The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography
Related Articles: The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography
- 3.1 A Geographic Overview
- 3.2 A Cradle of Civilizations
- 3.3 A Crossroads of Cultures
- 3.4 A Vital Economic Hub
- 3.5 Environmental Challenges
- 3.6 The Importance of Conservation
- 3.7 FAQs
- 3.8 Tips for Visiting the Mediterranean Region
- 3.9 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography

The Mediterranean Sea, a vast body of water cradled between Europe, Africa, and Asia, has played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human history. This ancient sea, a cradle of civilizations, has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the birth of languages and religions, and the development of trade routes that connected continents. Understanding the geography of the Mediterranean region is crucial for appreciating its historical significance, its diverse cultural tapestry, and its enduring influence on the modern world.
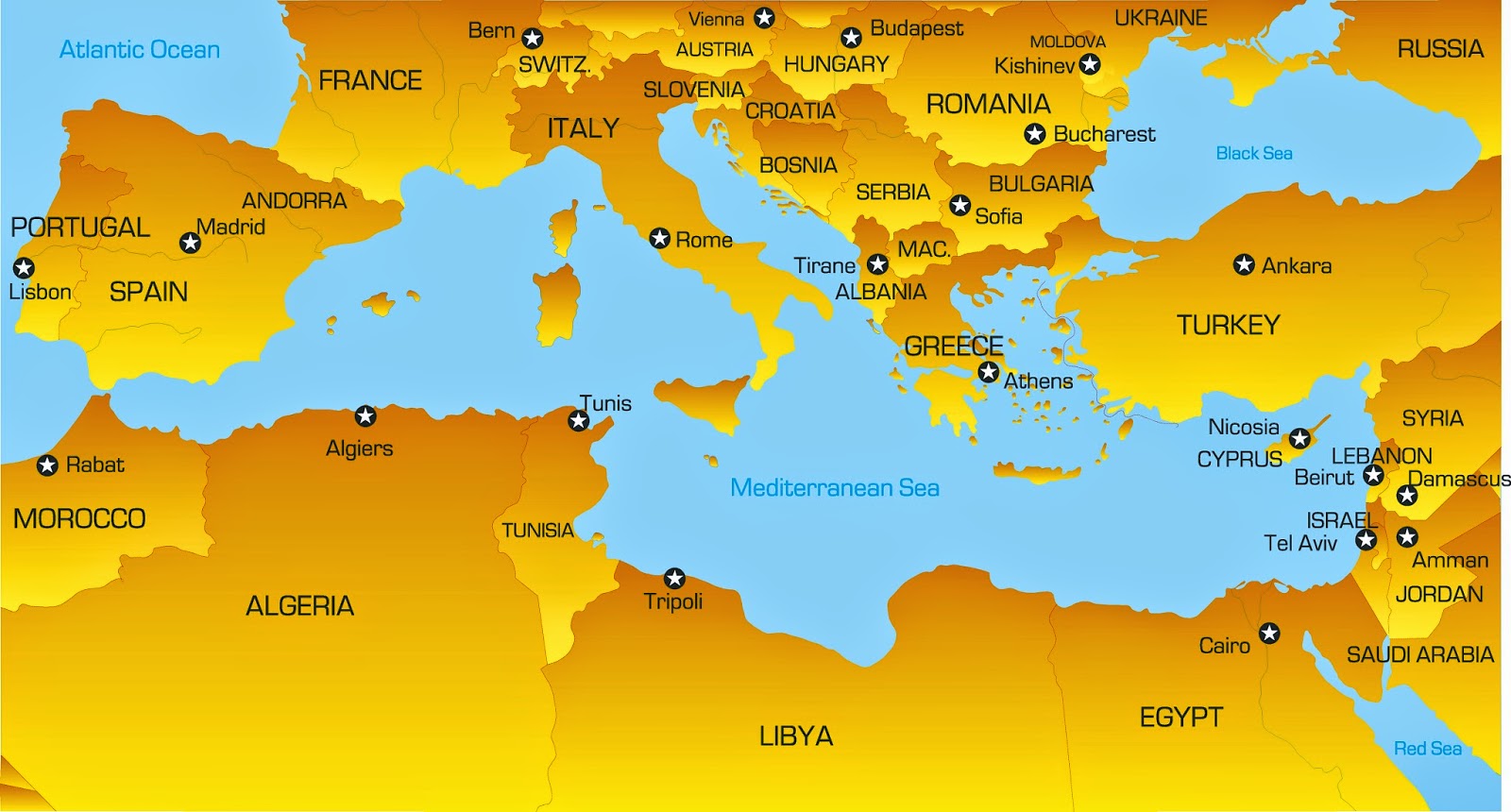
A Geographic Overview
The Mediterranean Sea, with its distinctive blue waters, stretches for over 2,500 kilometers, encompassing a surface area of approximately 2.5 million square kilometers. Its coastline, a mosaic of diverse landscapes, encompasses over 46,000 kilometers, touching upon 21 countries.
The Mediterranean Sea is divided into several sub-basins:
- The Western Mediterranean: This basin, including the Balearic Sea, the Ligurian Sea, and the Tyrrhenian Sea, is bordered by Spain, France, Italy, and the island of Corsica.
- The Central Mediterranean: This basin, including the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian Sea, and the Aegean Sea, is bordered by Italy, Greece, Albania, Montenegro, Croatia, Slovenia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Turkey.
- The Eastern Mediterranean: This basin, including the Levantine Sea, is bordered by Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Cyprus, and the island of Crete.
The Mediterranean Sea is characterized by its unique geographical features:
- The Strait of Gibraltar: This narrow strait connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean.
- The Suez Canal: This man-made waterway connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, providing a critical trade route between Europe and Asia.
- Numerous islands: The Mediterranean Sea is dotted with thousands of islands, ranging from small rocky outcrops to large, mountainous islands like Sicily, Sardinia, and Cyprus.
- Deep canyons and trenches: The Mediterranean Sea floor is characterized by deep trenches and canyons, including the Calypso Deep, the deepest point in the Mediterranean Sea.
A Cradle of Civilizations
The Mediterranean Sea has been a vital artery for human civilization since antiquity. Its strategic location, abundant resources, and favorable climate have attracted settlers and traders for millennia. The region witnessed the rise of powerful empires, including the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Ottomans. Each civilization left its mark on the region, contributing to its rich cultural heritage.
Ancient civilizations flourished along the Mediterranean shores, leaving behind a legacy of:
- Architecture: From the Parthenon in Athens to the Colosseum in Rome, the Mediterranean region is home to some of the world’s most iconic architectural marvels.
- Art and Literature: The Mediterranean Sea has been a source of inspiration for artists and writers for centuries, producing masterpieces like Homer’s epic poems and the works of Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci.
- Philosophy and Science: The Mediterranean region was a center of intellectual thought, giving rise to philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, and scientists like Archimedes and Ptolemy.
A Crossroads of Cultures
The Mediterranean Sea has served as a bridge between cultures, facilitating the exchange of ideas, goods, and people. The region’s diverse population, a blend of European, African, and Asian influences, has contributed to a rich tapestry of languages, religions, and customs.
The Mediterranean region is characterized by its cultural diversity, evidenced by:
- Languages: The region is home to a multitude of languages, including Arabic, Greek, Italian, Spanish, French, and Turkish.
- Religions: The Mediterranean region is a crossroads of major world religions, including Christianity, Islam, Judaism, and Eastern Orthodox Christianity.
- Cuisine: Mediterranean cuisine, renowned for its fresh ingredients and flavorful dishes, reflects the region’s diverse cultural influences.
A Vital Economic Hub
The Mediterranean Sea remains a vital economic hub, connecting countries and continents through trade and transportation. Its ports, including Genoa, Marseille, Piraeus, and Alexandria, serve as gateways for international trade, facilitating the movement of goods and people.
The Mediterranean Sea’s economic significance is evident in:
- Shipping and Trade: The Mediterranean Sea is a major shipping route, connecting Europe, Africa, and Asia.
- Tourism: The region’s beautiful beaches, ancient ruins, and vibrant cities attract millions of tourists each year.
- Fisheries: The Mediterranean Sea is a rich fishing ground, providing sustenance and livelihoods for coastal communities.
Environmental Challenges
Despite its economic importance, the Mediterranean Sea faces significant environmental challenges. Pollution from industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and coastal development threaten its delicate ecosystem. Overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change further exacerbate these challenges.
The Mediterranean Sea faces several environmental threats, including:
- Pollution: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge contribute to water pollution, harming marine life and ecosystems.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices deplete fish stocks and disrupt marine ecosystems.
- Climate change: Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and extreme weather events threaten marine life and coastal communities.
The Importance of Conservation
Protecting the Mediterranean Sea is crucial for its ecological health and the well-being of its surrounding communities. Conservation efforts aim to reduce pollution, promote sustainable fishing practices, and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Conservation efforts are essential for:
- Protecting marine biodiversity: The Mediterranean Sea is home to a diverse array of marine life, including whales, dolphins, sea turtles, and coral reefs.
- Ensuring sustainable fisheries: Sustainable fishing practices help to maintain healthy fish stocks and support coastal communities.
- Mitigating climate change: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting to climate change impacts are essential for protecting the Mediterranean Sea and its surrounding communities.
FAQs
Q: What are the major rivers that flow into the Mediterranean Sea?
A: The major rivers that flow into the Mediterranean Sea include the Nile River, the Rhône River, the Po River, and the Ebro River.
Q: What are the main islands in the Mediterranean Sea?
A: Some of the main islands in the Mediterranean Sea include Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, Crete, Corsica, Malta, and the Balearic Islands.
Q: What are the main countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea?
A: The countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea include Spain, France, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Albania, Greece, Turkey, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Egypt, Libya, Tunisia, Algeria, and Morocco.
Q: What are some of the historical events that took place in the Mediterranean region?
A: The Mediterranean region has witnessed a vast array of historical events, including the rise and fall of empires, the development of trade routes, the spread of religions, and the birth of art, literature, and philosophy. Some significant events include the Trojan War, the rise of the Roman Empire, the Crusades, and the Ottoman conquest.
Q: What are the main environmental challenges facing the Mediterranean Sea?
A: The Mediterranean Sea faces several environmental challenges, including pollution from industrial activities, agricultural runoff, and coastal development. Overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change further exacerbate these challenges.
Q: What are some of the conservation efforts being undertaken to protect the Mediterranean Sea?
A: Conservation efforts aim to reduce pollution, promote sustainable fishing practices, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. These efforts involve international cooperation, research, and public awareness campaigns.
Tips for Visiting the Mediterranean Region
- Plan your trip in advance: The Mediterranean region is a popular tourist destination, so it’s essential to book your flights and accommodations in advance, especially during peak season.
- Research the best time to visit: The Mediterranean climate is generally warm and sunny, but the best time to visit depends on your preferences. The shoulder seasons (spring and autumn) offer pleasant weather and fewer crowds.
- Pack for diverse weather: The Mediterranean climate can be unpredictable, so pack for a range of temperatures and weather conditions.
- Learn a few basic phrases: While English is widely spoken in tourist areas, learning a few basic phrases in the local language can enhance your travel experience.
- Try the local cuisine: The Mediterranean region is renowned for its delicious cuisine. Be sure to sample local specialties and fresh ingredients.
- Explore the historical sites: The Mediterranean region is rich in history and culture. Take the time to visit ancient ruins, museums, and historical landmarks.
- Respect the local culture: Be mindful of local customs and traditions when traveling in the Mediterranean region.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean Sea, a crossroads of history, culture, and geography, continues to hold immense significance in the modern world. Its strategic location, diverse cultures, and rich history make it a fascinating and rewarding destination for travelers. However, the region also faces significant environmental challenges, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts to protect its delicate ecosystem and ensure its sustainable future. By understanding the geography, history, and culture of the Mediterranean region, we can appreciate its enduring legacy and contribute to its preservation for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Mediterranean Sea: A Crossroads of History, Culture, and Geography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!