The Legacy of the Soviet Union: A Look at the Republics that Composed the USSR
Related Articles: The Legacy of the Soviet Union: A Look at the Republics that Composed the USSR
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Legacy of the Soviet Union: A Look at the Republics that Composed the USSR. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Legacy of the Soviet Union: A Look at the Republics that Composed the USSR

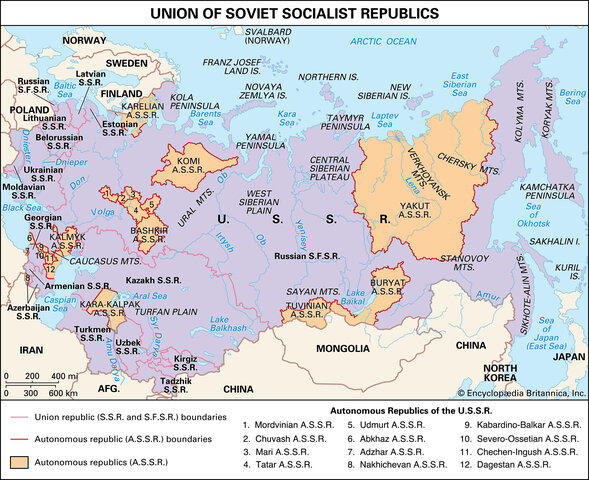
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), a vast and complex entity, dominated the geopolitical landscape for much of the 20th century. Its dissolution in 1991 marked a pivotal moment in history, leaving behind a legacy that continues to shape the world today. Understanding the constituent republics that formed the USSR is crucial for comprehending the historical, political, and social dynamics of this influential superpower.
The Foundation of the USSR: A Union of Republics
The USSR emerged from the ashes of the Russian Revolution, with the Bolshevik party consolidating power and establishing a socialist state. The initial core of the Soviet Union consisted of Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. However, the Soviet system aimed to expand its influence and encompass a diverse range of ethnicities and nationalities.
The Expansion and Growth of the USSR
The USSR’s territorial expansion was fueled by a combination of political maneuvering, military conquest, and ideological objectives. The following republics joined the Soviet Union in the years following its formation:
- 1922: Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan
- 1929: Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan
- 1940: Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia
These newly incorporated republics, along with the original three, became integral parts of the Soviet system, each contributing to the economic and military power of the USSR.
The USSR’s Internal Structure: A Federative System
The USSR functioned as a federation, with each republic possessing a degree of autonomy while remaining subject to the overarching authority of the central government in Moscow. This structure allowed for a balance between centralized control and regional self-governance.
The Republics of the USSR: A Diverse Mosaic
The USSR encompassed a vast geographical area, encompassing a wide range of cultures, languages, and ethnicities. Each republic possessed a distinct identity and history, contributing to the overall complexity and diversity of the Soviet Union.
The Collapse of the USSR: A Turning Point in History
By the late 1980s, the USSR was facing severe economic and political challenges. The rigid centralized system, coupled with internal ethnic tensions and a weakening economy, created a climate of instability. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the formation of 15 independent nations, each charting its own path towards a new future.
The Republics of the Former USSR: A New Era
The dissolution of the USSR marked a significant turning point in the global landscape. The former republics embarked on a journey of transition, grappling with the challenges of establishing independent states and building new identities.
The Republics of the Former USSR: A Look at their Individual Journeys
- Russia: As the largest and most powerful republic, Russia emerged as the successor state to the USSR. However, its transition to a market economy and democratic system was marked by significant challenges.
- Ukraine: Ukraine, a crucial agricultural and industrial center, gained independence and embarked on a path towards democratization and economic reforms.
- Belarus: Belarus, under the leadership of Alexander Lukashenko, retained a close relationship with Russia and maintained a more authoritarian system.
- Kazakhstan: Kazakhstan, rich in natural resources, pursued a path of economic development and modernization, leveraging its vast oil reserves.
- Uzbekistan: Uzbekistan, with a predominantly Muslim population, experienced a period of economic growth and political stability.
- Turkmenistan: Turkmenistan, under the authoritarian rule of Saparmurat Niyazov, pursued a policy of isolationism and strict control.
- Tajikistan: Tajikistan, a predominantly mountainous country, faced a protracted civil war after independence, eventually achieving a fragile peace.
- Kyrgyzstan: Kyrgyzstan, known as the "Switzerland of Central Asia," underwent a series of political upheavals and revolutions.
- Georgia: Georgia, under the leadership of Mikheil Saakashvili, implemented significant reforms and sought closer ties with the West.
- Armenia: Armenia, a predominantly Christian nation, faced challenges related to its conflict with Azerbaijan over the Nagorno-Karabakh region.
- Azerbaijan: Azerbaijan, rich in oil and gas reserves, pursued a policy of economic development and diversification.
- Lithuania: Lithuania, with a strong sense of national identity, joined the European Union and NATO.
- Latvia: Latvia, with a diverse population, sought to integrate into the European Union and promote economic growth.
- Estonia: Estonia, known for its technological advancements, became a leading member of the European Union and NATO.
The Legacy of the USSR: A Complex and Enduring Influence
The collapse of the USSR had profound implications for the global order. It led to the emergence of new nations, reshaped geopolitical alliances, and triggered a period of significant economic and social change. The legacy of the Soviet Union continues to shape the world today, influencing political, economic, and cultural dynamics.
FAQs about the Republics of the Former USSR
Q1: What are the main languages spoken in the former USSR republics?
The former USSR republics are characterized by a diverse linguistic landscape. Russian remains widely spoken, but each republic has its own official language. For example, Ukrainian is the official language of Ukraine, Belarusian is the official language of Belarus, and Kazakh is the official language of Kazakhstan.
Q2: How did the USSR’s collapse affect the economies of the former republics?
The collapse of the USSR led to significant economic challenges for the former republics. The transition to market economies, coupled with the loss of subsidies from Moscow, resulted in widespread economic hardship. However, some republics, such as Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan, have experienced significant economic growth in recent years.
Q3: What is the current political situation in the former USSR republics?
The political landscape in the former USSR republics is diverse, ranging from democracies to authoritarian regimes. Some republics, such as Ukraine, Georgia, and Lithuania, have embraced democratic values and institutions. Others, such as Belarus, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, have retained more authoritarian systems.
Q4: What are the main cultural differences between the former USSR republics?
The former USSR republics are characterized by a rich tapestry of cultures, traditions, and beliefs. Differences in language, religion, history, and customs contribute to the diverse cultural landscape of the region.
Tips for Understanding the Republics of the Former USSR
- Study the history of each republic: Understanding the historical background of each republic is crucial for comprehending its current situation.
- Explore the cultural diversity of the region: The former USSR republics offer a wealth of cultural experiences, from traditional music and dance to unique culinary traditions.
- Engage with contemporary news and media: Staying informed about current events in the region provides valuable insights into the political, economic, and social dynamics of the former USSR republics.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of the USSR
The USSR, a powerful and influential entity, left a lasting mark on the world. Its collapse in 1991 ushered in a new era, transforming the geopolitical landscape and shaping the destinies of its former republics. Understanding the history, culture, and current situation of the republics that composed the USSR is essential for comprehending the complex and evolving dynamics of this region. The legacy of the Soviet Union continues to resonate in the world today, influencing political, economic, and social developments, reminding us of the enduring impact of this once mighty superpower.

/a-globe-showing-the-union-of-soviet-socialist-republics-184937833-58b9dec03df78c353c4b74ee.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Legacy of the Soviet Union: A Look at the Republics that Composed the USSR. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!