The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation
Related Articles: The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation

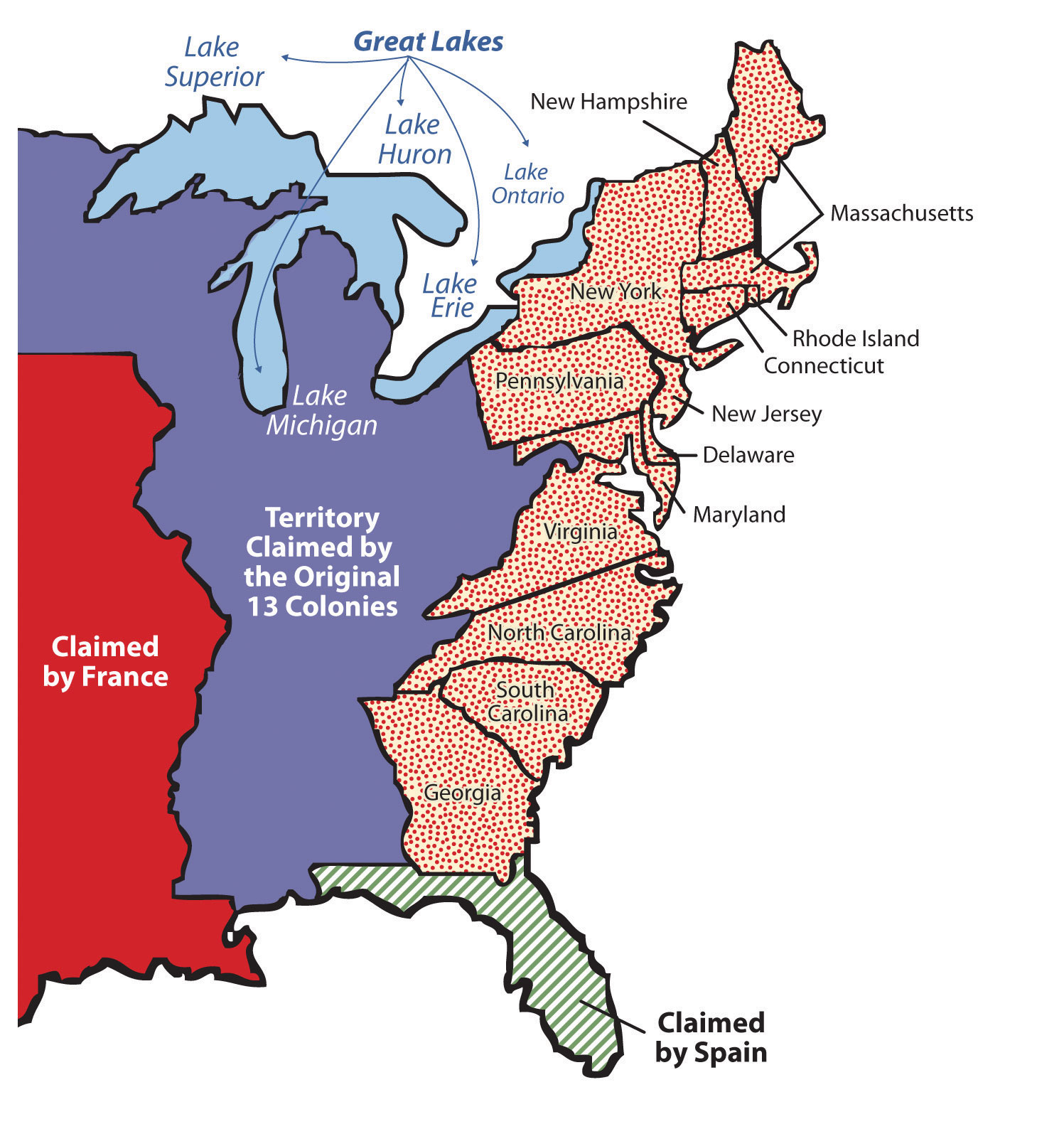
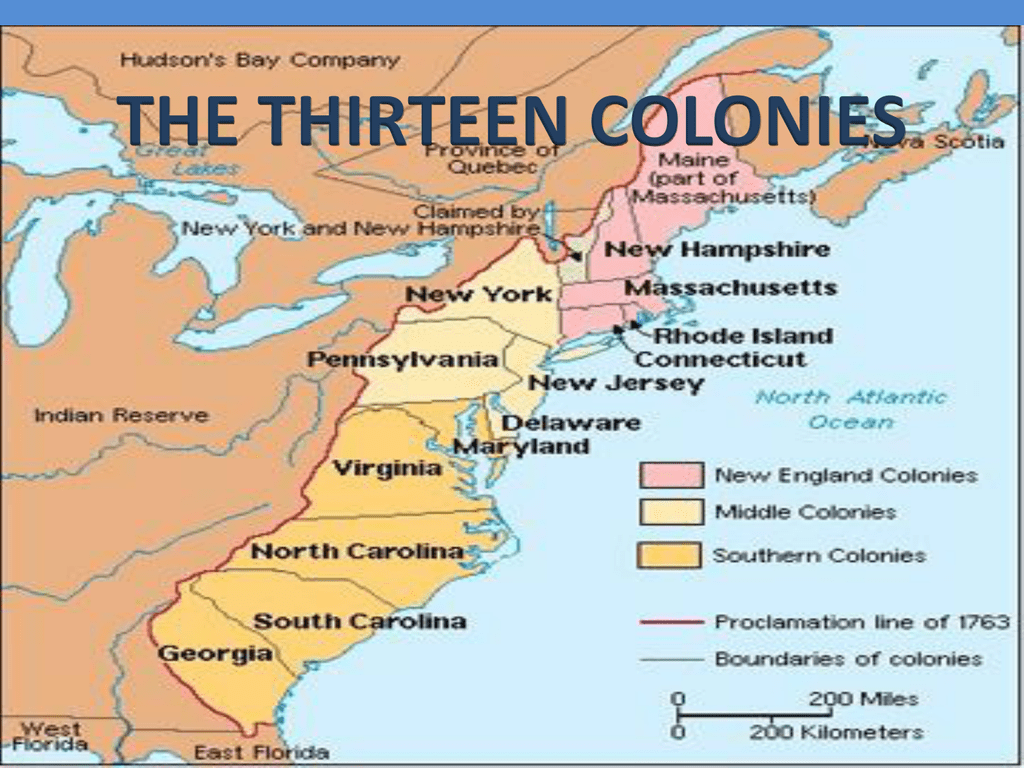
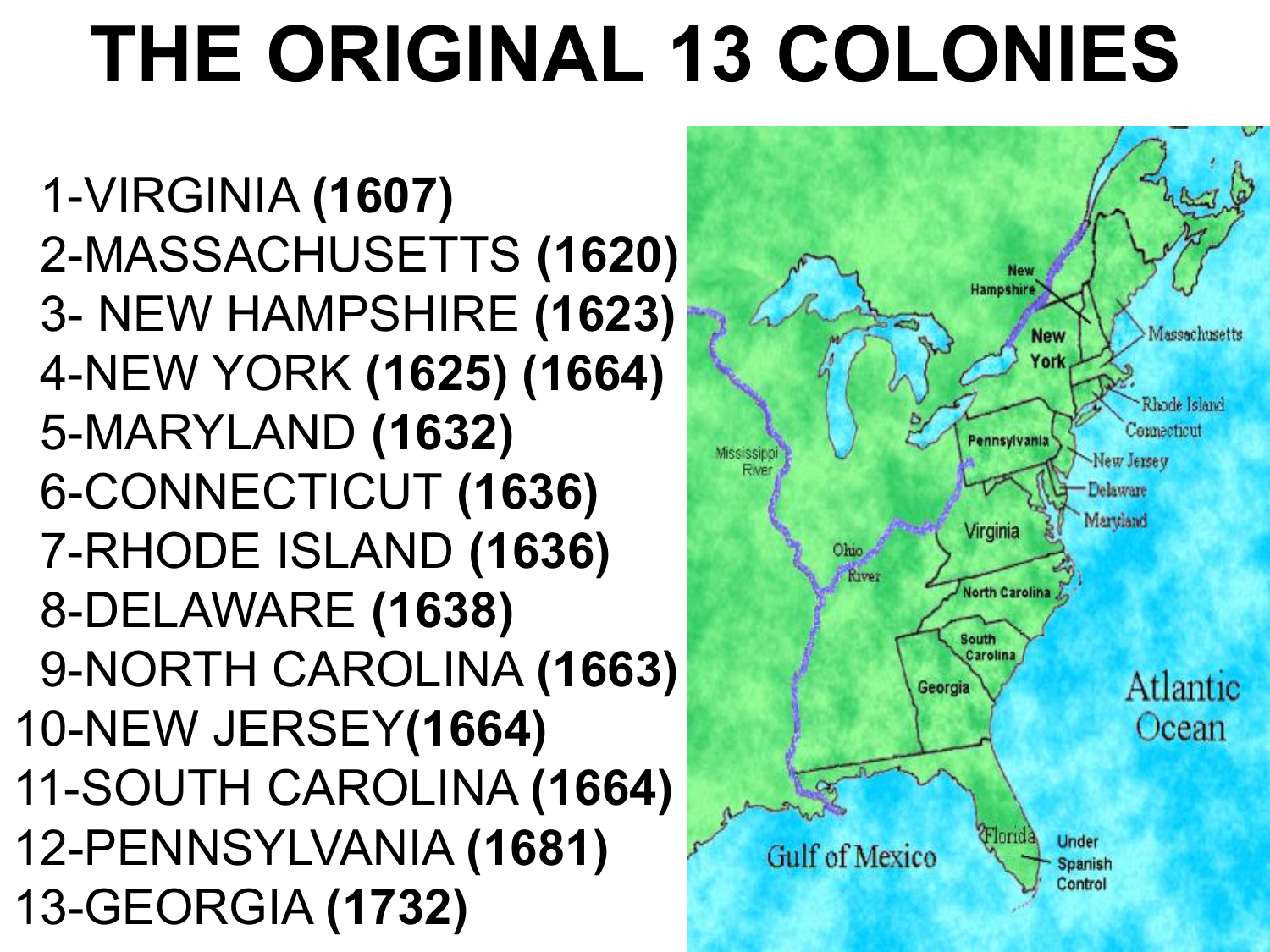
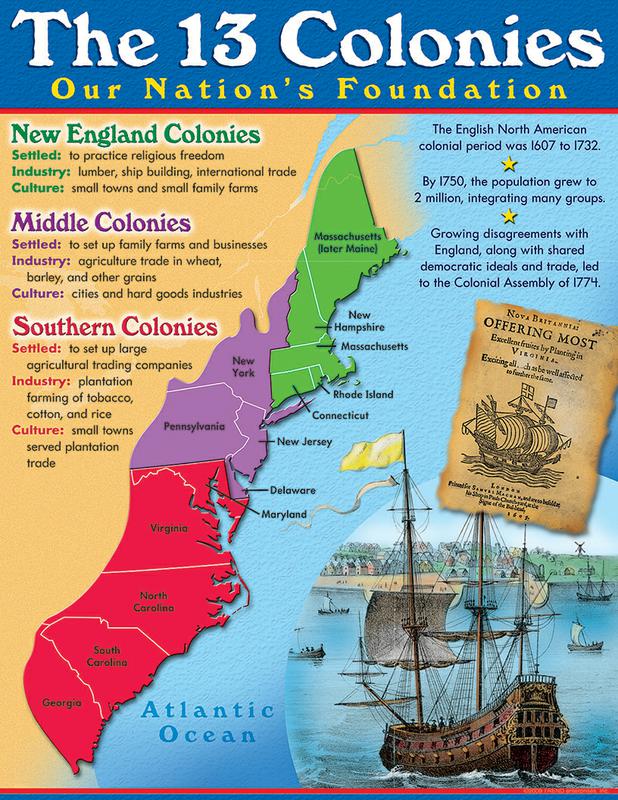
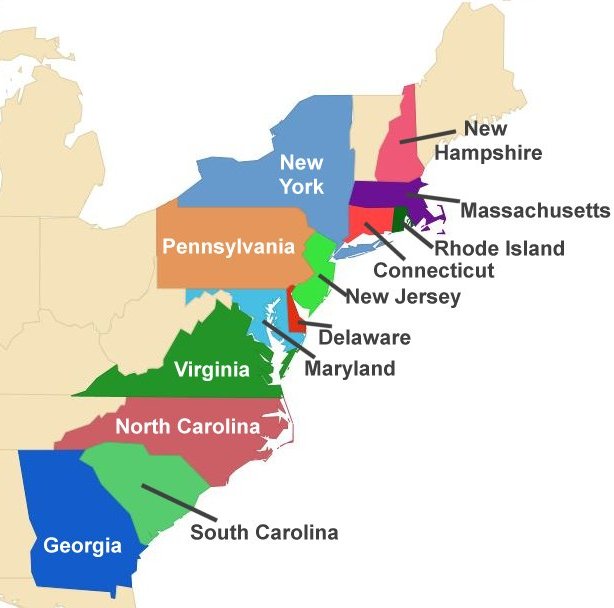
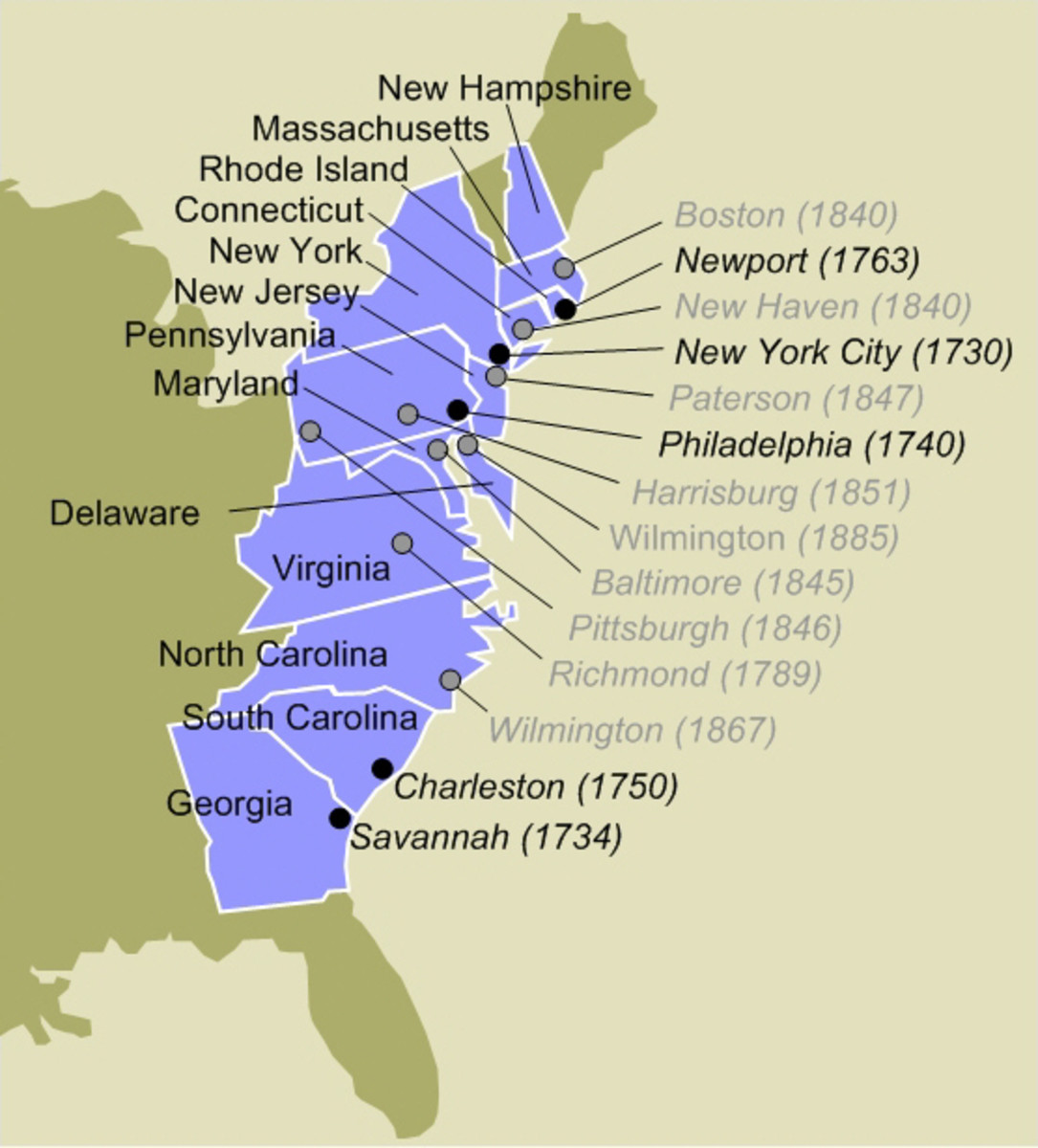
The map of the thirteen colonies, a cornerstone of American history, vividly depicts the geographical foundation upon which the United States of America was built. This collection of British colonies, stretching along the Atlantic coast, played a pivotal role in the American Revolution and ultimately gave birth to a new nation. Understanding the map of the thirteen colonies offers a deeper insight into the historical, cultural, and geographical context of early America, providing valuable context for understanding the nation’s development and its enduring legacy.
A Geographic Overview:
The thirteen colonies, each with its unique characteristics and contributions, spanned a significant portion of the eastern seaboard. They were:
- New Hampshire: Known for its rugged coastline and its role in the lumber industry, New Hampshire was a key player in the American Revolution.
- Massachusetts: The birthplace of the American Revolution, Massachusetts was home to prominent figures like John Adams and Samuel Adams, and served as the center of intellectual and political ferment.
- Rhode Island: A haven for religious dissenters, Rhode Island was a pioneer in establishing religious freedom and played a significant role in the development of maritime trade.
- Connecticut: Renowned for its strong agricultural economy and its influential role in the development of higher education, Connecticut was a crucial contributor to the American Revolution.
- New York: A major commercial hub, New York was a strategic battleground during the American Revolution and played a key role in shaping the nation’s economic landscape.
- New Jersey: A crucial link between the northern and southern colonies, New Jersey was a battleground during the American Revolution and contributed significantly to the nation’s agricultural economy.
- Pennsylvania: Founded by William Penn as a haven for religious freedom, Pennsylvania was a center of intellectual and cultural activity and a major contributor to the nation’s agricultural and industrial development.
- Delaware: A small but strategically important colony, Delaware played a crucial role in the American Revolution and was a key contributor to the nation’s agricultural economy.
- Maryland: Known for its tobacco plantations and its role in the development of the Chesapeake Bay region, Maryland was a key player in the American Revolution.
- Virginia: A major economic and political power, Virginia was the birthplace of several prominent figures, including George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and James Madison, and played a pivotal role in the American Revolution.
- North Carolina: Known for its agricultural economy and its role in the development of the Southern colonies, North Carolina was a key player in the American Revolution.
- South Carolina: A major producer of rice and indigo, South Carolina was a key player in the American Revolution and played a significant role in the development of the Southern economy.
- Georgia: Founded as a buffer colony to protect the other colonies from Spanish Florida, Georgia was a key player in the American Revolution and played a significant role in the development of the Southern economy.
The Significance of the Thirteen Colonies:
The map of the thirteen colonies represents more than just a collection of geographical entities. It embodies a crucial period in American history, marked by:
- The Birth of a Nation: The thirteen colonies, united by a shared desire for independence from British rule, forged a new nation based on the principles of liberty, self-governance, and individual rights.
- The American Revolution: The map highlights the battlegrounds where the colonists fought for their freedom, underscoring the sacrifices made and the resilience shown in achieving independence.
- A Foundation for Democracy: The thirteen colonies laid the groundwork for the development of a democratic society, establishing principles of representative government, individual rights, and the rule of law.
- Economic and Cultural Diversity: The map reveals the diverse economic activities and cultural traditions that flourished within the thirteen colonies, shaping the economic and cultural fabric of the nascent nation.
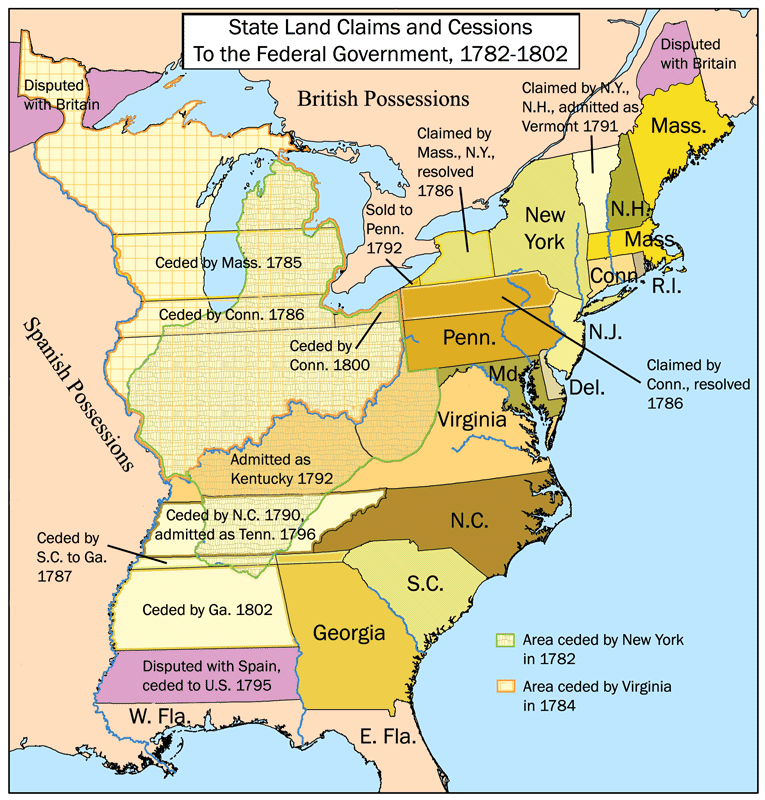
- A Legacy of Growth and Expansion: The thirteen colonies served as a springboard for westward expansion, contributing to the growth and development of the United States into a vast and powerful nation.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Understanding America:
By studying the map of the thirteen colonies, we gain a deeper understanding of:
- Geographic Influences: The map reveals the unique geographical characteristics of each colony, including its coastline, rivers, mountains, and forests, which shaped its economic activities and cultural development.
- Political and Social Dynamics: The map helps us understand the political and social dynamics of the thirteen colonies, including their internal conflicts, their relationships with Britain, and their evolving identities.
- The Roots of American Identity: By examining the map and its historical context, we gain insights into the origins of American identity, its values, and its aspirations.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are the key geographical features of the thirteen colonies?
- The thirteen colonies were characterized by their diverse geography, including the Atlantic coastline, the Appalachian Mountains, and the fertile river valleys.
-
What were the main economic activities of the thirteen colonies?
- The thirteen colonies had a diverse economy, ranging from agriculture (tobacco, rice, indigo) and fishing to shipbuilding, lumbering, and trade.
-
How did the thirteen colonies contribute to the American Revolution?
- The thirteen colonies played a crucial role in the American Revolution, providing troops, supplies, and leadership for the fight for independence.
-
What were the major political and social issues that shaped the thirteen colonies?
- The thirteen colonies faced a range of political and social issues, including religious freedom, slavery, taxation, and representation in government.
-
How did the thirteen colonies influence the development of the United States?
- The thirteen colonies provided the foundation for the United States, shaping its political system, economic development, and cultural identity.
Tips for Studying the Map of the Thirteen Colonies:
- Focus on the geographical location of each colony: Understanding the location of each colony in relation to others is crucial for comprehending their interactions and the factors that shaped their development.
- Explore the major cities and towns of each colony: Researching the key urban centers of the thirteen colonies provides insights into their economic and cultural importance.
- Consider the historical events that occurred in each colony: Understanding the key historical events that unfolded within each colony helps to grasp its evolution and its contribution to the development of the United States.
- Analyze the connections between the colonies: Exploring the relationships between the thirteen colonies, including trade patterns, political alliances, and shared challenges, offers a richer understanding of the forces that shaped the nation’s early history.
- Compare and contrast the different colonies: By examining the differences and similarities between the thirteen colonies, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse factors that contributed to the development of the United States.
Conclusion:
The map of the thirteen colonies serves as a visual testament to the origins of the United States, offering a window into a crucial period in American history. By studying this map and its historical context, we gain a deeper understanding of the nation’s founding principles, its early challenges, and its enduring legacy. It reminds us that the United States, a nation built on the ideals of liberty and self-governance, emerged from a collection of diverse colonies united by a shared vision for a new future. The map of the thirteen colonies remains a powerful symbol of the nation’s origins and the enduring spirit of those who fought for independence and shaped the destiny of a new nation.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Thirteen Colonies: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!