Japan’s Volcanic Landscape: A Map of Fire and Beauty
Related Articles: Japan’s Volcanic Landscape: A Map of Fire and Beauty
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Japan’s Volcanic Landscape: A Map of Fire and Beauty. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan’s Volcanic Landscape: A Map of Fire and Beauty
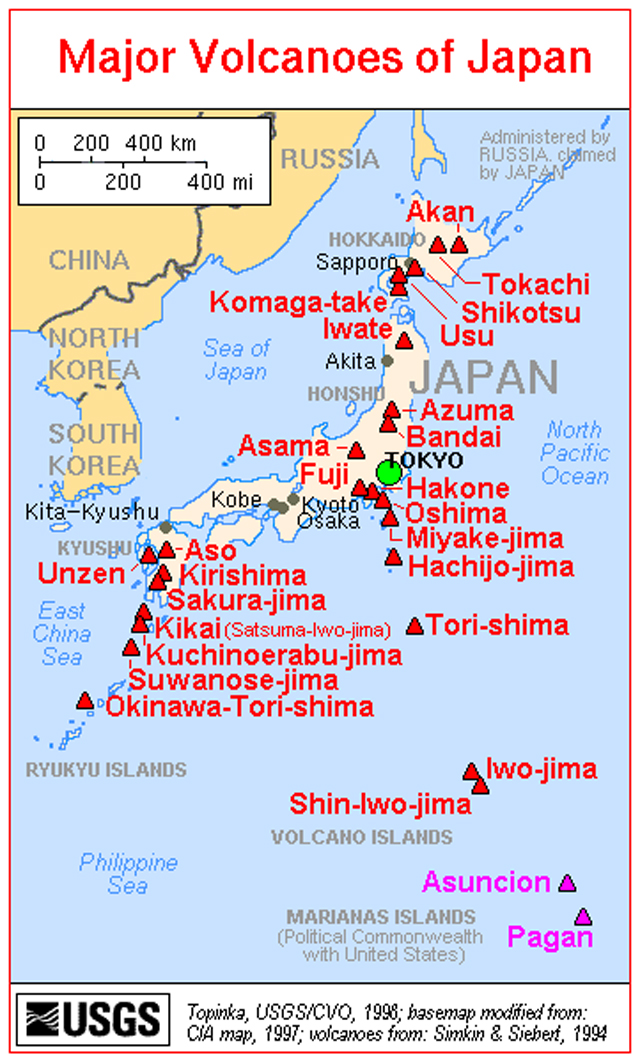
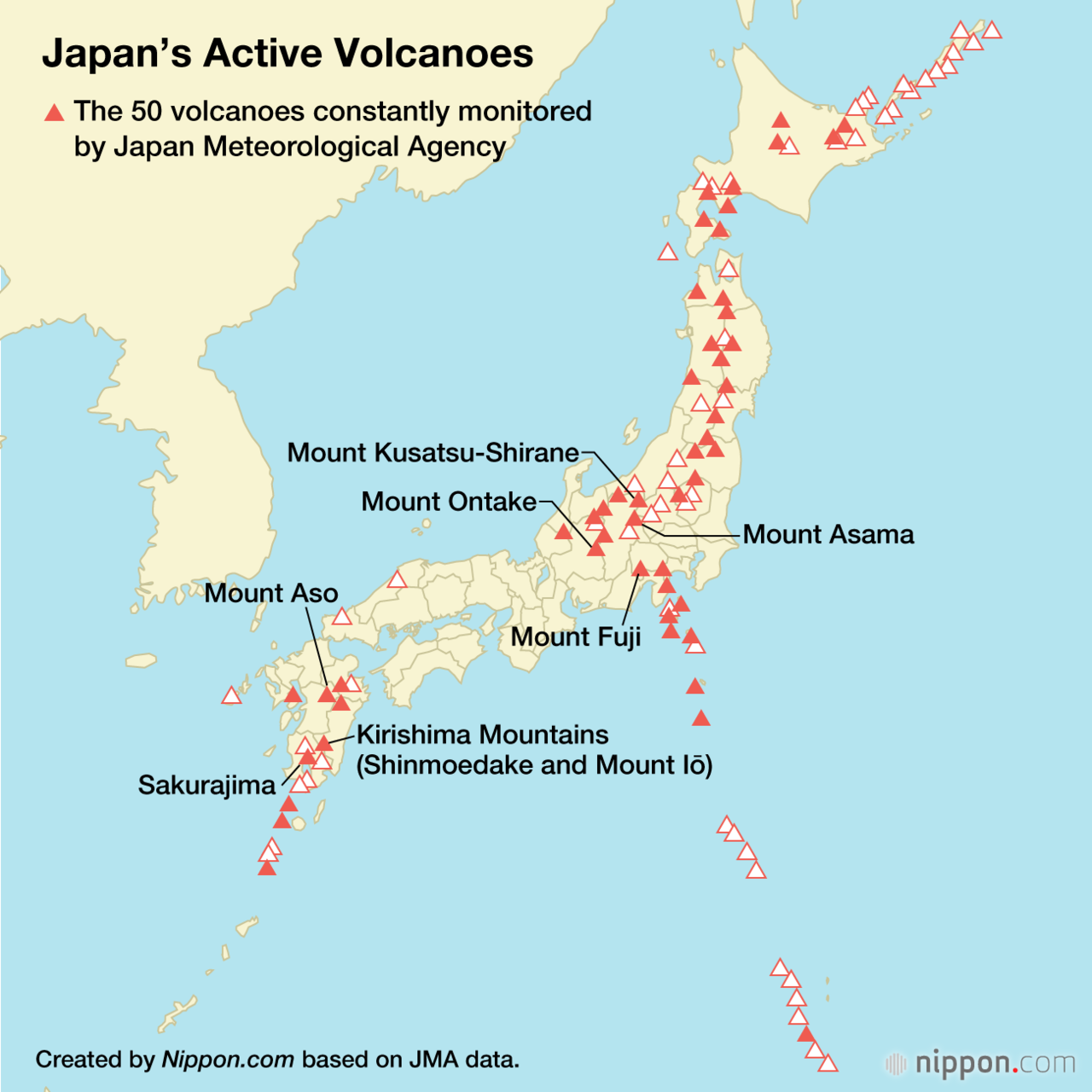
Japan, an archipelago nation nestled in the volatile Pacific Ring of Fire, boasts a remarkable volcanic landscape. This dynamic terrain, sculpted by the relentless forces of the Earth, is a testament to the country’s unique geological history and its ongoing interaction with the planet’s fiery underbelly. A comprehensive map of Japan’s volcanoes, a visual representation of this natural wonder, unveils a fascinating story of geological activity, cultural significance, and the constant dance between destruction and creation.
Unveiling the Ring of Fire: Japan’s Volcanic Heritage
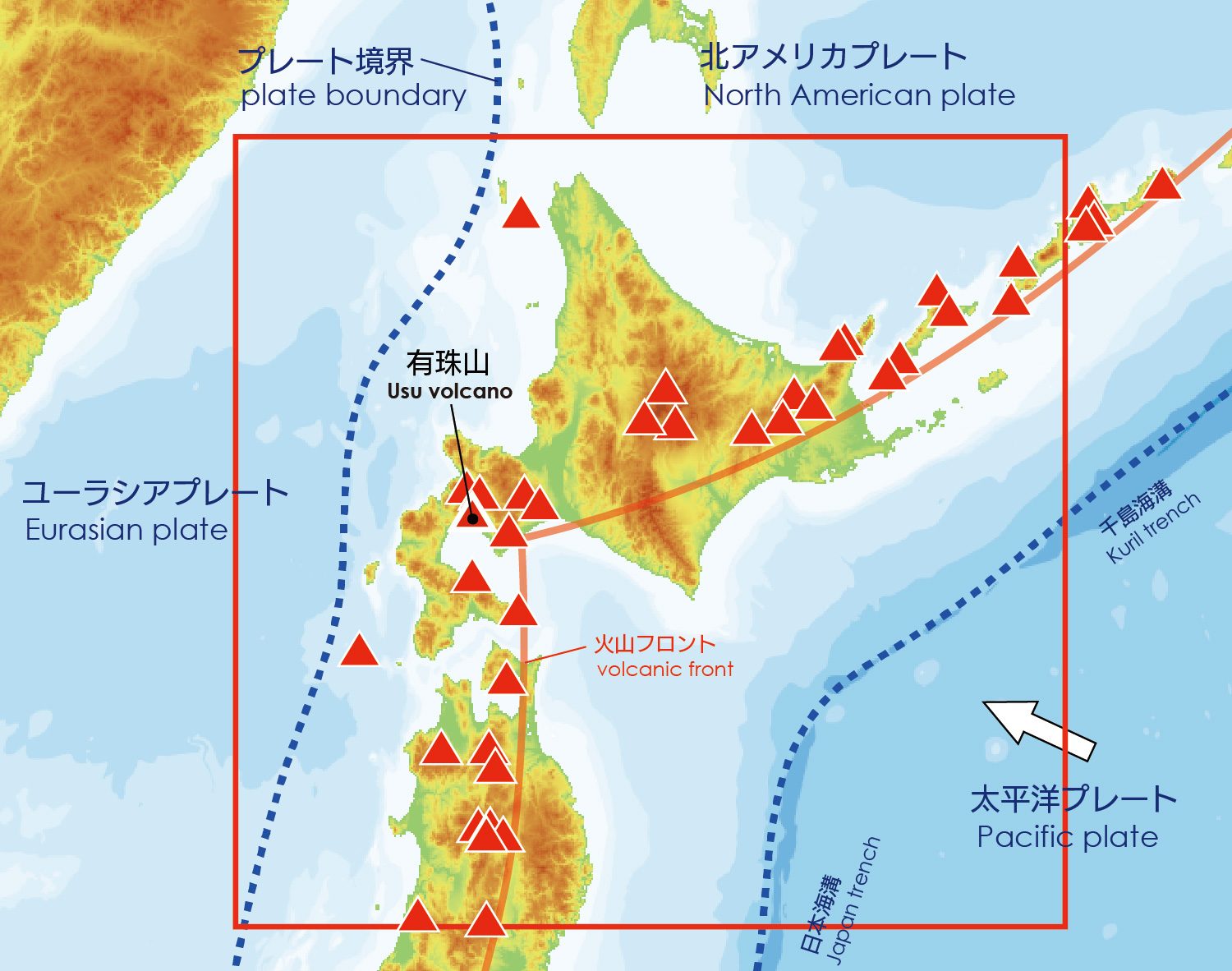
The Pacific Ring of Fire, a horseshoe-shaped zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity, encircles the Pacific Ocean. Japan, positioned directly on this ring, is one of the most volcanically active regions on Earth. This geological setting has shaped the nation’s landscape, its cultural identity, and its very existence.
The map of Japan’s volcanoes reveals a breathtaking tapestry of active and dormant cones, volcanic craters, and geothermal features scattered across the archipelago. This volcanic landscape is a product of plate tectonics, the constant movement of the Earth’s crust. The Pacific Plate, denser than the Eurasian Plate, subducts beneath it, leading to the melting of rock and the formation of magma. This magma, seeking an escape route, rises to the surface, creating volcanic eruptions that have shaped Japan’s terrain for millennia.
A Tapestry of Volcanic Forms
Japan’s volcanic map showcases a diverse array of volcanic features, each with its own unique characteristics and history:
-
Active Volcanoes: The map highlights numerous active volcanoes, those that have erupted in recent history or show signs of potential activity. These volcanoes are constantly monitored by scientists, providing valuable insights into the dynamics of volcanic activity and potential hazards.
-
Dormant Volcanoes: These volcanoes, while not currently erupting, have the potential to become active again. Their presence on the map serves as a reminder of the inherent geological instability of the region and the need for ongoing monitoring and preparedness.
-
Extinct Volcanoes: These volcanoes have not erupted for thousands of years and are considered unlikely to erupt again. While their activity has ceased, they still provide valuable information about the geological history of the region.
-
Volcanic Craters: These depressions in the Earth’s surface are formed by volcanic eruptions. Some craters are filled with water, forming stunning volcanic lakes, while others remain barren, showcasing the raw power of nature.
-
Geothermal Features: Japan’s volcanic activity also manifests in the form of hot springs, geysers, and fumaroles, all of which are fueled by the heat from the Earth’s interior. These features are often associated with volcanic areas and contribute to the region’s unique landscape and geothermal energy potential.
A Symphony of Beauty and Danger
Japan’s volcanic landscape is a breathtaking testament to the raw power and beauty of nature. The map reveals a tapestry of towering peaks, shimmering lakes, and verdant forests, all sculpted by the forces of volcanic activity. Yet, this beauty is intertwined with the inherent danger of these geological giants.
Volcanic eruptions, while awe-inspiring spectacles, can also be devastating natural disasters. The map serves as a reminder of the potential hazards associated with volcanic activity, emphasizing the importance of preparedness, risk mitigation, and ongoing monitoring.
Volcanoes and Japanese Culture
Volcanoes are deeply embedded in Japanese culture, shaping its myths, legends, and artistic expressions. The map of Japan’s volcanoes reveals a landscape that has inspired countless stories, from the mythical origins of the islands to the legends of fire deities and volcanic spirits.
-
Mount Fuji: The iconic Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano and a symbol of Japan, is a revered site of pilgrimage and a source of inspiration for artists and poets. Its majestic silhouette, perpetually capped with snow, embodies the harmony between nature’s power and beauty.
-
Spiritual Significance: Many volcanoes in Japan are considered sacred sites, associated with deities and spirits. These sites are often the subject of pilgrimages and rituals, reflecting the profound connection between the Japanese people and their volcanic landscape.
-
Artistic Inspiration: Volcanoes have inspired countless works of art, literature, and music. From the fiery landscapes of traditional Japanese paintings to the evocative imagery of contemporary art, volcanoes continue to capture the imagination and inspire artistic expression.
The Importance of the Volcanic Map
The map of Japan’s volcanoes serves as a vital tool for understanding and managing the risks associated with volcanic activity. It provides:
-
A Visual Representation: The map offers a clear and concise visual representation of the distribution of volcanoes across the archipelago. This visual aid helps scientists, policymakers, and the public understand the potential hazards and risks associated with volcanic activity.
-
Data for Risk Assessment: The map provides valuable data for assessing volcanic risks, including the frequency and intensity of eruptions, the potential impact on surrounding areas, and the effectiveness of existing mitigation measures. This information is crucial for developing effective disaster preparedness plans and minimizing the potential damage caused by volcanic events.
-
Monitoring and Research: The map serves as a reference point for ongoing monitoring and research efforts. Scientists use the map to track volcanic activity, analyze seismic data, and develop models to predict future eruptions. This information is essential for issuing timely warnings and evacuations, saving lives and minimizing property damage.
-
Public Awareness: The map helps raise public awareness about the importance of volcanic risk mitigation and preparedness. By providing visual information about the distribution of volcanoes and the potential hazards they pose, the map encourages responsible behavior and promotes a culture of preparedness.
FAQs about Japan’s Volcanic Map
Q: How many volcanoes are there in Japan?
A: Japan has over 100 volcanoes, of which approximately 110 are active.
Q: What is the most active volcano in Japan?
A: Mount Sakurajima, located in Kagoshima Prefecture, is considered one of the most active volcanoes in Japan, with frequent eruptions.
Q: What is the highest volcano in Japan?
A: Mount Fuji, standing at 3,776 meters (12,388 feet), is the highest volcano in Japan and a prominent landmark.
Q: Are there any volcanic hot springs in Japan?
A: Yes, Japan has numerous volcanic hot springs, known as "onsen," which are popular tourist destinations for their therapeutic properties.
Q: Are there any risks associated with living near volcanoes?
A: Yes, living near volcanoes poses various risks, including volcanic eruptions, ashfall, landslides, and gas emissions. However, Japan has a robust system of volcanic monitoring and disaster preparedness to mitigate these risks.
Tips for Volcano Viewing and Safety
-
Research and Plan: Before visiting a volcano, research its activity level, potential hazards, and recommended safety precautions.
-
Follow Official Guidelines: Adhere to official warnings and advisories issued by local authorities and volcanic monitoring agencies.
-
Stay on Designated Trails: Stick to designated trails and avoid venturing into restricted areas.
-
Be Aware of Gas Emissions: Be mindful of volcanic gas emissions, which can be harmful to health.
-
Carry a First Aid Kit: Pack a basic first aid kit for any potential emergencies.
Conclusion
Japan’s volcanic landscape is a testament to the dynamic forces that shape our planet. The map of Japan’s volcanoes serves as a visual reminder of the beauty, power, and potential hazards associated with these geological giants. It is a vital tool for understanding, monitoring, and managing the risks associated with volcanic activity, ensuring the safety and well-being of communities living in the shadow of these fiery giants. Through ongoing research, monitoring, and public awareness, Japan continues to navigate the delicate balance between the awe-inspiring power of its volcanoes and the need for responsible stewardship of this extraordinary landscape.
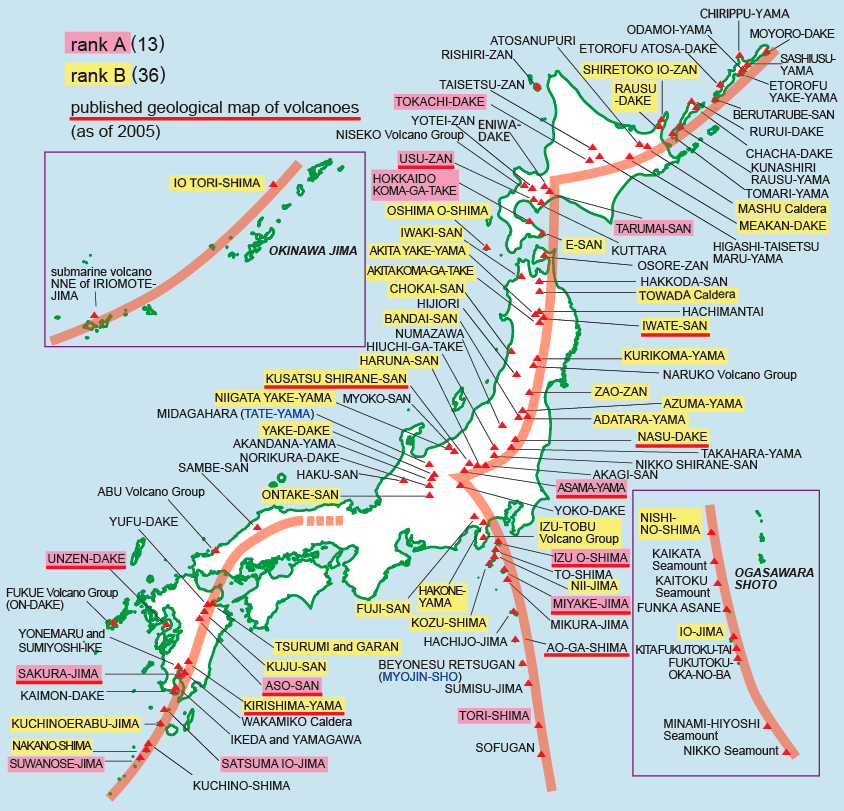
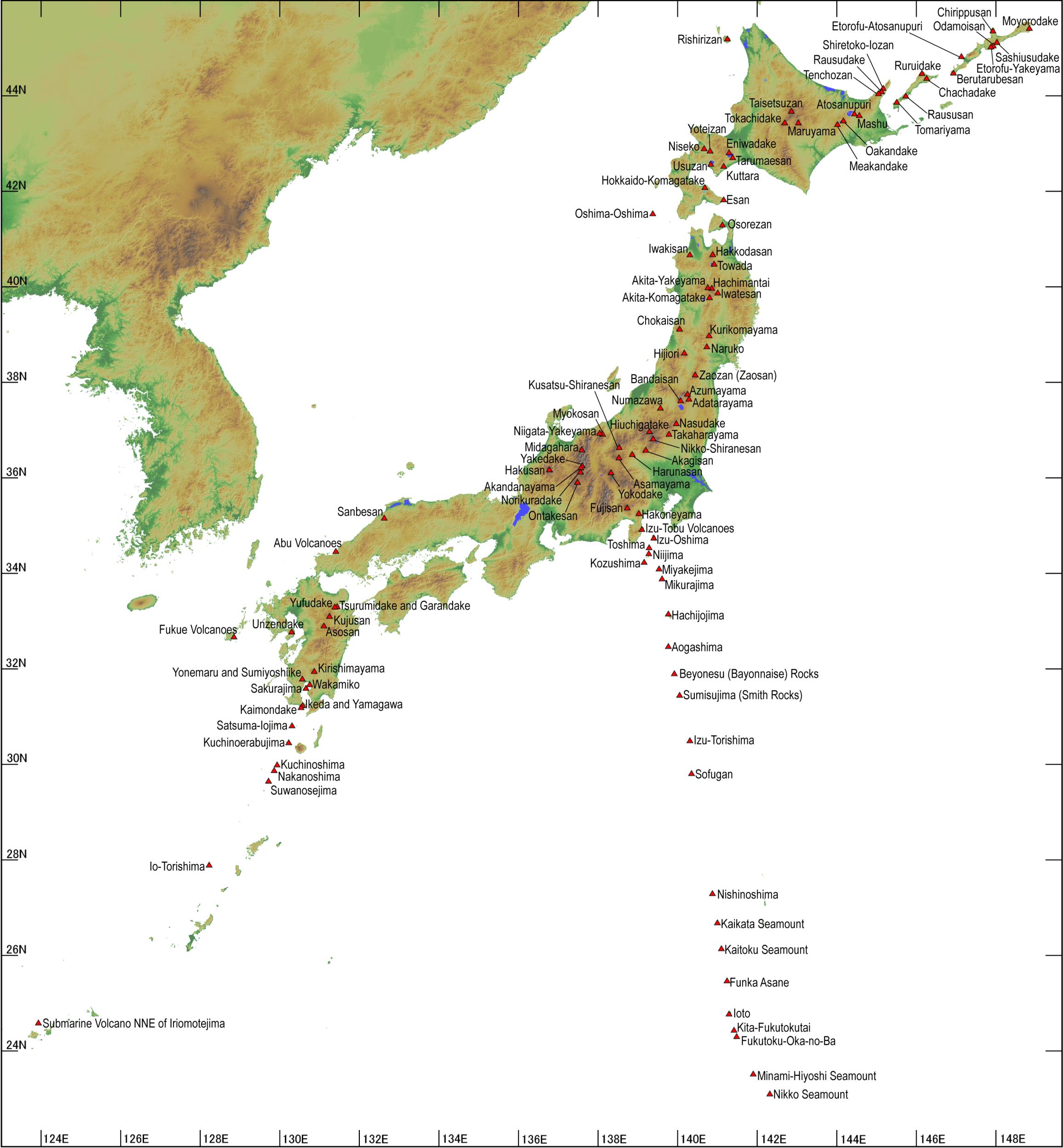
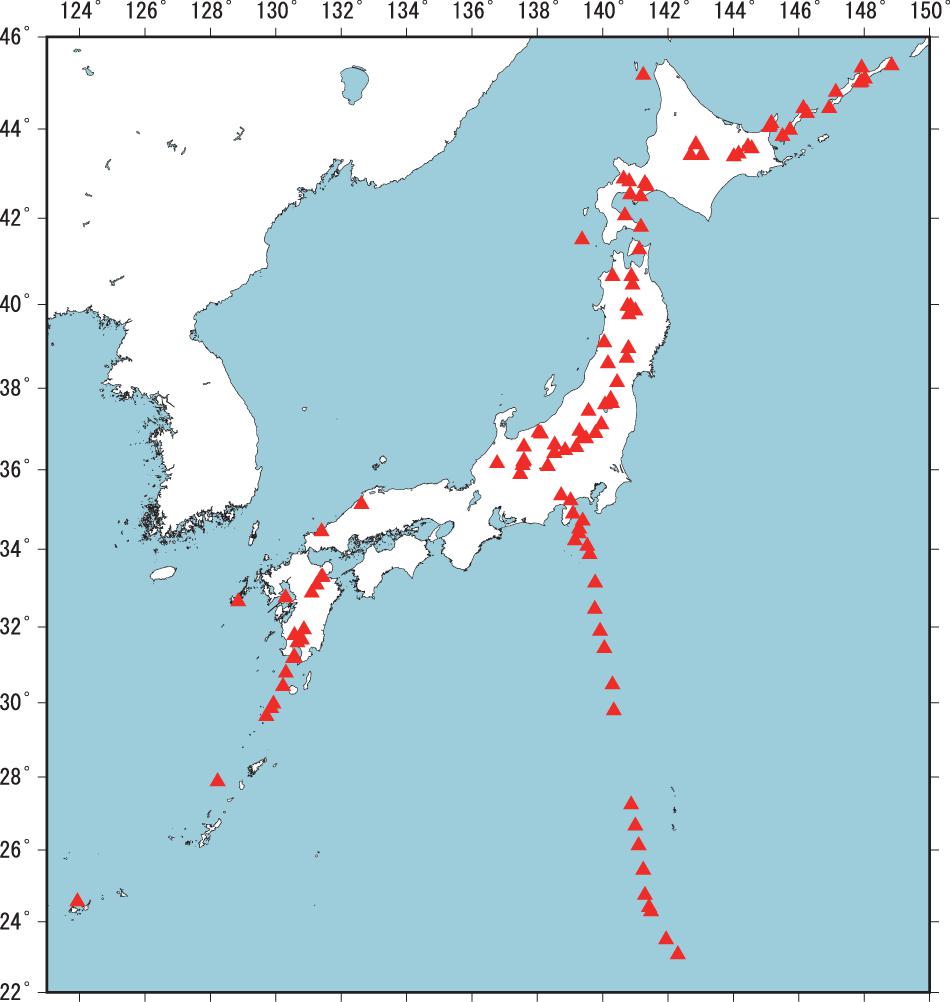


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan’s Volcanic Landscape: A Map of Fire and Beauty. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!