The Great Lakes: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse
Related Articles: The Great Lakes: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Great Lakes: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Great Lakes: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse

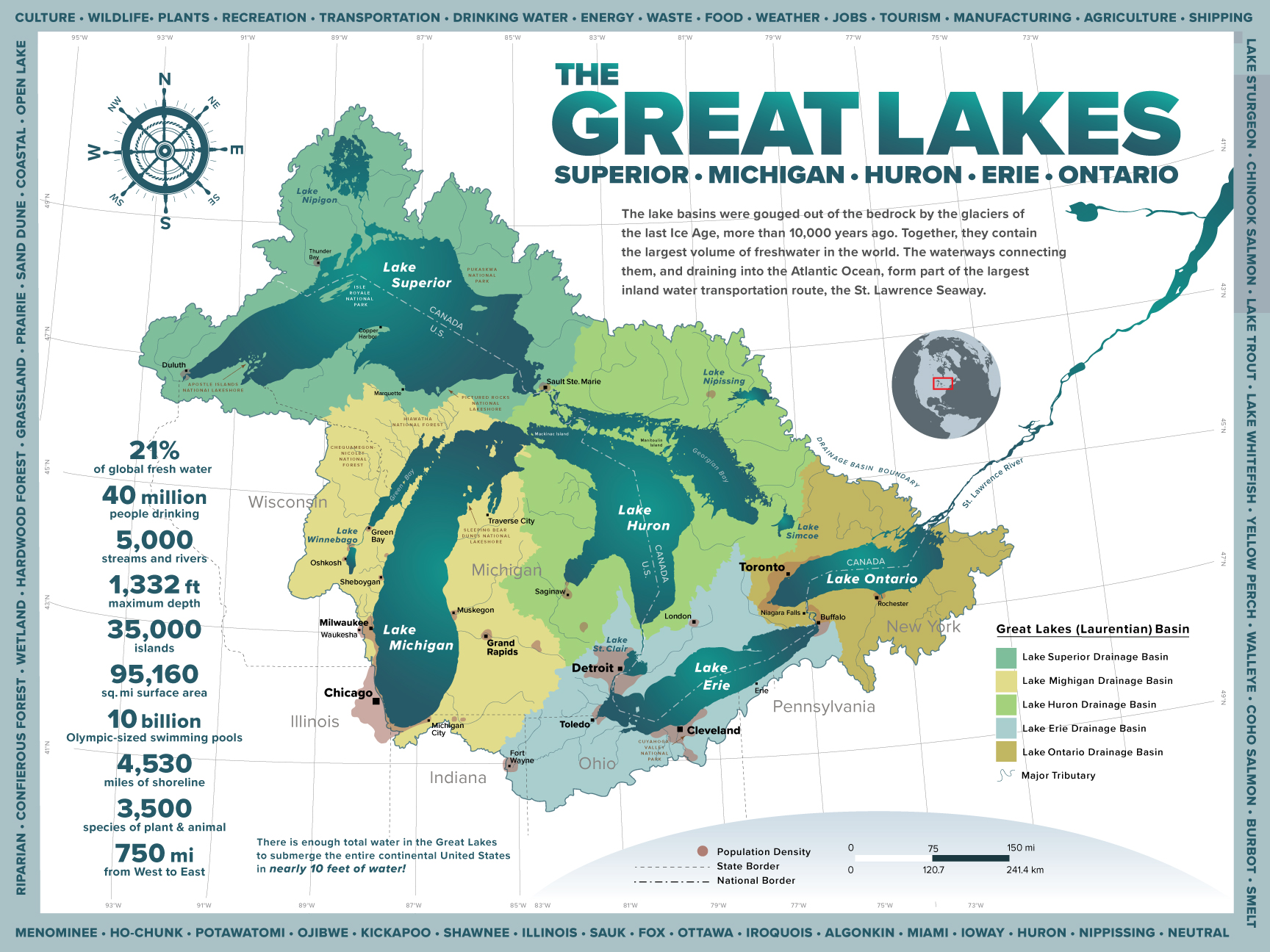
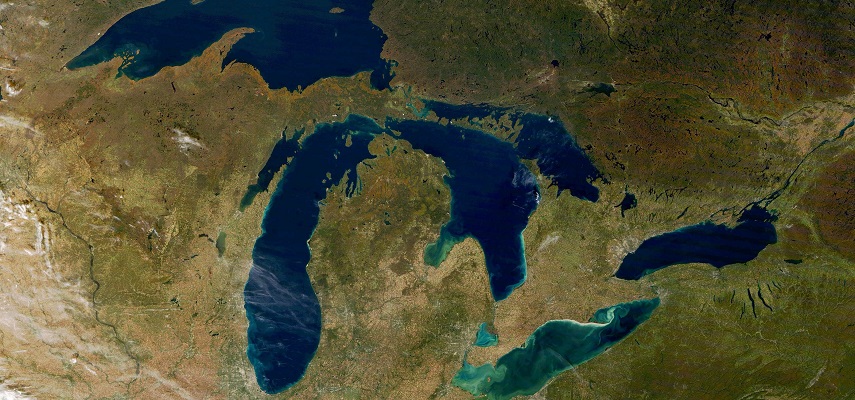
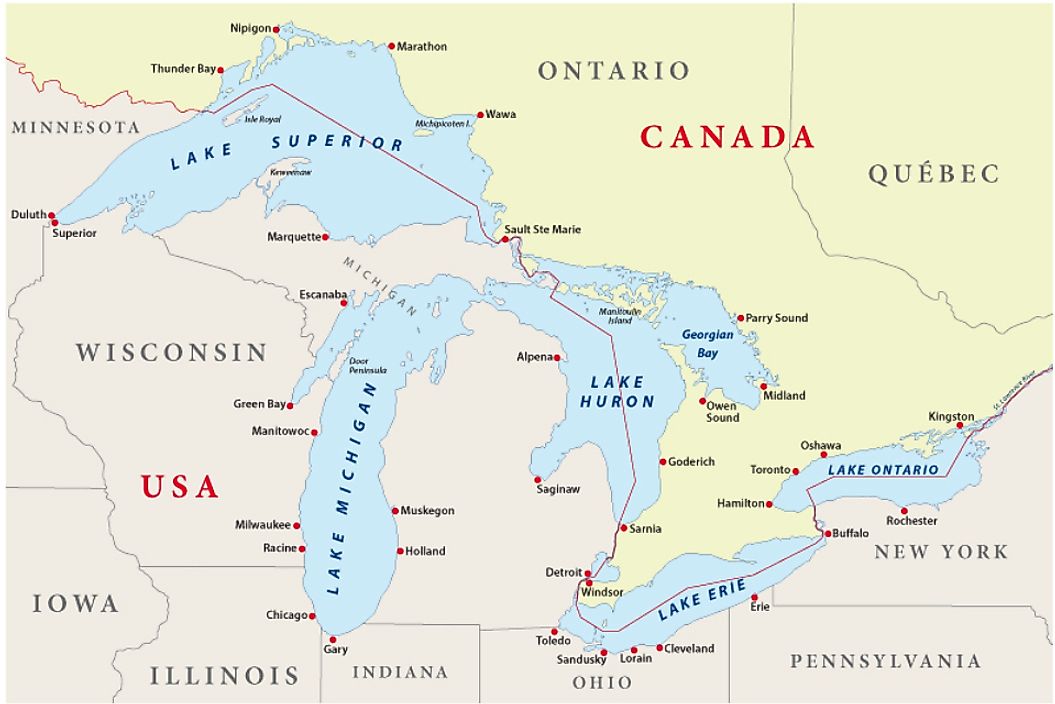
The Great Lakes, a collection of five interconnected freshwater lakes situated on the border of Canada and the United States, constitute one of the most significant geographical features in North America. This vast system, encompassing Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, holds a staggering 20% of the world’s freshwater supply, making it a vital resource for both countries.
A Geographical Tapestry
The Great Lakes region, stretching across a vast expanse of over 240,000 square kilometers, boasts a diverse landscape. The lakes themselves are a spectacle of natural beauty, with their crystalline waters reflecting the surrounding forests, rolling hills, and bustling cities. The region’s geology is equally impressive, with ancient glacial formations, towering cliffs, and fertile river valleys shaping the terrain.
Beyond the Surface: A Deep Dive into the Geography
-
Lake Superior: The largest and deepest of the Great Lakes, Superior is a behemoth of freshwater, holding more water than all the other Great Lakes combined. Its vastness and rugged shoreline are home to numerous islands, lighthouses, and scenic vistas.
-
Lake Michigan: The only Great Lake entirely within the United States, Michigan is known for its sandy beaches, vibrant cities like Chicago, and charming coastal towns. Its vast expanse provides ample opportunities for boating, fishing, and water sports.
-
Lake Huron: The second-largest lake by surface area, Huron shares a boundary with Michigan, forming a single body of water known as Lake Michigan-Huron. The lake is known for its many islands, including Mackinac Island, a popular tourist destination.
-
Lake Erie: The shallowest and warmest of the Great Lakes, Erie is a popular destination for recreational activities. Its proximity to major cities like Cleveland and Buffalo makes it a hub for tourism and commerce.
-
Lake Ontario: The smallest of the Great Lakes, Ontario is known for its scenic beauty and its role in the St. Lawrence Seaway, which connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean.
Beyond the Water: The Great Lakes Basin
The Great Lakes basin, encompassing the land surrounding the lakes, is a region of significant economic and environmental importance. The region is home to a diverse population, thriving industries, and rich natural resources.
-
A Hub of Economic Activity: The Great Lakes basin is a major center for manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and tourism. The region’s abundant freshwater resources, fertile land, and strategic location have made it a magnet for industry and commerce.
-
A Cradle of Biodiversity: The Great Lakes basin is home to a rich diversity of flora and fauna, including numerous species of fish, birds, mammals, and plants. The region’s diverse ecosystems support a vibrant ecosystem, contributing to the overall health of the environment.
Navigating the Waters: The Importance of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are not only a source of natural beauty and economic prosperity but also play a crucial role in the lives of millions of people.
-
A Lifeline for Transportation: The Great Lakes have long served as a vital transportation corridor, connecting major cities and industries throughout the region. The St. Lawrence Seaway, a system of canals and locks, allows ocean-going vessels to access the Great Lakes, facilitating trade and commerce.
-
A Source of Drinking Water: The Great Lakes provide drinking water to millions of people in both Canada and the United States. The lakes’ vast freshwater reserves are essential for ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water.
-
A Vital Ecosystem: The Great Lakes are home to a diverse ecosystem, supporting a vast array of wildlife and plant life. The lakes’ health is crucial for maintaining the balance of the region’s ecosystem and ensuring the survival of many species.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their immense value, the Great Lakes face numerous challenges, including pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
-
Pollution: Industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge pose significant threats to the health of the Great Lakes. These pollutants can contaminate the water, harming aquatic life and posing risks to human health.
-
Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species, such as zebra mussels and Asian carp, has disrupted the ecological balance of the Great Lakes, harming native species and impacting the ecosystem.
-
Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the Great Lakes in various ways, including rising water temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased frequency of extreme weather events. These changes pose risks to the lakes’ ecosystem and human communities.
A Collaborative Effort
Addressing the challenges facing the Great Lakes requires a collaborative effort from governments, businesses, and communities.
-
Environmental Regulations: Governments play a crucial role in enacting and enforcing environmental regulations to protect the Great Lakes from pollution and other threats.
-
Sustainable Practices: Businesses and individuals can adopt sustainable practices to minimize their environmental impact on the Great Lakes. This includes reducing pollution, conserving water, and supporting efforts to protect the ecosystem.
-
Community Engagement: Public awareness and community engagement are essential for fostering a sense of stewardship and responsibility for the Great Lakes.
FAQs
Q: What is the largest of the Great Lakes?
A: The largest of the Great Lakes is Lake Superior, both by surface area and volume.
Q: How many states border the Great Lakes?
A: Eight states border the Great Lakes: Minnesota, Wisconsin, Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York.
Q: What is the St. Lawrence Seaway?
A: The St. Lawrence Seaway is a system of canals and locks that connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean, allowing ocean-going vessels to access the lakes.
Q: What are some of the major cities located on the Great Lakes?
A: Major cities located on the Great Lakes include Chicago, Detroit, Cleveland, Toronto, and Buffalo.
Q: What are some of the major industries in the Great Lakes region?
A: The Great Lakes region is a major center for manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and tourism. Key industries include automotive manufacturing, steel production, agriculture, and tourism.
Q: What are some of the threats to the Great Lakes?
A: The Great Lakes face numerous threats, including pollution, invasive species, and climate change.
Q: What can be done to protect the Great Lakes?
A: Protecting the Great Lakes requires a collaborative effort from governments, businesses, and communities. This includes enacting and enforcing environmental regulations, adopting sustainable practices, and fostering public awareness and community engagement.
Tips for Exploring the Great Lakes
-
Plan your trip in advance: The Great Lakes region offers a wide array of attractions and activities, so planning your trip in advance can help you make the most of your time.
-
Consider the seasons: The Great Lakes region experiences distinct seasons, each offering unique opportunities for exploration. Summer is ideal for boating, swimming, and hiking, while fall offers stunning foliage displays.
-
Explore the islands: The Great Lakes are home to numerous islands, each offering unique landscapes and experiences. Consider visiting Mackinac Island, Isle Royale, or Pelee Island.
-
Embrace the local culture: The Great Lakes region boasts a rich cultural heritage, with vibrant cities, charming towns, and diverse culinary traditions. Take the time to explore the local culture and immerse yourself in the region’s unique character.
Conclusion
The Great Lakes are a vital resource for both Canada and the United States, providing economic prosperity, recreational opportunities, and a source of freshwater for millions of people. The region’s diverse landscape, rich history, and vibrant culture make it a destination for travelers from around the world. By understanding the importance of the Great Lakes and the challenges they face, we can work together to protect this valuable resource for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Great Lakes: A Geographical and Economic Powerhouse. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!