The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics
Related Articles: The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics
- 3.1 A Border Shaped by History
- 3.2 A Geography of Diversity
- 3.3 A Geopolitical Crossroads
- 3.4 FAQs about the Russia-China Border
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding the Russia-China Border
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics
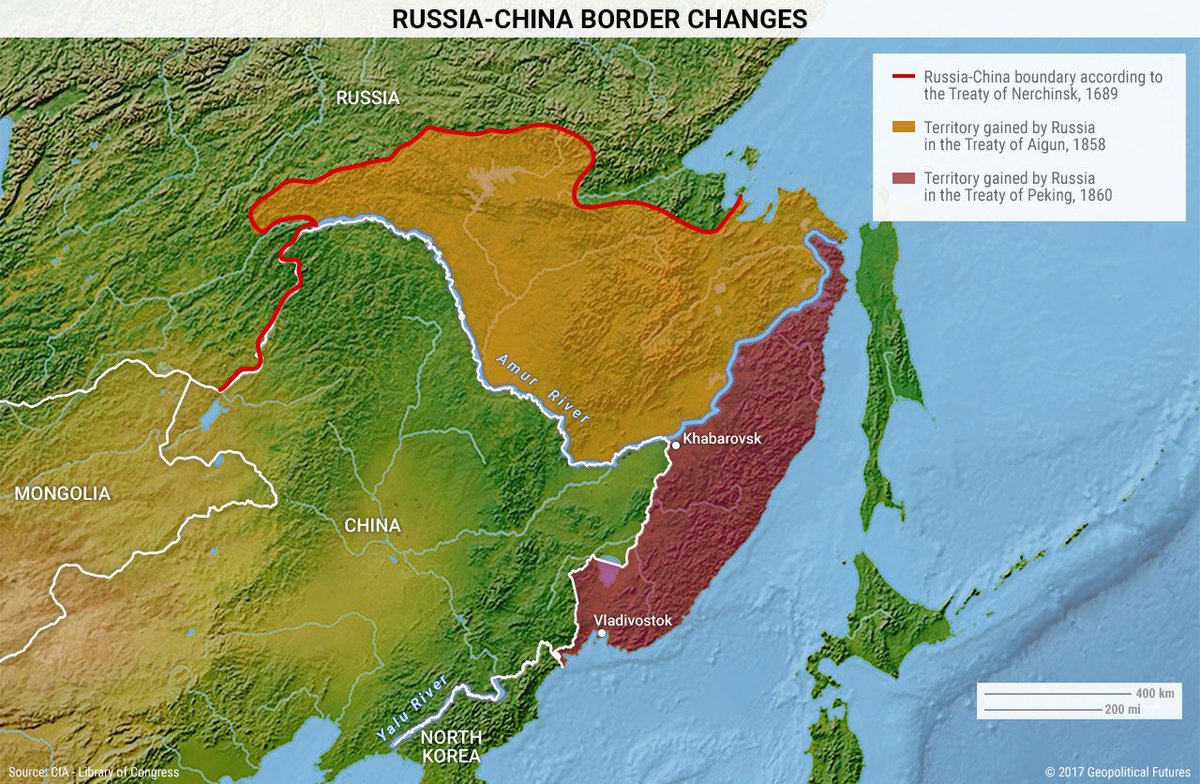
The Russia-China border, stretching over 4,209 kilometers (2,616 miles), is a vast and complex geographical feature that has shaped the destinies of both nations for centuries. This intricate boundary, marked by mountains, rivers, and vast stretches of sparsely populated terrain, serves as a physical manifestation of the historical, cultural, and geopolitical interactions between two of the world’s largest and most influential countries.
A Border Shaped by History
The current Russia-China border is the product of a long and tumultuous history, marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. The two nations have shared a complex relationship, characterized by both trade and territorial disputes. The present border emerged from the 19th and 20th centuries, shaped by treaties, wars, and political upheavals.
- The Qing Dynasty and the Russian Empire: The 17th century witnessed the expansion of both the Qing Dynasty and the Russian Empire into the sparsely populated regions of the Amur River basin and the Ussuri River basin. This expansion led to territorial disputes, culminating in the Treaty of Nerchinsk in 1689, which established the first formal boundary between the two empires. This treaty, however, was not fully respected and further conflicts arose in the following centuries.
- The 19th Century and the Unequal Treaties: The 19th century saw Russia gain significant territorial concessions from China through a series of unequal treaties, including the Treaty of Aigun in 1858 and the Treaty of Beijing in 1860. These treaties ceded vast swathes of land to Russia, including the Amur River valley and the Ussuri River basin, which remain part of Russia today.
- The Soviet Union and the People’s Republic of China: After the Russian Revolution of 1917 and the establishment of the Soviet Union, the relationship between the two nations continued to be fraught with tensions. The border was redefined in 1924 with the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship. However, ideological differences and geopolitical competition during the Cold War strained relations, leading to a brief border conflict in 1969.
- Post-Cold War Era and the Present: With the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, Russia and China embarked on a period of rapprochement. They have since established a strategic partnership, with the border serving as a conduit for increased trade and economic cooperation. However, historical grievances and unresolved territorial disputes remain, especially in the region of the Amur River basin and the disputed islands in the Sea of Japan.
A Geography of Diversity
The Russia-China border traverses a remarkable diversity of landscapes, from the towering peaks of the Altai Mountains to the vast plains of the Amur River valley. This geographical diversity has shaped the history of the border and continues to influence the lives of the people who live along it.
- The Altai Mountains: The Altai Mountains, a UNESCO World Heritage site, form a natural barrier along the western portion of the border. This mountainous region is characterized by high peaks, deep valleys, and vast forests, making it sparsely populated and difficult to traverse.
- The Amur River Valley: The Amur River, the longest river in Eastern Russia, flows along the eastern portion of the border. The Amur River valley is a fertile region, providing important agricultural resources for both Russia and China. This region is also home to significant deposits of natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals.
- The Ussuri River Basin: The Ussuri River, a tributary of the Amur River, forms a significant portion of the border in the southeast. This region is characterized by dense forests and wetlands, making it a challenging terrain for transportation and development.
A Geopolitical Crossroads
The Russia-China border is not merely a physical boundary but a geopolitical crossroads, where the interests of two global powers intersect. The border serves as a point of contact for trade, diplomacy, and security, making it a crucial element in the regional and global geopolitical landscape.
- Economic Cooperation: The Russia-China border is a vital conduit for trade between the two countries, facilitating the exchange of goods, services, and investments. This economic cooperation has been growing steadily in recent years, driven by the complementary nature of their economies.
- Security Cooperation: The border also plays a significant role in security cooperation between Russia and China. Both countries share concerns about terrorism, separatism, and cross-border crime, leading to increased collaboration in security matters.
- Strategic Partnership: The Russia-China border reflects the evolving strategic partnership between the two countries. This partnership, rooted in shared interests and common challenges, has become a significant factor in the global power balance.
FAQs about the Russia-China Border
1. What is the total length of the Russia-China border?
The Russia-China border stretches over 4,209 kilometers (2,616 miles).
2. What are the main geographical features of the border?
The border traverses a diverse range of landscapes, including the Altai Mountains, the Amur River valley, and the Ussuri River basin.
3. What are the historical origins of the border?
The current border is the result of a long and complex history, marked by treaties, wars, and political upheavals.
4. What are the major treaties that have shaped the border?
Significant treaties include the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689), the Treaty of Aigun (1858), the Treaty of Beijing (1860), and the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship (1924).
5. What are the main challenges facing the border?
Challenges include historical grievances, unresolved territorial disputes, and the potential for cross-border crime and terrorism.
6. What is the significance of the border in the current geopolitical landscape?
The border serves as a point of contact for trade, diplomacy, and security, making it a crucial element in the regional and global geopolitical landscape.
7. What is the future outlook for the Russia-China border?
The future of the border is likely to be shaped by the evolving relationship between Russia and China, their economic and security interests, and the geopolitical dynamics in the region.
Tips for Understanding the Russia-China Border
- Study the historical context: Understanding the historical events and treaties that have shaped the border is crucial for grasping its present-day significance.
- Explore the geographical features: Familiarize yourself with the diverse landscapes, rivers, and mountain ranges that define the border.
- Analyze the geopolitical implications: Consider the border’s role in trade, diplomacy, security, and the evolving strategic partnership between Russia and China.
- Stay informed about current events: Keep abreast of developments related to the border, including political negotiations, economic agreements, and security concerns.
Conclusion
The Russia-China border is a multifaceted entity, a tapestry woven from history, geography, and geopolitics. It is a testament to the complex and dynamic relationship between two of the world’s most influential nations, reflecting their shared past, present-day interactions, and the potential for their future cooperation and competition. Understanding this border is essential for comprehending the regional and global geopolitical landscape, as it serves as a crucial point of contact for trade, diplomacy, and security, shaping the destinies of both Russia and China.

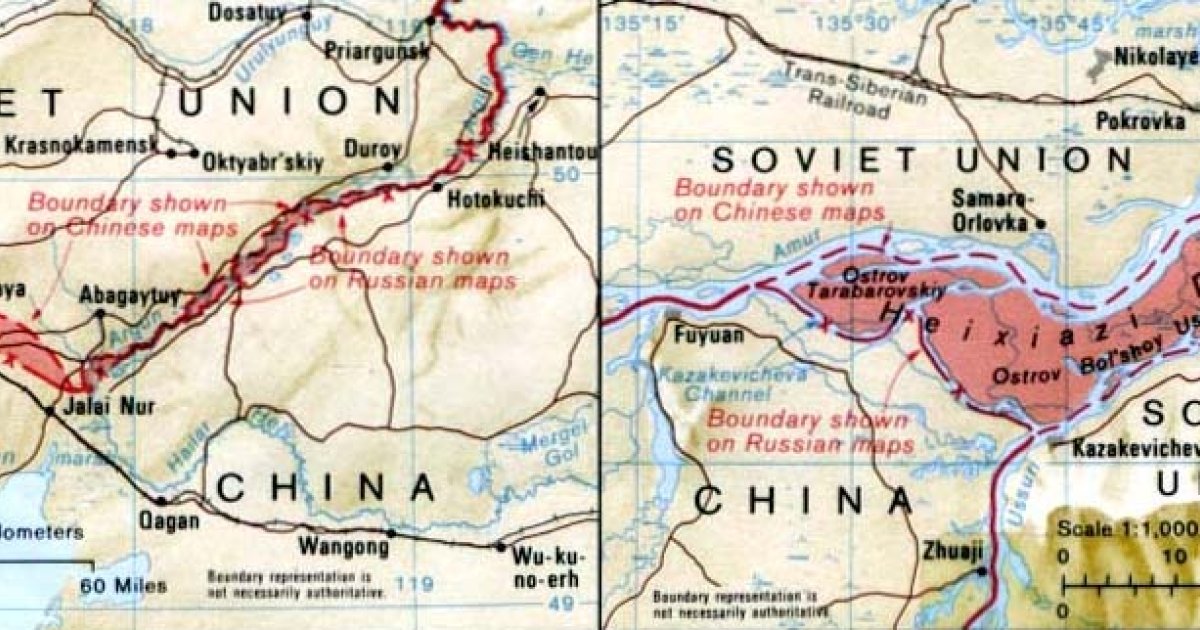


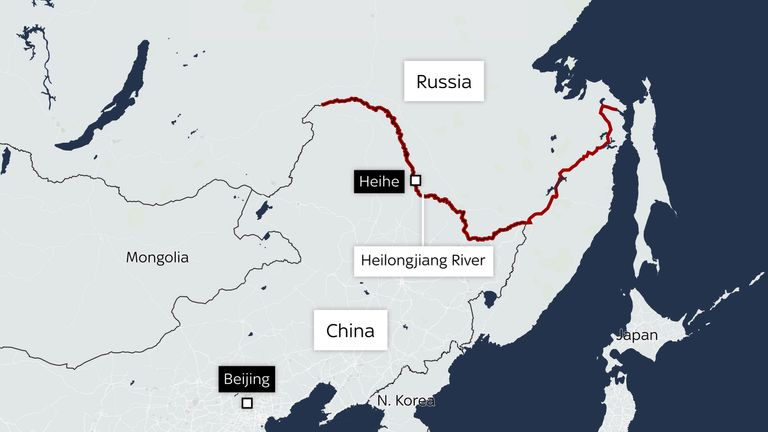



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Russia-China Border: A Tapestry of History, Geography, and Geopolitics. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!