Masada: A Map Unveiling Ancient History and Resilience
Related Articles: Masada: A Map Unveiling Ancient History and Resilience
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Masada: A Map Unveiling Ancient History and Resilience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Masada: A Map Unveiling Ancient History and Resilience

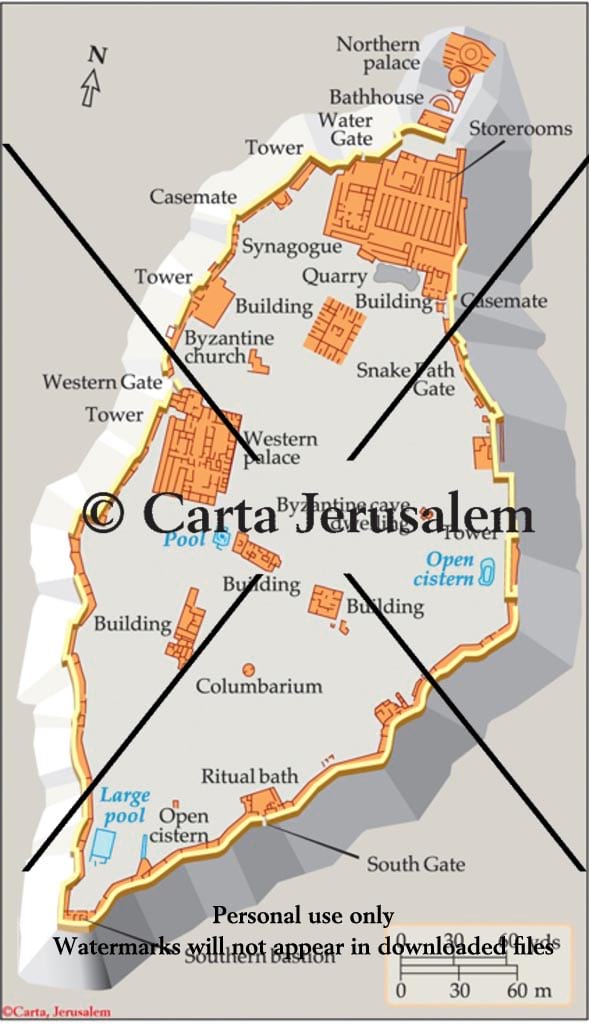
Masada, a towering fortress perched atop a plateau overlooking the Dead Sea, stands as a testament to a pivotal moment in Jewish history. Its strategic location, encompassing a vast area encompassing both natural and man-made fortifications, has captivated historians and archaeologists for centuries. Understanding Masada requires delving into its intricate map, a crucial tool for deciphering its history, significance, and enduring legacy.
The Topography of Resilience: A Detailed Look at the Masada Map
The Masada map unveils a complex network of structures and features meticulously designed for defense and survival. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of its key elements:
1. The Plateau:
- Natural Fortification: Masada’s defining characteristic is its natural plateau, rising dramatically above the surrounding desert landscape. This sheer cliff face, reaching heights of over 400 meters, provided a formidable natural barrier against attackers.
- Area: The plateau encompasses an area of approximately 60 acres, offering ample space for the fortress’s inhabitants and their necessities.
2. The Walls:
- Defensive Structure: The Romans, during their siege of Masada, described the fortress’s walls as "impregnable." These walls, constructed from locally sourced stone, encircled the plateau, creating a formidable perimeter.
- Double Walls: The walls were designed in a double-layered system, offering additional protection and creating a maze-like defensive system.
- Towers: Strategically positioned towers along the walls provided observation posts and vantage points for archers and defenders.
3. The Gates:
- Limited Access: Masada had three main gates, strategically placed to control access to the fortress. The most prominent, the Western Gate, provided access to the plateau’s main area.
- Defensive Features: The gates were fortified with additional walls, towers, and moats, further strengthening the fortress’s defenses.
4. The Interior:
- Residential Areas: Within the walls, the plateau housed residential areas, including homes, barracks, and storage rooms.
- Synagogue: A prominent synagogue, located on the plateau’s highest point, served as the center of religious life for the fortress’s inhabitants.
- Palaces: The fortress also boasted luxurious palaces, including Herod’s Palace, which served as the residence of the Roman-appointed king of Judea, Herod the Great.
5. The Water System:
- Essential Resource: Masada’s water system was critical for its survival, as water was scarce in the desert.
- Cisterns: The Romans found a complex network of cisterns within the fortress, designed to collect and store rainwater.
- Aqueducts: Aqueducts, carefully engineered to channel water from nearby sources, provided a constant flow of water to the cisterns.
6. The Roman Siege:
- Strategic Location: Masada’s strategic location, commanding the surrounding landscape, made it a crucial target for the Roman Empire.
- Siege of Masada: The siege of Masada, lasting for nearly three years, was a pivotal event in Jewish history. The Romans employed advanced siege tactics and engineering, eventually constructing a massive ramp to reach the plateau.
- Mass Suicide: Faced with inevitable defeat, the Jewish rebels within Masada chose mass suicide rather than surrender to the Romans. This tragic event became a symbol of Jewish resistance and martyrdom.
Masada: A Map of Significance and Legacy
The Masada map transcends its role as a simple geographical representation. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the following:
- Military Strategy: The map reveals the ingenuity and sophistication of the fortress’s defenses, highlighting the strategic thinking behind its design.
- Daily Life: The map provides insights into the daily lives of the people who lived within the fortress, showcasing their resilience and resourcefulness in a harsh environment.
- Cultural Identity: The synagogue and other religious structures on the plateau underscore the importance of faith and tradition for the Jewish people during this turbulent period.
- Symbol of Resistance: Masada’s history of rebellion and ultimate sacrifice continues to resonate with Jews and others around the world, inspiring a sense of courage and defiance in the face of oppression.
FAQs about Masada:
1. What is the best time to visit Masada?
- The best time to visit Masada is during the shoulder seasons (spring and autumn) when the weather is pleasant and crowds are smaller. Avoid visiting during the summer months (June-August) due to extreme heat.
2. How can I get to Masada?
- Masada is accessible by car, bus, or taxi. There is a parking lot near the entrance, and buses run regularly from Jerusalem and other major cities.
3. What are the opening hours of Masada?
- Masada is open daily from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM. However, opening hours may vary depending on the season.
4. Is there an entrance fee to Masada?
- Yes, there is an entrance fee to Masada. The cost varies depending on the type of ticket and the time of year.
5. What are some tips for visiting Masada?
- Wear comfortable walking shoes, as there is a significant amount of walking involved.
- Bring plenty of water, as it can be hot and dry.
- Apply sunscreen and wear a hat to protect yourself from the sun.
- Consider visiting Masada at sunrise or sunset for a breathtaking view.
6. What are some other attractions near Masada?
- The Dead Sea, known for its high salt content and buoyancy, is located just a short distance from Masada.
- Ein Gedi, a nature reserve with waterfalls and hiking trails, is also nearby.
- Qumran, the site where the Dead Sea Scrolls were discovered, is within a short drive.
7. How long does it take to explore Masada?
- Allow at least 3-4 hours to explore Masada, including the hike up the Snake Path or the cable car ride, visiting the ruins, and enjoying the views.
8. Are there any guided tours available for Masada?
- Yes, guided tours are available for Masada. These tours can provide valuable insights into the history and significance of the site.
9. Is Masada suitable for children?
- Masada is suitable for children, but it is important to be aware of the heat and the amount of walking involved.
10. Is it possible to camp at Masada?
- Camping is not permitted at Masada. However, there are several campgrounds located nearby.
Conclusion:
Masada, through its intricate map, reveals a story of resilience, faith, and resistance. It is a place where the past comes alive, offering a glimpse into the challenges and triumphs of a bygone era. Understanding its topography, its history, and its enduring legacy allows us to appreciate the human spirit’s capacity for both extraordinary defense and tragic sacrifice. Masada remains a powerful reminder of the enduring significance of history and its ability to shape our present and future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Masada: A Map Unveiling Ancient History and Resilience. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!