Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact
Related Articles: Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact
- 3.1 Delving into the Doldrums: A Journey through the Equatorial Belt
- 3.2 Mapping the Doldrums: A Dynamic and Shifting Zone
- 3.3 Navigating the Doldrums: Historical Challenges and Modern Solutions
- 3.4 The Doldrums Beyond the Sea: Impact on Climate and Weather
- 3.5 Understanding the Doldrums: Importance and Benefits
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions about the Doldrums
- 3.7 Tips for Navigating the Doldrums
- 3.8 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact
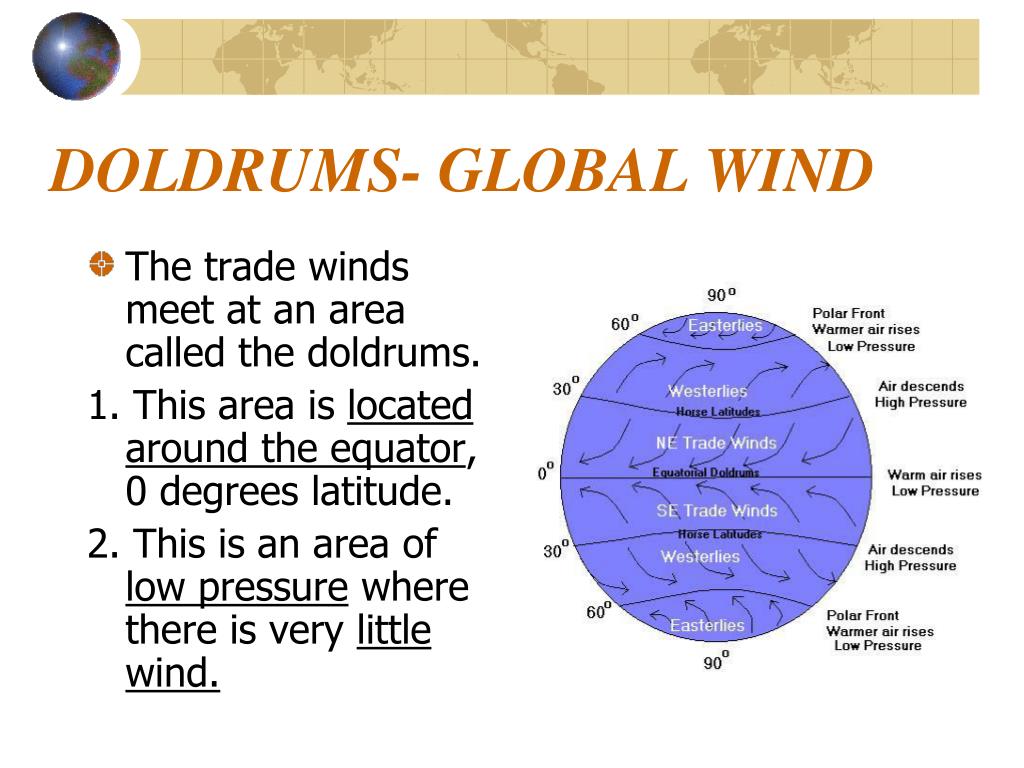
The Earth’s atmosphere is a complex system, driven by solar energy and planetary rotation. This intricate dance of forces creates predictable patterns of wind, pressure, and precipitation, which are crucial for understanding weather and climate. One such pattern is the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), a region of low pressure and light, variable winds often referred to as the doldrums.
Delving into the Doldrums: A Journey through the Equatorial Belt
The doldrums are not a fixed geographical location but rather a zone that shifts seasonally along the equator. This region, marked by low atmospheric pressure, is characterized by:
- Light and Variable Winds: Unlike the strong, consistent trade winds that prevail in the surrounding areas, the doldrums experience weak, erratic winds that can change direction unpredictably. This can pose challenges for sailing vessels, as they may become becalmed for extended periods.
- High Humidity and Precipitation: The convergence of air masses from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres creates a region of high humidity and abundant rainfall. This can lead to dense cloud cover and frequent thunderstorms, further complicating navigation.
- Calm Seas: The lack of strong winds often results in calm seas, which can be both a blessing and a curse. While it provides a peaceful environment for sailors, it also makes it difficult to maintain a consistent course.
Mapping the Doldrums: A Dynamic and Shifting Zone
The doldrums are not static; they migrate north and south throughout the year, following the sun’s path. This movement is driven by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface, which creates a cycle of rising and sinking air masses. During the Northern Hemisphere’s summer, the doldrums shift north towards the Tropic of Cancer, and conversely, during the Southern Hemisphere’s summer, they shift south towards the Tropic of Capricorn.
This seasonal shift creates a dynamic map of the doldrums, with their exact location varying depending on the time of year. Sailors and meteorologists alike rely on these maps to anticipate the challenges posed by the doldrums and plan their routes accordingly.
Navigating the Doldrums: Historical Challenges and Modern Solutions
Historically, the doldrums have been a source of frustration and danger for sailors. Ships could be trapped for weeks, running out of supplies and facing the threat of starvation. The lack of wind made it impossible to sail, and the heavy rains and thunderstorms posed significant risks. This led to the development of strategies for navigating the doldrums, such as:
- Sailing Close to the Wind: By sailing at a slight angle to the wind, ships could make slow but steady progress even in light conditions.
- Using the Trade Winds: By taking advantage of the trade winds that blow consistently on either side of the doldrums, sailors could bypass the region altogether.
- Waiting for Favorable Winds: If caught in the doldrums, sailors would often wait for a change in wind direction before attempting to sail further.
With the advent of modern technology, navigation has become significantly easier. Weather forecasting and satellite imagery provide real-time information on wind patterns, enabling sailors to plan their routes more accurately and avoid the doldrums altogether.
The Doldrums Beyond the Sea: Impact on Climate and Weather
The doldrums play a crucial role in global climate patterns. The convergence of air masses and the resulting precipitation contribute to the high rainfall experienced in equatorial regions. This rainfall, in turn, fuels the lush rainforests that are vital for the Earth’s ecosystem.
The doldrums also influence weather patterns in surrounding regions. The strong trade winds that originate on either side of the doldrums drive weather systems and influence rainfall patterns across vast areas.
Understanding the Doldrums: Importance and Benefits
The study of the doldrums is essential for understanding the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. By analyzing the dynamics of the ITCZ and its influence on wind, precipitation, and temperature, scientists can gain insights into:
- Climate Change: The shifting patterns of the doldrums can be a telltale sign of climate change, as the warming of the planet alters the balance of air pressure and wind circulation.
- Weather Forecasting: Accurate predictions of the doldrums’ location and strength are crucial for weather forecasting, especially in regions prone to extreme weather events.
- Oceanographic Research: The doldrums play a vital role in ocean currents and nutrient distribution, influencing marine ecosystems and fisheries.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Doldrums
Q: What are the doldrums, and where are they located?
A: The doldrums, also known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ), are a region of low atmospheric pressure and light, variable winds located near the equator. They are not a fixed location but shift seasonally north and south following the sun’s path.
Q: Why are the doldrums called "doldrums"?
A: The term "doldrums" refers to the calm, sluggish conditions experienced in this region. The lack of strong winds can make sailing difficult, leading to long periods of stagnation.
Q: How do the doldrums affect weather patterns?
A: The convergence of air masses in the doldrums creates a region of high humidity and frequent thunderstorms, contributing to the high rainfall experienced in equatorial regions. The strong trade winds that originate on either side of the doldrums also influence weather patterns across vast areas.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by sailors navigating the doldrums?
A: Sailors navigating the doldrums face challenges such as unpredictable winds, heavy rainfall, and the risk of being becalmed for extended periods. These conditions can make it difficult to maintain a consistent course and can lead to delays and even danger.
Q: How has modern technology improved navigation through the doldrums?
A: Modern technology, such as weather forecasting and satellite imagery, provides real-time information on wind patterns, enabling sailors to plan their routes more accurately and avoid the doldrums altogether.
Tips for Navigating the Doldrums
- Plan Your Route Carefully: Consult weather forecasts and charts to anticipate the location and strength of the doldrums.
- Be Prepared for Delays: The doldrums can cause significant delays, so plan your voyage accordingly.
- Monitor Wind Patterns: Keep a close eye on wind direction and speed, and be prepared to adjust your course as needed.
- Use Modern Technology: Take advantage of weather forecasting and satellite imagery to aid in navigation.
- Be Patient: Navigating the doldrums requires patience and adaptability. Don’t rush your journey, and be prepared to wait for favorable winds.
Conclusion
The doldrums, a region of low pressure and light winds near the equator, are a fascinating and dynamic feature of the Earth’s atmosphere. They play a crucial role in global climate patterns, influencing weather and rainfall across vast areas. While historically posing significant challenges for sailors, modern technology has made navigation through the doldrums much easier. Understanding the dynamics of the doldrums is essential for anyone interested in weather, climate, and the intricate workings of our planet.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Winds: Understanding the Doldrums and Their Impact. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!