Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
Related Articles: Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
- 3.1 The Significance of Boundary Lines
- 3.2 Understanding the Evolution of Boundary Lines
- 3.3 The Importance of Boundary Lines
- 3.4 Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Boundary Lines
- 3.5 FAQs about Boundary Lines on Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
Maps, those ubiquitous representations of our planet, are more than just visual guides. They are powerful tools that communicate information about our world, and at the heart of this communication lie boundary lines. These lines, often depicted as simple strokes of color or thin lines, hold immense significance, defining and shaping our understanding of the world’s political, geographical, and cultural landscapes.
The Significance of Boundary Lines
Boundary lines on maps serve a multifaceted purpose, encompassing:
1. Political Boundaries: These lines delineate the territories of sovereign states, marking the limits of their jurisdiction and authority. They are crucial for defining national identities, governing systems, and international relations.
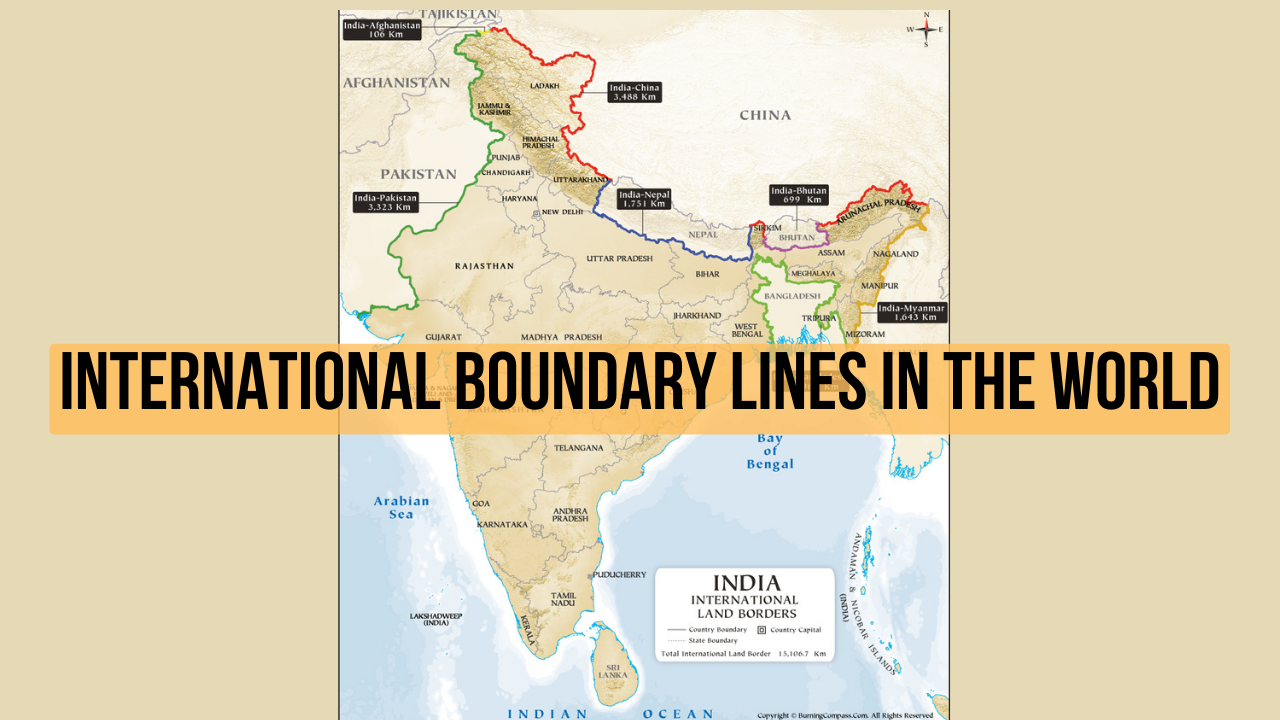
- Examples: The border between the United States and Mexico, the line separating India and Pakistan, and the demarcation of the European Union.
2. Administrative Boundaries: These lines define the territories of local administrative units, such as states, counties, cities, and towns. They help organize governance, resource allocation, and service delivery within a larger political entity.
- Examples: State lines within the United States, county borders within a state, and municipal boundaries within a city.
3. Geographical Boundaries: These lines mark natural or artificial features that divide geographical areas, such as mountains, rivers, or man-made structures. They often reflect distinct ecological zones, geological formations, or historical developments.
- Examples: The line of the Rocky Mountains, the course of the Mississippi River, and the Great Wall of China.
4. Cultural Boundaries: While less tangible, these lines indicate areas with distinct cultural identities, languages, religions, or traditions. They often reflect historical interactions, migrations, and social dynamics, shaping the unique character of different regions.
- Examples: The line separating the Indo-European and Uralic language families, the demarcation of different religious communities, and the boundaries of traditional tribal lands.
Understanding the Evolution of Boundary Lines
Boundary lines are not static entities; they evolve over time, reflecting political shifts, geographical changes, and societal transformations.
-
Historical Shifts: Political boundaries have been redrawn throughout history due to wars, treaties, and revolutions. The fall of the Soviet Union, the creation of new nation-states in Africa, and the reunification of Germany are prime examples of significant boundary shifts.
-
Geographical Changes: The course of rivers, the movement of glaciers, and the rise and fall of sea levels can alter geographical boundaries. The shrinking of the Aral Sea, the shifting of the Nile River’s course, and the impact of climate change on coastal regions are examples of geographical changes affecting boundaries.
-
Social and Cultural Dynamics: Cultural boundaries can shift as people migrate, languages evolve, and new identities emerge. The spread of globalization, the growth of multiculturalism, and the rise of digital communication have all influenced cultural boundaries.
The Importance of Boundary Lines
Understanding boundary lines is crucial for several reasons:
-
International Relations: Boundary lines form the basis of international law, defining territorial sovereignty, resource rights, and diplomatic relations.
-
Resource Management: Boundary lines guide the management of shared resources, such as water bodies, mineral deposits, and biodiversity.
-
Economic Development: Boundary lines shape regional economies, influencing trade patterns, infrastructure development, and investment flows.
-
Social Cohesion: Boundary lines can foster a sense of belonging and identity within communities, but they can also create tensions and conflicts if they are perceived as unfair or arbitrary.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Boundary Lines
Boundary lines are not without their challenges and controversies.
-
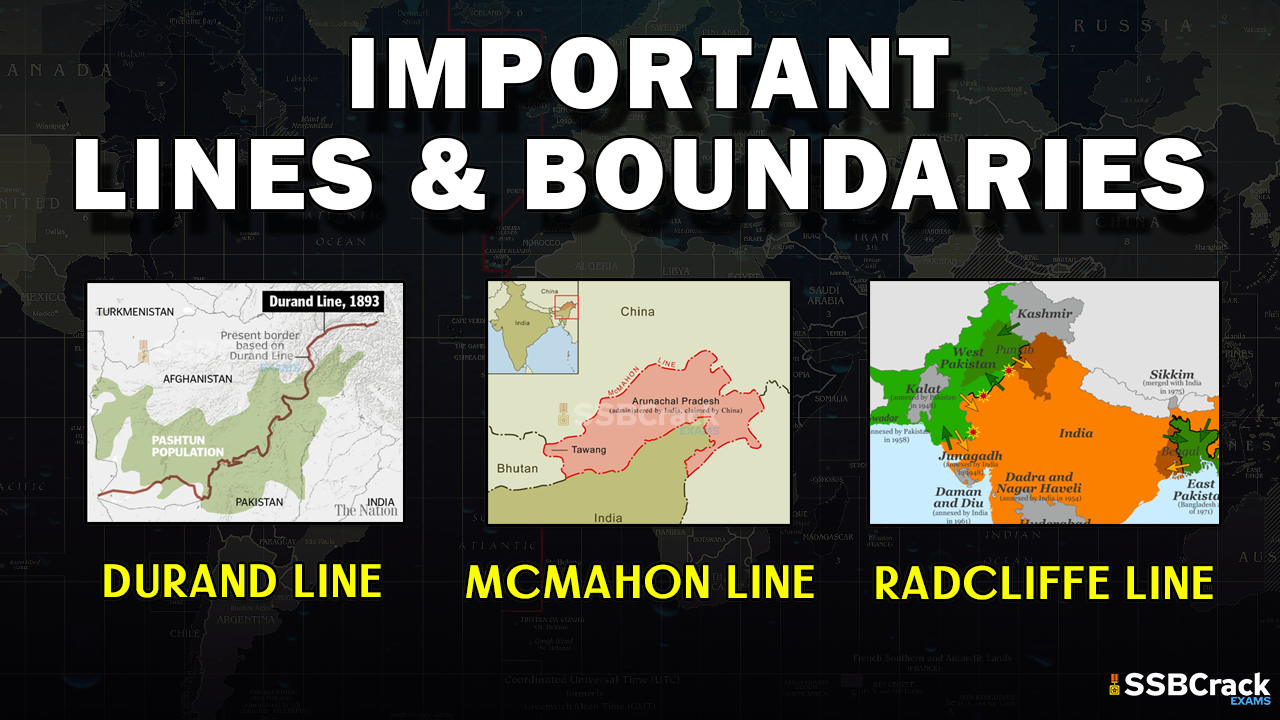
Disputes and Conflicts: Disputes over boundary lines can lead to conflicts, ranging from diplomatic tensions to armed conflicts. The ongoing territorial disputes in the South China Sea, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and the Kashmir issue are examples of complex boundary disputes.
-
Migration and Displacement: Boundary lines can restrict movement and create barriers for migrants and refugees, leading to displacement and humanitarian crises.
-
Environmental Degradation: Boundary lines can sometimes lead to the fragmentation of ecosystems, hindering conservation efforts and contributing to environmental degradation.
-
Social Inequality: Boundary lines can reinforce existing social inequalities, creating economic disparities and unequal access to resources.
FAQs about Boundary Lines on Maps
1. What are the different types of boundary lines?
Boundary lines can be categorized as political, administrative, geographical, and cultural. Political boundaries delineate territories of sovereign states, while administrative boundaries define territories of local administrative units. Geographical boundaries mark natural or artificial features, and cultural boundaries indicate areas with distinct cultural identities.
2. How are boundary lines established?
Boundary lines can be established through treaties, agreements, historical precedent, or physical features. They can also be defined by legal processes, such as surveying and mapping.
3. Why are boundary lines important in international law?
Boundary lines form the basis of international law, defining territorial sovereignty, resource rights, and diplomatic relations. They are essential for maintaining international order and resolving disputes.
4. How do boundary lines affect resource management?
Boundary lines guide the management of shared resources, such as water bodies, mineral deposits, and biodiversity. They can create challenges in coordinating resource management across different jurisdictions.
5. What are some examples of boundary disputes?
Boundary disputes can arise over territorial claims, resource rights, or historical grievances. Some examples include the South China Sea disputes, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and the Kashmir issue.
6. How can boundary lines contribute to social inequality?
Boundary lines can reinforce existing social inequalities, creating economic disparities and unequal access to resources. They can also create barriers to social mobility and hinder opportunities for marginalized communities.
Tips for Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps
-
Pay attention to the legend: The legend of a map provides information about the symbols used to represent different types of boundaries.
-
Consider the scale of the map: The scale of a map determines the level of detail and the types of boundaries that are depicted.
-
Research the historical context: Understanding the historical context of boundary lines can provide insights into their origins and significance.
-
Explore different types of maps: Different types of maps, such as political maps, geographical maps, and thematic maps, can provide different perspectives on boundary lines.
-
Engage in critical thinking: Question the assumptions and interpretations associated with boundary lines, recognizing their potential for both positive and negative impacts.
Conclusion
Boundary lines on maps are more than just lines on a page. They are powerful symbols that reflect the complex realities of our world, shaping political landscapes, influencing social dynamics, and driving international relations. Understanding the significance and evolution of boundary lines is crucial for navigating a world increasingly interconnected and shaped by the lines that divide and unite us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delineating the World: Understanding Boundary Lines on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!