Navigating the Land of the Apache: A Guide to the Reservations
Related Articles: Navigating the Land of the Apache: A Guide to the Reservations
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Land of the Apache: A Guide to the Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Land of the Apache: A Guide to the Reservations

The Apache people, a diverse group of Indigenous nations with a rich history and culture, have inhabited the southwestern United States for centuries. Their ancestral lands, now encompassed by various reservations, hold profound significance for the Apache people, serving as a vital link to their past, present, and future. Understanding the geographical landscape of these reservations is crucial for appreciating the complexities of Apache life, the challenges they face, and the resilience they embody.
This article delves into the intricate tapestry of Apache reservations, providing a comprehensive overview of their locations, histories, and cultural significance. It explores the unique challenges faced by the Apache people in maintaining their sovereignty and traditions within the modern world.
A Mosaic of Reservations: Geographical Overview
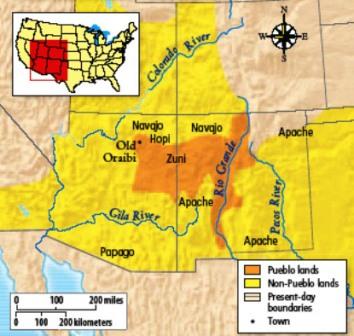
The term "Apache" encompasses various distinct nations, each with its own language, cultural practices, and historical experiences. These nations are not unified under a single reservation system, but rather occupy distinct geographical territories across Arizona, New Mexico, and Oklahoma.
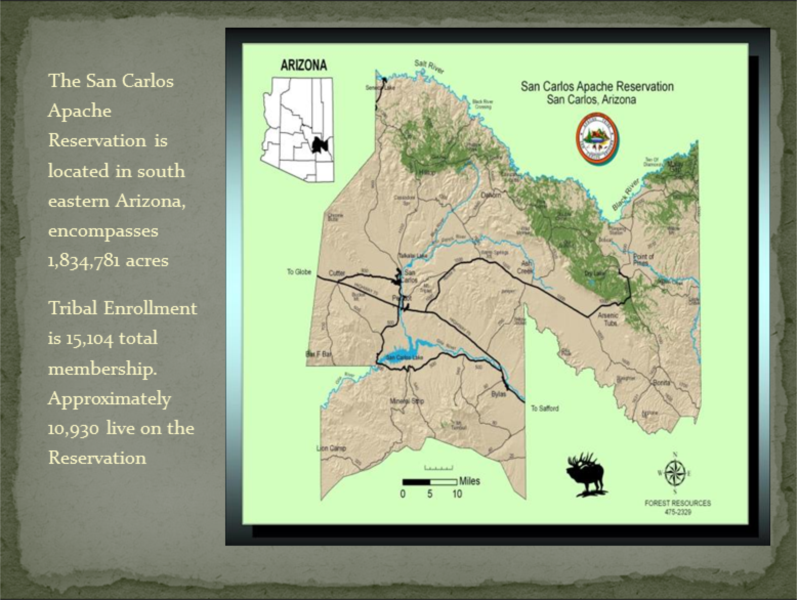
1. San Carlos Apache Reservation, Arizona:
Located in southeastern Arizona, the San Carlos Apache Reservation is the largest Apache reservation in the United States. It covers approximately 1.7 million acres, encompassing a diverse landscape of mountains, canyons, and desert. The San Carlos Apache Tribe, with its rich cultural heritage, has actively preserved its traditions and language, making the reservation a vibrant center of Apache culture.
2. Fort Apache Reservation, Arizona:
Situated in the White Mountains of eastern Arizona, the Fort Apache Reservation is home to the White Mountain Apache Tribe. This reservation, covering over 1.6 million acres, is known for its stunning natural beauty, including the Apache Sitgreaves National Forest. The White Mountain Apache Tribe has a strong commitment to environmental stewardship, actively managing the reservation’s resources for future generations.
3. Mescalero Apache Reservation, New Mexico:
Nestled in the Sacramento Mountains of southern New Mexico, the Mescalero Apache Reservation encompasses over 700,000 acres. The Mescalero Apache Tribe has successfully developed economic opportunities on the reservation, including a casino and a ski resort, while maintaining a strong connection to their ancestral lands.
4. Jicarilla Apache Reservation, New Mexico:
Located in northern New Mexico, the Jicarilla Apache Reservation covers over 600,000 acres, encompassing a diverse landscape of mountains, forests, and grasslands. The Jicarilla Apache Tribe is known for its strong cultural traditions, including its vibrant arts and crafts scene. The reservation also boasts a thriving oil and gas industry, contributing significantly to the tribe’s economic well-being.
5. Apache Tribe of Oklahoma:
The Apache Tribe of Oklahoma, located in southwestern Oklahoma, represents a unique historical chapter in the Apache story. This tribe was relocated to Oklahoma in the late 19th century during the Indian Removal Act. While geographically separated from their ancestral lands, the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma has preserved its cultural traditions and language, maintaining a strong sense of identity.
Beyond Geographical Boundaries: The Significance of Reservations
The Apache reservations are more than just geographical territories; they represent a vital lifeline for the Apache people. These lands hold profound cultural and spiritual significance, connecting them to their ancestors and their future.
1. Cultural Preservation:
Reservations provide a safe space for the Apache people to practice their traditions, languages, and ceremonies. They serve as a sanctuary for cultural expression, safeguarding the richness and diversity of Apache heritage.
2. Economic Development:
Reservations offer opportunities for economic self-sufficiency, allowing the Apache people to control their resources and create jobs within their communities. Many reservations have developed businesses, casinos, and other enterprises, generating revenue and promoting economic growth.
3. Self-Governance:
Reservations grant the Apache people a degree of self-governance, allowing them to make decisions about their own affairs and manage their resources. This autonomy is crucial for preserving their sovereignty and cultural identity.
4. Environmental Stewardship:
The Apache people have a deep respect for the natural world, recognizing the interconnectedness of all living things. Reservations provide a platform for environmental stewardship, allowing the Apache people to manage their lands sustainably and protect their natural resources for future generations.
Challenges and Resilience: Navigating the Modern World
Despite their significance, Apache reservations face numerous challenges in the modern world. These challenges include:
1. Poverty and Unemployment:
Despite economic development efforts, poverty and unemployment remain significant issues on many reservations. Limited access to education, healthcare, and job opportunities often hinder economic progress.
2. Environmental Degradation:
The Apache people have faced environmental degradation due to resource extraction, pollution, and climate change. These challenges threaten the health of their lands and the well-being of their communities.
3. Loss of Cultural Identity:
The pressures of assimilation and modernization threaten to erode traditional Apache cultures. Language loss, cultural appropriation, and the influence of dominant society can undermine the preservation of their unique heritage.
4. Government Policies:
Federal policies and regulations often fail to recognize the unique needs and rights of the Apache people, leading to inequalities and injustices. These policies can hinder economic development, limit self-governance, and threaten the sovereignty of the reservations.
Despite these challenges, the Apache people demonstrate incredible resilience and determination. They have fought for their rights, preserved their traditions, and adapted to the changing world while maintaining a strong sense of community. Their ongoing struggle for self-determination and cultural preservation serves as a testament to their strength and resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Apache Reservations
1. How many Apache reservations are there in the United States?
There are five federally recognized Apache reservations in the United States: San Carlos Apache Reservation, Fort Apache Reservation, Mescalero Apache Reservation, Jicarilla Apache Reservation, and the Apache Tribe of Oklahoma.
2. What are the main cultural practices of the Apache people?
Apache culture is rich and diverse, with a strong emphasis on tradition, storytelling, and spiritual connection to the land. Their cultural practices include:
- Language: The Apache people speak various languages, including San Carlos Apache, White Mountain Apache, Mescalero Apache, and Jicarilla Apache.
- Ceremonies: Apache ceremonies are often centered around healing, spiritual renewal, and honoring their ancestors.
- Arts and Crafts: Apache arts and crafts are renowned for their beauty and craftsmanship, including beadwork, pottery, and basket weaving.
3. What are the economic opportunities on Apache reservations?
Apache reservations have developed various economic opportunities, including:
- Gaming: Casinos are a major source of revenue for many reservations, providing jobs and generating economic growth.
- Tourism: Reservations often attract tourists seeking cultural experiences, natural beauty, and outdoor recreation.
- Resource Management: Some reservations manage natural resources, such as timber, oil, and gas, generating revenue and supporting economic development.
4. What are the challenges faced by the Apache people in maintaining their sovereignty?
Apache reservations face challenges in maintaining their sovereignty, including:
- Federal Government Policies: Policies that limit self-governance and resource control can hinder economic development and cultural preservation.
- Economic Disparities: Poverty and unemployment are prevalent on many reservations, limiting opportunities for economic self-sufficiency.
- Environmental Degradation: Pollution, resource extraction, and climate change threaten the health of their lands and the well-being of their communities.
Tips for Visiting Apache Reservations
When visiting Apache reservations, it is essential to show respect for their culture and traditions:
- Obtain Permission: Always seek permission from the tribe before entering their lands or participating in cultural events.
- Dress Appropriately: Avoid wearing revealing clothing or attire that may be disrespectful.
- Be Aware of Cultural Norms: Respect tribal customs and traditions, including language, ceremonies, and dress.
- Support Local Businesses: Patronize businesses owned by the Apache people, contributing to their economic well-being.
- Leave No Trace: Respect the environment by leaving no trace of your visit, including trash or damage to the natural landscape.
Conclusion
Apache reservations hold immense cultural and historical significance, providing a vital link to the past, present, and future of the Apache people. They serve as a testament to their resilience, their commitment to cultural preservation, and their ongoing struggle for self-determination. Understanding the complexities of these reservations and the challenges faced by the Apache people is crucial for appreciating their unique contributions to American society and for promoting a more just and equitable future for all Indigenous peoples.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Land of the Apache: A Guide to the Reservations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!