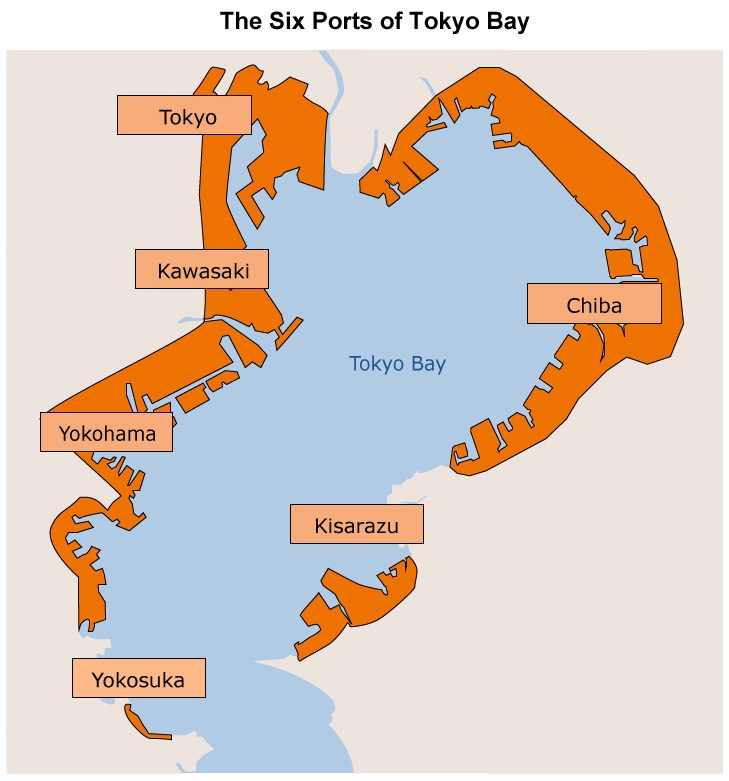
The mouth of Tokyo Bay, where it opens to the Pacific Ocean, is a crucial point for maritime traffic. It serves as the gateway for international trade, facilitating the movement of goods and people between Japan and the rest of the world. The presence of major ports like Yokohama Port and Tokyo Port further underscores the bay’s vital role in global commerce.
Historical Echoes in the Bay’s Waters
Tokyo Bay’s waters have witnessed centuries of history, from the Edo period to the modern era. It has been a stage for significant historical events, shaping the city’s identity and influencing its trajectory.
A Gateway for Trade and Culture:
During the Edo period (1603-1868), Tokyo Bay served as a vital artery for trade, connecting the city to other regions of Japan and the world. It facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural influences, contributing to the city’s economic growth and cultural development.
The Impact of Modernization:
The Meiji Restoration (1868) marked a period of rapid modernization in Japan, and Tokyo Bay played a central role in this transformation. The bay witnessed the construction of modern infrastructure, including ports, railways, and industries, propelling the city into the ranks of global powers.
The Challenges of a Thriving Metropolis
While Tokyo Bay’s role in the city’s growth is undeniable, its development has also come with its share of challenges. The relentless expansion of the city, coupled with industrial activities, has resulted in environmental pressures that require careful management.
Environmental Concerns:
Pollution from industrial activities, sewage discharge, and runoff from urban areas has posed significant threats to the bay’s water quality. This has led to concerns about the health of marine ecosystems and the potential impact on human health.
The Need for Sustainable Solutions:
Addressing these environmental challenges is crucial for the long-term sustainability of Tokyo Bay and the surrounding region. The city has implemented various initiatives to mitigate pollution, conserve marine resources, and promote sustainable practices. These efforts include:
- Wastewater treatment: Improving wastewater treatment facilities to reduce the discharge of pollutants into the bay.
- Pollution monitoring: Establishing a robust monitoring system to track water quality and identify sources of pollution.
- Marine conservation: Implementing conservation measures to protect endangered marine species and their habitats.
- Public awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of environmental protection and promoting responsible practices.
A Glimpse into the Future of Tokyo Bay
The future of Tokyo Bay is intertwined with the aspirations and challenges of the city it serves. The bay’s role as a crucial transportation hub, a center for economic activity, and a vital natural resource will continue to evolve.
Balancing Growth and Sustainability:
The city faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. This requires innovative solutions to address the challenges of pollution, climate change, and resource management.
Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements in areas such as renewable energy, waste management, and marine conservation will play a crucial role in shaping the future of Tokyo Bay.
A Beacon of Hope:
Despite the challenges, Tokyo Bay remains a beacon of hope for a sustainable future. The city’s commitment to environmental protection and its innovative approach to urban planning offer a model for other coastal cities around the world.
FAQs about Tokyo Bay
1. What are the major ports located in Tokyo Bay?
Tokyo Bay is home to several major ports, including:
- Yokohama Port: Japan’s busiest port, handling a vast volume of international trade.
- Tokyo Port: Located in the heart of the city, serving as a hub for domestic and international shipping.
- Chiba Port: A major port for container shipping and industrial activities.
- Kawasaki Port: A significant port for container handling and industrial development.
2. What are the main industries located around Tokyo Bay?
The area surrounding Tokyo Bay is a hub for various industries, including:
- Shipping and logistics: The bay’s ports serve as vital gateways for international trade, supporting a thriving shipping and logistics industry.
- Manufacturing: The bay’s industrial zones are home to a wide range of manufacturing industries, from automobiles and electronics to chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
- Tourism: The bay’s scenic beauty and cultural attractions draw tourists from around the world, supporting a thriving tourism industry.
- Fishing: The bay’s waters support a significant fishing industry, providing fresh seafood to the city and beyond.
3. What are the major environmental challenges facing Tokyo Bay?
Tokyo Bay faces several environmental challenges, including:
- Water pollution: Industrial activities, sewage discharge, and urban runoff contribute to water pollution, impacting the bay’s ecosystem and human health.
- Climate change: Rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and ocean acidification pose threats to the bay’s coastal areas and marine life.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices can deplete fish stocks and disrupt the marine ecosystem.
- Habitat loss: Land reclamation and coastal development have led to the loss of critical habitats for marine species.
4. What measures are being taken to address the environmental challenges facing Tokyo Bay?
The city of Tokyo and surrounding municipalities are implementing various measures to address the environmental challenges facing Tokyo Bay, including:
- Wastewater treatment: Upgrading wastewater treatment facilities to reduce the discharge of pollutants into the bay.
- Pollution monitoring: Implementing a robust monitoring system to track water quality and identify sources of pollution.
- Marine conservation: Establishing marine protected areas and implementing conservation measures to protect endangered species and their habitats.
- Sustainable development: Promoting sustainable development practices in coastal areas to minimize environmental impact.
- Public awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of environmental protection and promoting responsible practices.
5. What is the future outlook for Tokyo Bay?
The future of Tokyo Bay is intertwined with the aspirations and challenges of the city it serves. The bay’s role as a crucial transportation hub, a center for economic activity, and a vital natural resource will continue to evolve. The city faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability. This requires innovative solutions to address the challenges of pollution, climate change, and resource management. Technological advancements in areas such as renewable energy, waste management, and marine conservation will play a crucial role in shaping the future of Tokyo Bay. Despite the challenges, Tokyo Bay remains a beacon of hope for a sustainable future. The city’s commitment to environmental protection and its innovative approach to urban planning offer a model for other coastal cities around the world.
Tips for Exploring Tokyo Bay
- Visit the Tokyo Bay Aqua-Line: This impressive bridge and tunnel system offers stunning views of the bay and connects Tokyo to the Boso Peninsula.
- Take a ferry ride: Explore the bay’s islands and enjoy breathtaking views of the city skyline from the water.
- Visit the Odaiba district: This artificial island features a variety of attractions, including museums, shopping malls, and amusement parks.
- Explore the Tokyo waterfront: Stroll along the bay’s waterfront and enjoy the city’s vibrant atmosphere.
- Attend a festival: Tokyo Bay hosts several festivals throughout the year, celebrating the city’s culture and heritage.
Conclusion
Tokyo Bay, a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, stands as a testament to the intricate relationship between a city and its surrounding environment. Its historical significance, economic importance, and environmental challenges underscore the complexities of urban development. As Tokyo continues to grow and evolve, the bay will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the city’s future. By fostering a balance between economic progress and environmental sustainability, Tokyo can ensure that Tokyo Bay continues to thrive as a vital artery for the city and a symbol of hope for a sustainable future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tokyo Bay: A Gateway to a Thriving Metropolis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!